Fat, One of the major components of the cell membrane.
What is lipids?
What is the nucleus?
Membrane-bound organelles, has a nucleus and has complex linear DNA.
What is a eukaryote?
Three elements that only plant cells have.
What is a cell wall, chloroplasts and the central vacuole?
The central dogma of microbiology.
What is DNA to RNA to Protein to you?
A building block of protein.
What is an amino acid?
This organelle packages and ships proteins, like UPS.
What is the Golgi Apparatus?
Invented the microscope and coined the term "cell".
Who is Robert Hooke?
The type of cell division that gametes go through.
What is meiosis?
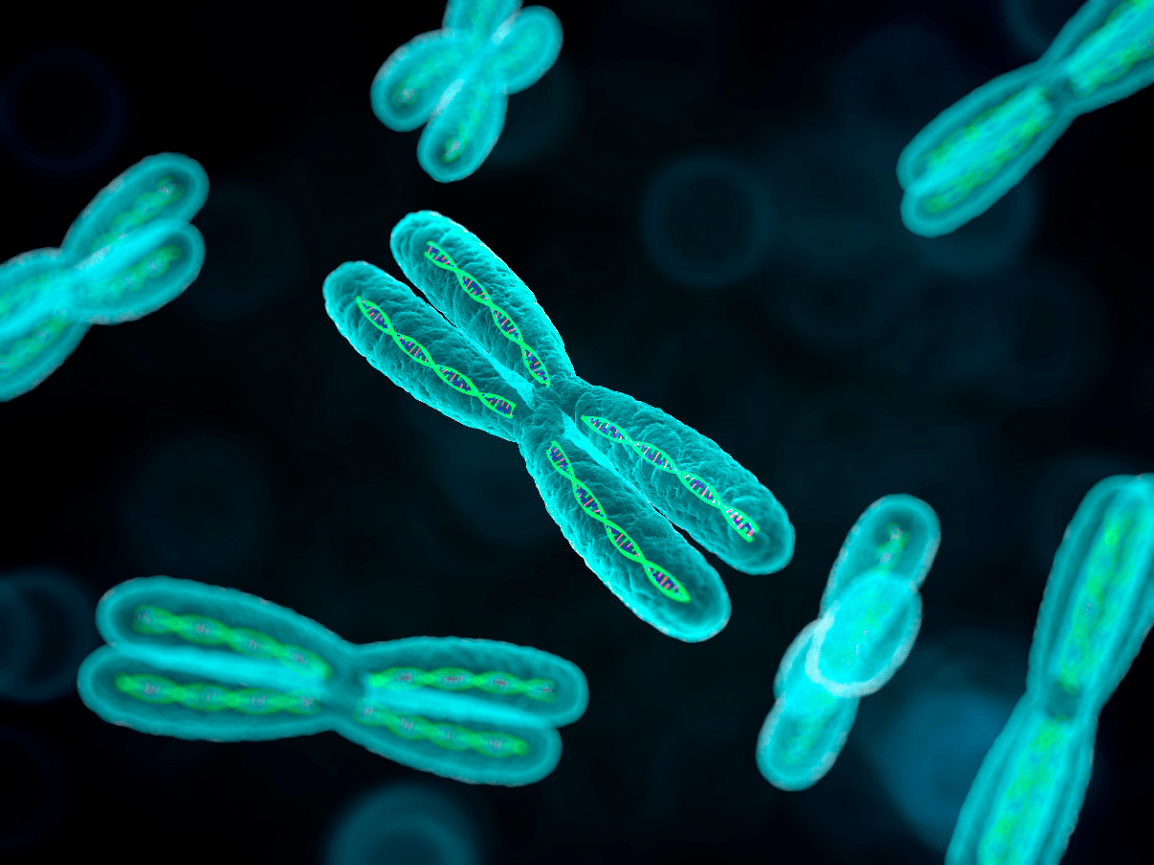
What is a chromosome?
Carries the genetic code.
What is DNA?
This is organelle makes proteins, the workbench.
What is a ribosome?
The basic unit of life, cells come from other cells and all life is composed of cells.
What is the cell theory?
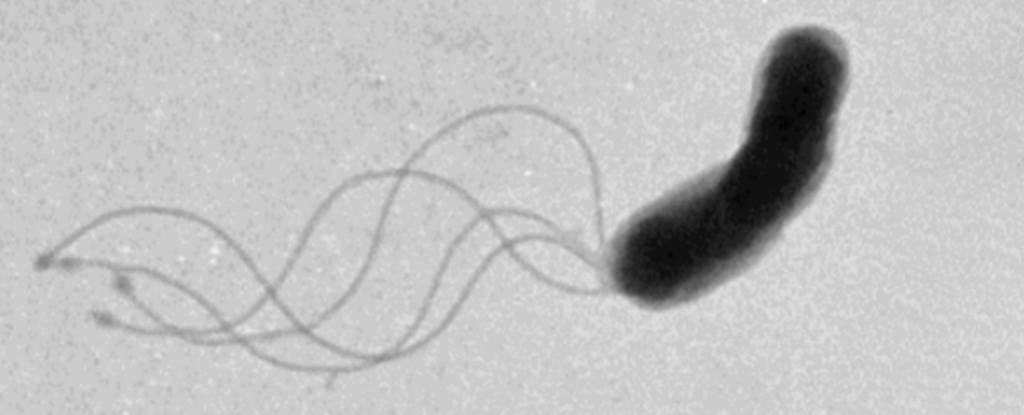
What is flagella?
The process of going from a section of DNA to RNA.
What is transcription?
Glucose is an example of this macromolecule.
What is a carbohydrate?
What is a vacuole?
Energy currency of the cell.
What is ATP?
The type of cell division that somatic cells go through.
What is mitosis?
What is DNA replication?
A sugar, phosphate and nucleic acids.
What is a nucleotide?
Responsible for digestion, destroying bacteria, worn out organelles and apoptosis (programmed cell death).
What is a lysosome?
The organelles in the endomembrane system.
What are the nucleus, ribosome, rough ER, golgi apparatus, secretory vesicle/lysosome?
Small, uncharged molecules that go through the cell membrane with the concentration gradient?
What is passive transport, simple diffusion?
The three types of RNA and what each does.
What is mRNA (carries message of gene from DNA), rRNA (subunits of a ribosome) and tRNA (transfers the correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide).