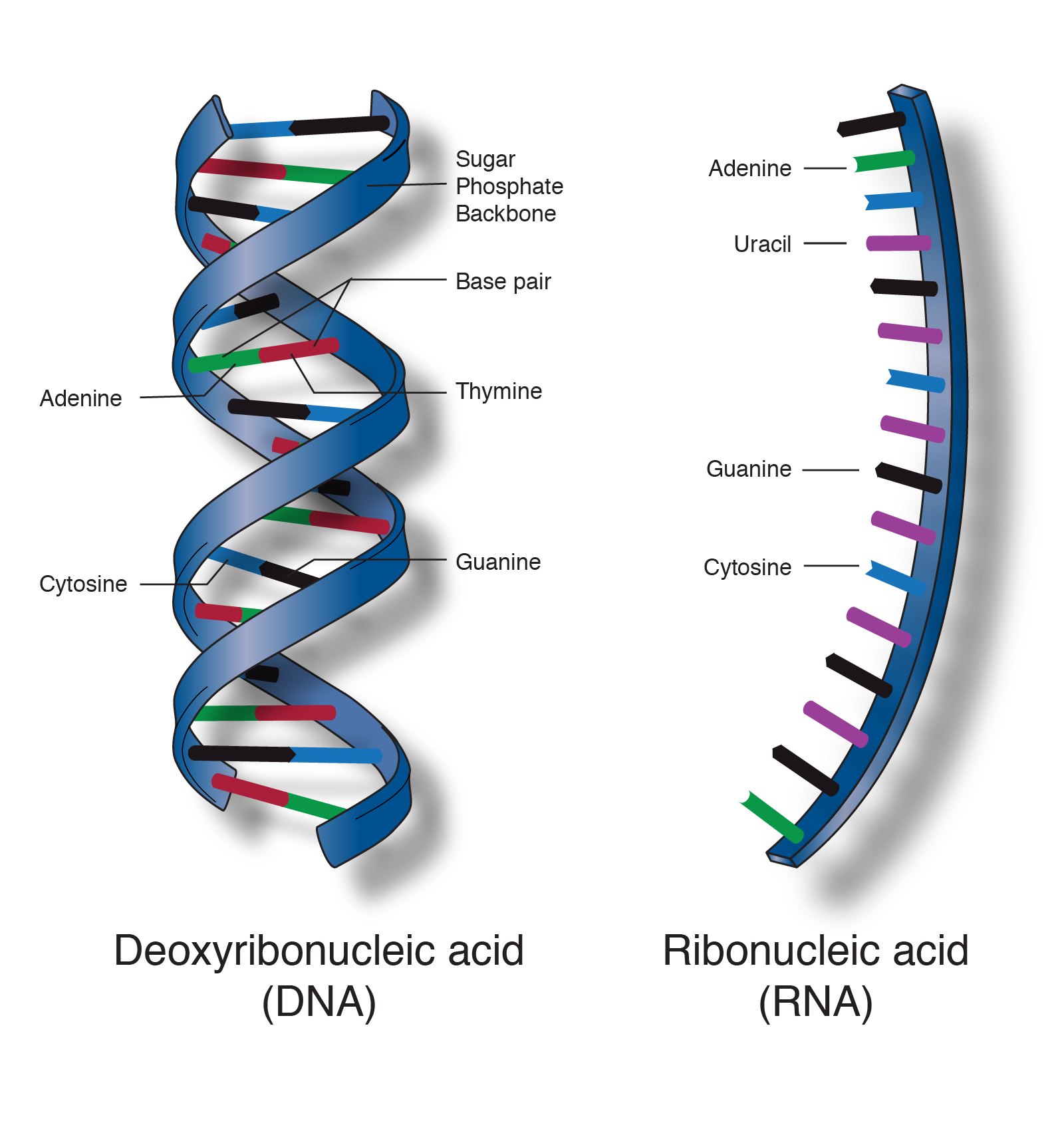
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is what type of macromolecule
a. carbohydrate
b. lipid
c. protein
d. nucleic acid
d. nucleic acid
The purpose of replication is two make two identical copies of DNA
a. True
b. False
a. True!

