Define recruitment
the number of fish that survive to enter a fishery
Define Bottom-up control
the environmental conditions, productivity, and type of primary producers control the ecosystem structure
Describe two reasons that scientists use modeling
Understand your system
Synthesize datasets
Test hypotheses
Conduct "What if" experiments
Inform management
Difficult and often impossible to do whole-system manipulations
Cover vast areas and distances
Deal with complex, open systems
Need predictions on issues of socioeconomic importance
What is an estuary? Give an example of an estuary (that's not the Chesapeake Bay because that's cheating)
An estuary is “a semi-enclosed coastal body of water which has a free connection with the open sea and within which sea water is measurably diluted with freshwater derived from land drainage"
Examples: Puget Sound, Narragansett Bay, Tampa Bay, Gulf of St. Lawrence
Define upwelling and one place it can occur
Physical process caused by a divergent flow that results in deep water being brought to the surface
Places it can occur: Coastal Upwelling Systems, Cold-Core Rings, Equatorial Upwelling (ENSO), Island Upwelling, River Plumes, andDivergent Fronts
Fishing must be at a level that ensures it can continue indefinitely and the fish population can remain productive and healthy
Describe the difference between positive and negative feedback loops
Positive feedback loops enhance or amplify changes; this tends to move a system away from its equilibrium state and make it more unstable.
Negative feedbacks tend to dampen or buffer changes; this tends to hold a system to some equilibrium state making it more stable.
Name the parameters used by Behrenfeld & Falkowski to model Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
Hint: this is done by using satellite data
Chlorophyll-a
Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR)
Sea surface temperature (SST)
Describe the gradients from the head to the mouth of the estuary of the following variables: Salinity, turbidity, nutrients
Salinity increases
Turbidity decreases
Nutrients decrease
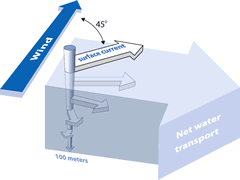
Draw a diagram that describes Ekman sprial
Describe 3 factors that influence fish population
Sampling Techniques
Food Supply
Temperature
Success/strength of cohort
Growth rate
Rank coastal areas, oceanic areas, and upwelling zones from most steps to least steps in the food chain before you get to fish
Oceanic (5)
Coastal (3)
Upwelling (1.5)
State variable: component of the model that has its own governing equation
Forced: exogenous variables that impact the system but are not modeled
What is eutrophication? Describe one harmful effect of eutrophication to aquatic species
An increase in the rate of supply of organic matter to an ecosystem
Excessive (often toxic) blooms
Reduced light penetration and seagrass decline
Oxygen depletion -- dead zones --fish kills
What do POC sedimentation rates look like for upwelling regions?
Sedimentation of organic carbon is high beneath upwelling regions. As single cells or aggregated diatoms can sink to the bottom transporting organic carbon to depth. Mesozooplankton and fish that feed on diatoms produce large, rapidly sinking fecal pellets which can also reach the ocean floor.
Describe one pattern observed in modern fisheries
Total fisheries yields continue to increase (because of an increase in aquaculture
Large changes in the nations involved in fishing has occurred as well
Rise in deep sea species catch
Removal of all large predators/higher trophic levels from oceans
Decline in fisheries with low diversity
Based on Ryther's model, what three things do you need to know to predict fish production?
Phytoplankton production in the sea
How long in the food chain until you get to fish?
Transfer efficiency
Pick and describe a climate change effect to the ocean other then warming temperatures
Openended, but:
Ocean acidification - hamper ability for organisms to create calcium carbonate shells/ degrade existing ones
Spread of invasive species - impact food webs & fisheries
Ocean deoxygenation (coastal hypoxia and expansion of OMZs)
Describe how benthic-pelagic coupling shapes food webs in estuaries
Production in water column coupled to benthic community (worms, clams, mussels, oysters, etc.) that depend on detritus for food.
Demersal fish feed on benthic organisms, that recycle nutrients/return nutrients to pelagic food web
Benthic organisms also graze on phytoplankton (top-down control on phytoplankton)
Below are the rotational directions of an eddy that spun off of the Gulf Stream. Label it as either a warm core ring or cold core ring. Explain how you know which is which.
