The smallest living unit of an organism
Cell
The process that takes in CO2 and water and release glucose and oxygen
Photosynthesis
A diagram that shows the feeding relationships between organism and how energy is transferred
A Food Web
A species that is the first to arrive in a new area, often carried by wind or ocean currents
Pioneer Species
A human introduced, non-native species, that harms native species
Invasive Species
A collection of cells working together to perform a function
Tissue
The process where glucose is broken into (ATP) energy, water, and CO2
Cellular Respiration (Aerobic)
The amount of energy transferred between each trophic level in food pyramid
10%
This form of ecological succession proceeds more quickly than the other
Secondary succession
Diseases spread faster in populations as this increases
Population Density
A collection of tissue serving a single function
Organ
During alcoholic fermentation, glucose is broken into these three components
Ethanol (alcohol), CO2, and ATP (energy)
The lowest level of a food chain is occupied by this type of organism that harnesses energy from the environment
Producer
Areas of high biodiversity are also more resistant to this ecological pressure
Environmental change
Humans contribute to global climate change by emitting this potent greenhouse gas
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Food is broken down into smaller particles for absorption by these body chemicals
Enzymes
Within the nitrogen cycle, nitrogen is removed from the atmosphere by these soil dwelling organisms
Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria
The type of organism that feeds exclusively on producers
Primary Consumers
An ecological relationship that benefits both organisms
Mutualism
A mechanism that keeps populations from growing exponentially
Limiting Factor
When body temperature increases, blood vessels dilate, and sweat is produced to return the body to homeostasis. This is an example of this kind of feedback loop
Negative Feedback Loop
Of the four macromolecules, this type is type is most responsible for power the cells
Carbohydrates
Based on the food web, identify the tertiary consumer(s)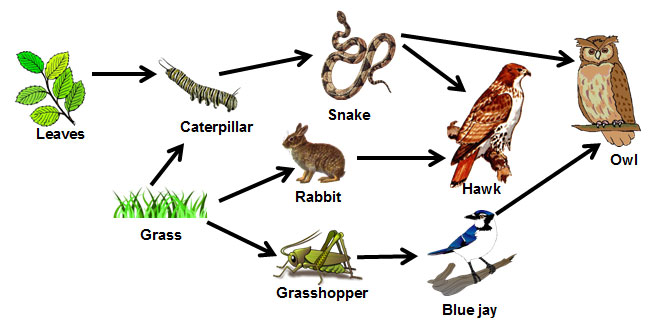
Owls and Hawks
Because competition increases as population size grows, populations cannot grow forever. This ecological concept defines when they reach the point where they cannot grow further.
Carrying Capacity
Which of these two populations is growing
A B
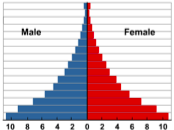
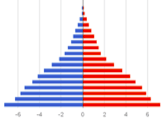
B
Blood clotting is an example of this kind of feedback loop

Positive Feedback Loop
The bonds between these two components of ATP are broken to release energy 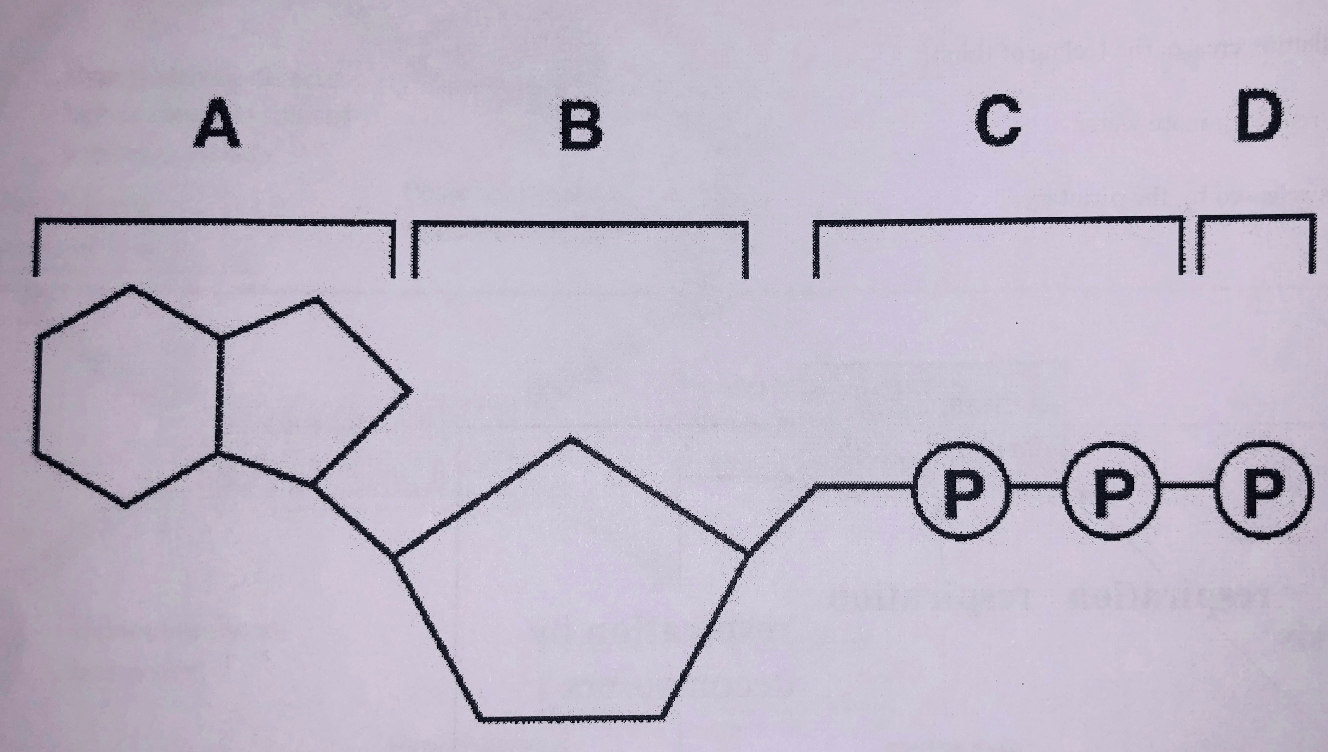
Between C & D
If the producers create 7,300 cal of energy, this amount of energy will exist on the forth trophic level
7.3 cal
When wolves were reintroduced to Yellowstone they brought stability back to the environment. They are an example of this kind of species
Keystone Species
The population in the diagram is experiencing this population dynamic
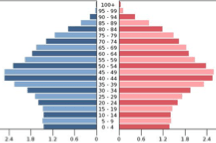
Decreasing Population Size
During respiration, this is the area that begins with highest concentration of CO2

The Capillary