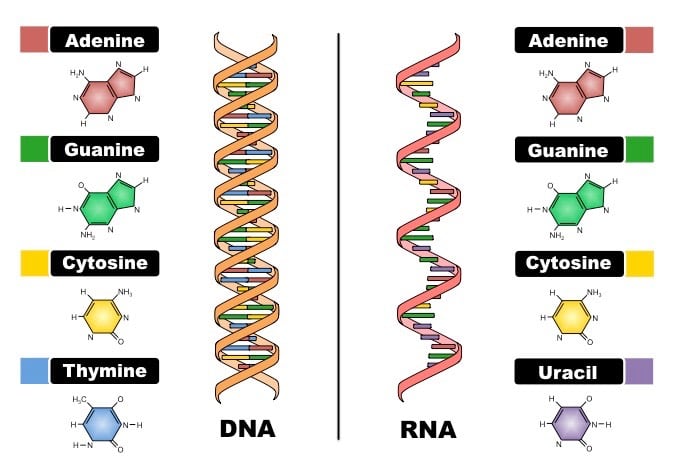
What base does RNA have that DNA does not?
a. Thymine
b. Uracil
c. Guanine
d. Adenine
b. Uracil; RNA does NOT have Thymine
a. True
b. False
b. False

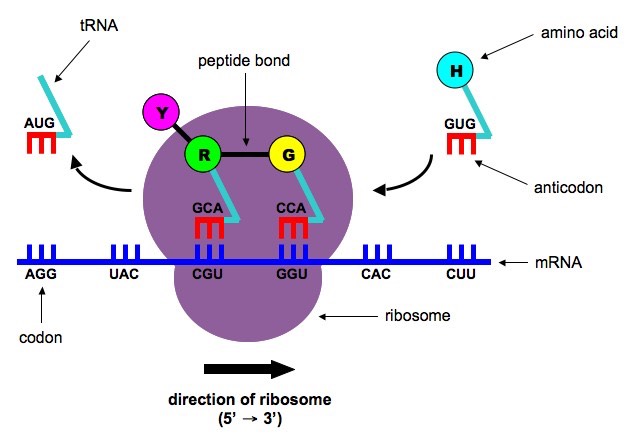
How many nitrogen bases are required to make a codon?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
c. 3
DNA is made up of which monomer (building block):
a. monosaccharide
b. nucleotide
c. glycerol & fatty acid
d. amino acid
b. nucleotide
/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)
The bonds that are broken when DNA is replicated:
a. hydrogen
b. ionic
c. covalent
a. hydrogen bonds (what hold the nitrogen bases of 2 DNA strands together)

The monomer (building block) of proteins:
a. monosaccharide
b. fatty acids & glycerol
c. nucleotide
d. amino acid
d. amino acid

