The monomer of lipids.
What is Fatty Acid?
The 3 statements of The Cell Theory.
What is All cells come from preexisting cells, Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things, and All living things are composed of one or more cells?
The organelle that produces ATP.
What is Mitochondria?
This is what happens to the DNA strand during DNA replication.
What is Unwinds and Unzips?
All sperm and egg cells are different.
The monomer of proteins.
What is Amino Acid?
The acronym we made for remembering the 8 Characteristics of life.
What is CORD GERMS?
The products of photosynthesis.
What is Glucose and Oxygen?
The result of DNA replication.
What are 2 identical strands of DNA?
The number of chromosomes in each of the daughter body cells AFTER mitosis when the beginning body cell had 12 chromosomes.
12 chromosomes.
The monomer of nucleic acids.
What is Nucleotide?
What CORD stands for in our 8 Characteristics of Life acronym.
What is Cellular Organization, Reproduction, and DNA (Heredity)?
The reactants of Cellular Respiration.
What are Glucose and Oxygen?
DNA replication occurs during the S phase, which occurs ______ the cell divides.
What is Before?
During this phase of mitosis, the sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell.
Anaphase.
The monomer of carbohydrates (starch)
What is Monosaccharides?
What GERMS stands for in our acronym for the 8 Characteristics of Life.
What is Growth & Development, Evolution, Respond to Stimuli, Metabolism, and Stable Internal Balance (Homeostasis)?
The product of Cellular Respiration is ______ and the product of Photosynthesis is ________.
What is Carbon Dioxide and Glucose?
A mutation that causes a change in all codons/proteins after the mutation.
What is Frameshift Mutation?

Metaphase
The biological macromolecule is responsible for helping structures performing their functions.
What is Proteins?
True/False: All living things require oxygen to breathe.
What is False?
Carbohydrates are broken down into _____ which are converted to ______.
A type of mutation that is caused by ADDING an additional nucleotide.
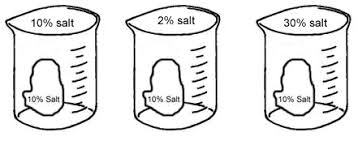
Beaker A = Cell stays the same size
Beaker B = Cell gets bigger
Beaker C = Cell gets smaller