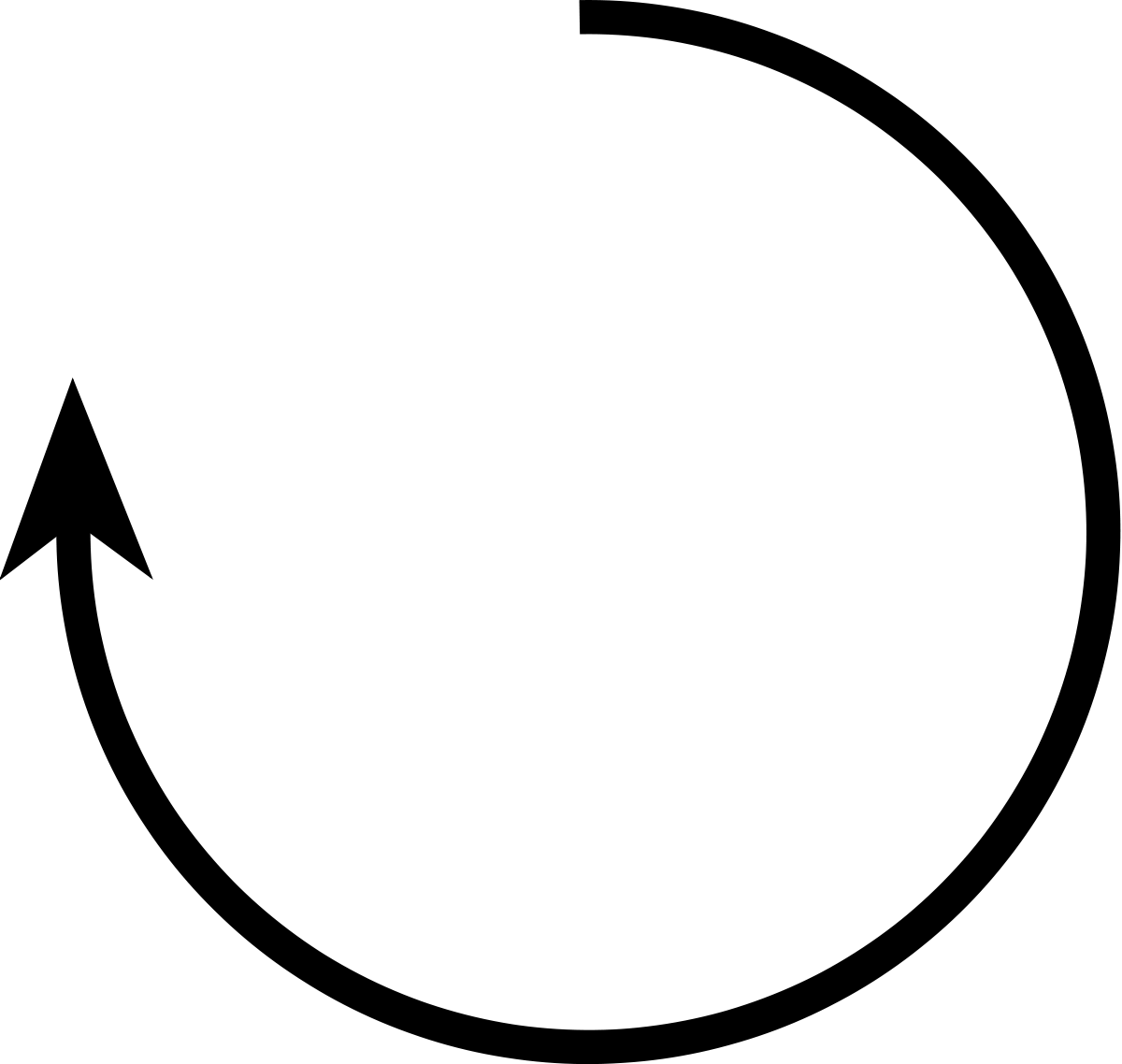
Warm core ring (anti-cyclonic/ clockwise)
Water comes off from the right, inside the ring (water is piling up)
Compare and contrast Match-Mismatch Hypothesis and Critical Period Hypothesis
Critical period hypothesis: survival during the first feeding stage is critical for determining the success of that particular year class’s survival
Match-mismatch hypothesis: this concept suggests that the availability of a resource (prey) during the fish larvae stage determines the success of that particular year class’s survival
Define top-down control and give an example of top-down control in the Chesapeake Bay
When a top predator controls the structure or population dynamics of the ecosystem
removal of piscivorous fish results in (ex. striped bass)
increase in planktivorous fish
decreased zooplankton population
enhanced phytoplankton biomass
reduced water clarity
Do you think we should geoengineer the ocean to increase carbon dioxide removal? If you want to geoengineer the ocean, describe the method you would pick and why? If not, why not?
Yes: to be used as carbon credits, enhance fisheries, traded commercially
Iron fertilization: stimulate primary productivity/ carbon dioxide removal due to overcoming nutrient limitation (ideally in HNLC zones)
Enhanced Upwelling: Increase volume of nutrient rich waters upwelled and Fuel larger phytoplankton blooms which fix CO2 and transport to depth
Deep Ocean CO2 storage: Capture atmospheric CO2 and directly inject into deep oceans (large storage capacity)
No: Maximum removal would only solve 10-20% of the problem
Oxygen depletion
Ecological/microbial shifts & food web disruption
We really don't know what would happen
Describe a current environmental problem that commonly occurs in estuaries like the Chesapeake Bay
Hypoxia (low oxygen) in bottom waters due to water column stratification
Stratification greatest in the summer (greatest difference between salinity and temperature), water not mixing and no new oxygen being introduced - also impacted by the respiration of the biomass from the spring bloom that depletes the bottom water
Higher flow rates (and nutrients) lead to more hypoxia
There are a ton of other examples of this too!
Describe one effect of El Nino has on ocean biology
-Low chlorophyll in equatorial Pacific
-Rebound of chlorophyll soon after
-Higher trophic level effect- decline in fisheries