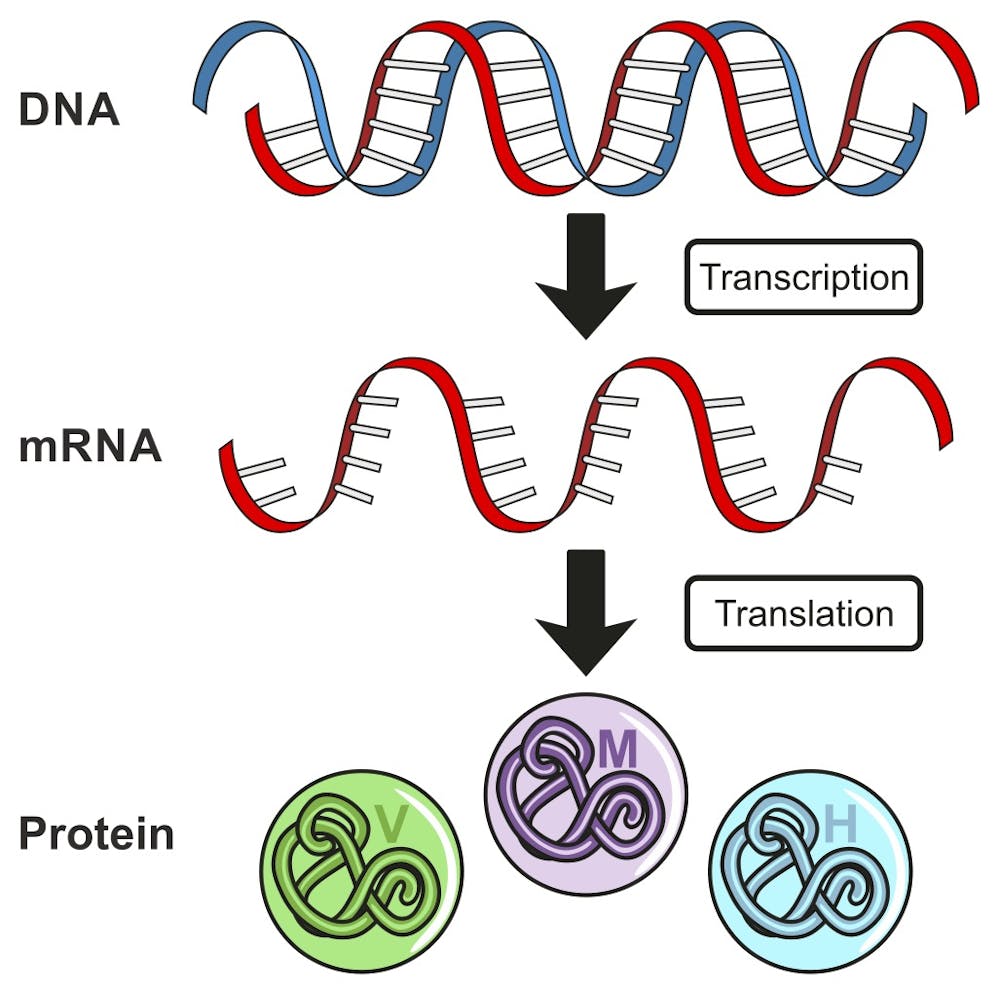
During transcription, DNA is rewritten as:
a. amino acid
b. ribosome
c. mRNA
d. chromosome
c. mRNA
Which type of RNA transfers each amino acid to the ribosome?
a. mRNA
b. tRNA
c. rRNA
b. tRNA

a. double helix
b. single helix
c. single strand
a. double helix
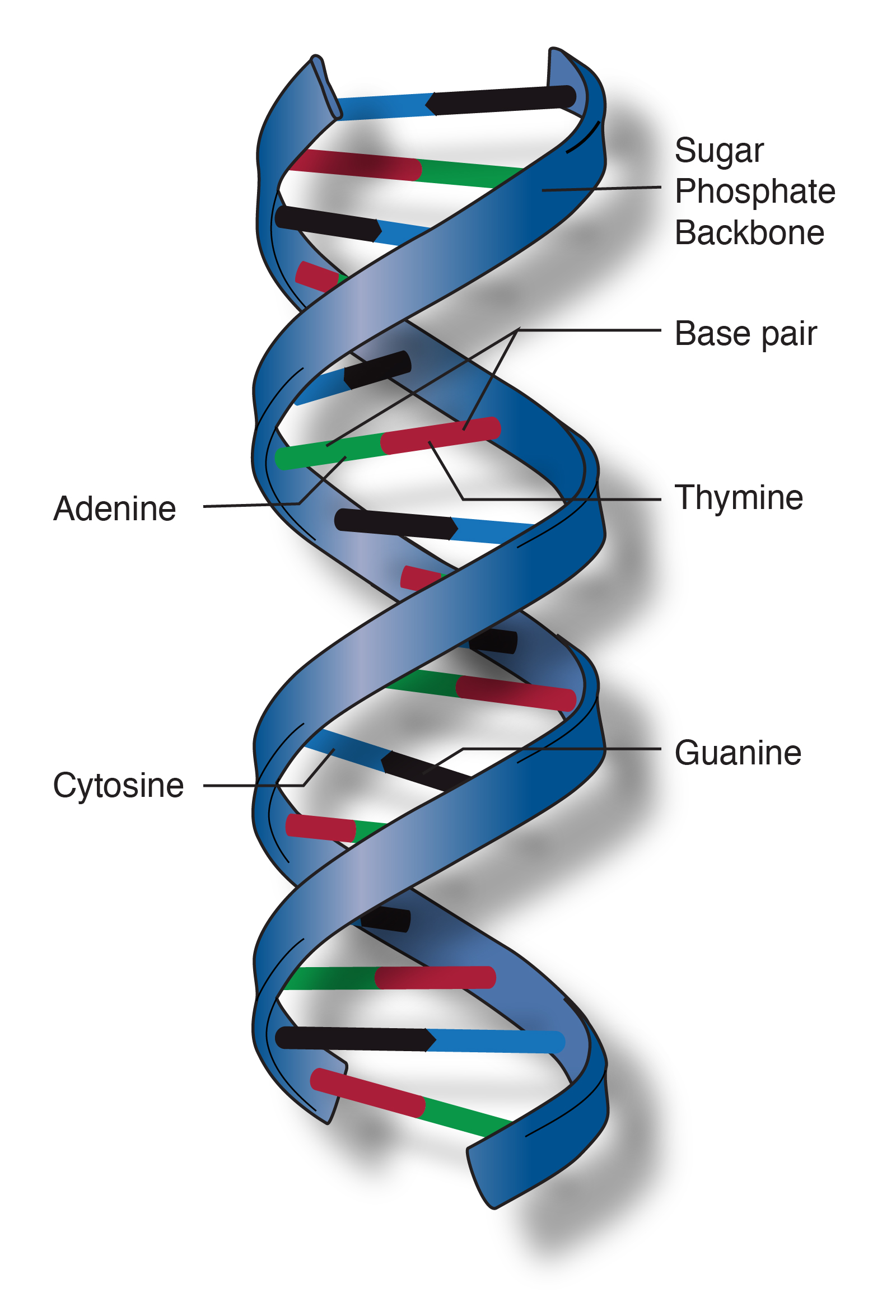
What nitrogenous base pairs with Adenine?
a. Guanine
b. Uracil
c. Thymine
d. Cytosine
c. Thymine (remember this is *just* DNA replication)
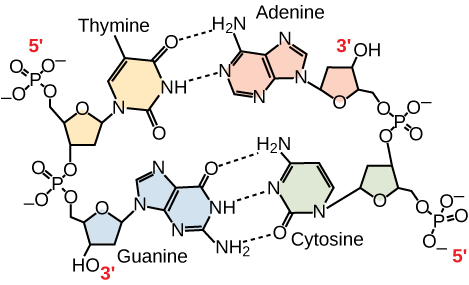
How many strands does RNA have?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
a. 1
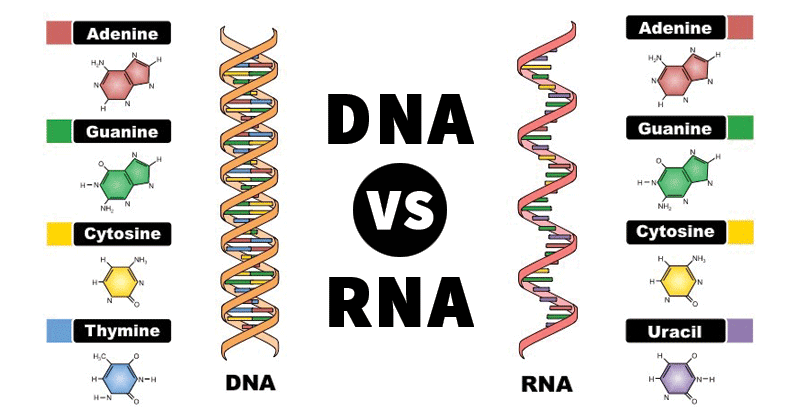
a. Thymine
b. Guanine
c. Cytosine
d. Uracil
d. Uracil
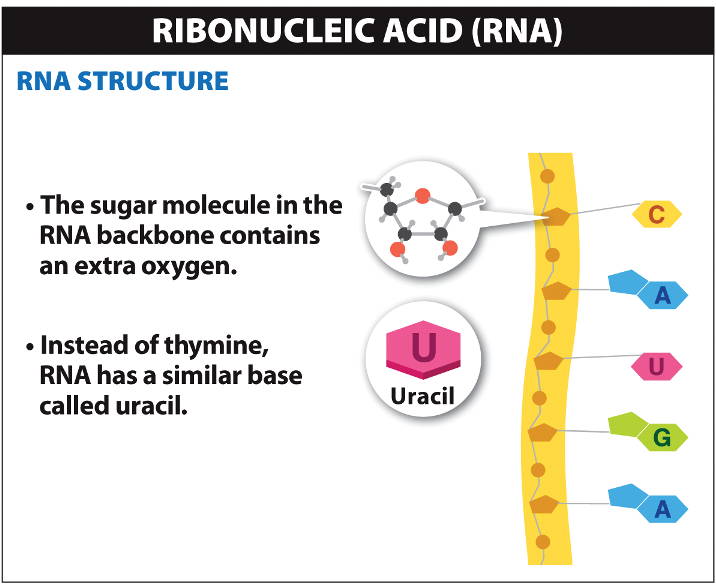
Translation takes place in the:
a. ribosome
b. mitochondria
c. nucleus
d. chloroplast
a. ribosome

