What are amphibians?
These cold-blooded animals lay eggs in water and go through metamorphosis from tadpoles to adults.
What is an angiosperm?
A flowering plant
What is the nitrogenous base complementary to Adenine?
Thymine
What's the function of the frontal lobe?
Integrate information from other parts of the brain and control reasoning, critical thinking, memory, and personality
What are the three levels of biodiversity?
Genetic diversity, species diversity, ecosystem diversity
What is skin?
This is the largest organ in most animals and acts as a barrier to protect internal organs.
What primary organelle in plant cells converts light energy into ATP?
Chloroplast
What phase during the cell cycle does the cell replicate its DNA?
S phase
What are reflex arcs?
simple connection of neurons that results in a reflex action in response to a stimulus
Why is genetic diversity important for the survival of a species?
Relates to adaptation, resistance to diseases, and environmental changes
What is echolocation?
Some animals, like bats and dolphins, use high-frequency sound waves to detect objects and navigate their environment.
What type of growth in meristematic tissue refers to the increase in circumference or width?
Secondary Growth
What is this type of chromosomal mutation called?
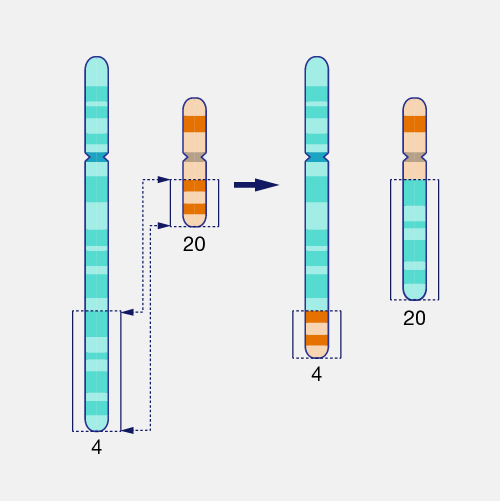
Translocation
What connects the brain to the peripheral nervous system?
Spinal cord (and cranial nerves)
How does habitat destruction impact species diversity in an ecosystem?
Habitat destruction reduces available space, food, and shelter, which can lead to population decline or extinction of species. This disrupts interactions like predation, pollination, and competition, leading to the loss of species diversity and ecosystem collapse
What's the difference between cold-blooded and warm-blooded animals?
Cold-blooded animals rely on the environment to regulate their body temperature, while warm-blooded animals maintain a constant internal temperature using their own metabolic energy.
What is the function of the xylem & phloem?
X: Transport water & deliver nutrients/minerals
P: Transport sugars
What's the structure of a nucleotide?
A nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
How does insulin lower blood glucose levels?
Insulin lowers blood glucose by promoting glucose uptake into muscle and fat cells and by stimulating glycogen synthesis in the liver. It also inhibits glucose production and glycogen breakdown, keeping blood sugar levels in balance.
How do human activities such as monoculture farming affect genetic and ecosystem diversity?
Monoculture reduces genetic diversity by planting the same crop. It weakens resistance to pests and diseases and reduces ecosystem diversity.
What is indeterminate growth?
Unlike mammals, some reptiles, such as snakes and lizards, can continue to grow throughout their lives due to their ectothermic metabolism.
What are the three types of ground tissue?
Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma
🧬 How CRISPR-Cas9 edits genes?
Cas9 is a DNA-cutting enzyme guided by RNA that targets and cuts specific DNA sequences, allowing scientists to edit genes through natural repair mechanisms.
What are the two systems that regulate and coordinate the function of the body's other systems?
a) digestive and circulatory
b) respiratory and excretory
c) immune and lymphatic
d) endocrine and nervous
Endocrine and nervous systems
Give an example when increasing species diversity in an ecosystem resulted in a negative outcome.
Non-native species can disrupt local ecosystems.
Example: Introducing zebra mussels to North American lakes increased species count, but they outcompeted native mussels and damaged food chains and water infrastructure.