What type of bond holds the nitrogen bases together?
a. covalent
b. hydrogen
c. ionic
b. hydrogen bond! 
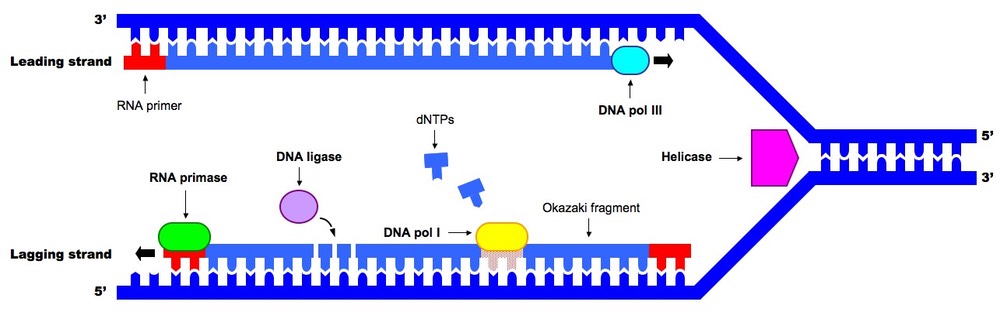
The name for the enzyme that pulls the DVA apart during replication:
a. helicase
b. polymerase
c. ligase
a. helicase (purple)
first step of DNA replication
Protein synthesis has two steps: 1. Transcription and 2....
a. Transportation
b. Transfer
c. Translation
d. Transmodification
c. Translation

What does the "m" stand for in mRNA?
a. mitosis
b. messenger
c. memory
d. mission
b. messenger
a. carbohydrate
b. lipid
c. protein
d. nucleic acid
c. protein

The rungs (steps) of DNA's 'twisted ladder' is made of:
a. the phosphates
b. the sugars
c. the nitrogenous bases
c. nitrogenous bases (pay close attention to how the bases are paired)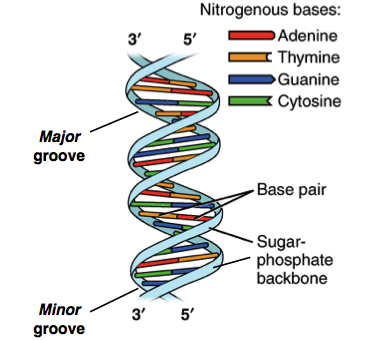
The enzyme necessary for adding DNA nucleotides:
a. helicase
b. polymerase
c. ligase
b. polymerase; poly = many (copies!)

Segments of DNA that code for proteins and traits are called:
a. genes
b. chromosomes
c. nucleotides
d. bases
a. genes

a. first
b. second
a. first

Using a codon chart, tell me which amino acid is created with given this codon: AUG
a. Met
b. Ala
c. Stop
d. Ser
a. Met (start amino acid for polypeptide chain)
