Name main organ in the circulatory system
Heart
Name one "molecule of life"
Carbohydrate, Lipid, Protein, or Nucleic Acid
True or False? The Biosphere is the largest level in ecological organization?

The basic unit for all forms of life (and also this category)
Cell
Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, what do they store?
Compact genetic information/DNA
At what structure does gas exchange into the circulatory system in the lungs? Hint: air sac
Alveoli
Name two of the 6 elements that organic molecules ("molecules of life") are mostly made of?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, or Sulfur
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms.
Biome
A thin flexible barrier made of lipids that surrounds all cells and regulates what enters and exits the cells.
Cell membrane
Genetic variation among a group of offspring could be cause by:
a mutation
crossing over of homologous chromosomes from each parent during meiosis
The basic working unit (a specialized cell) of the brain and nervous system
Neuron
An enzyme is a specialized protein that does what?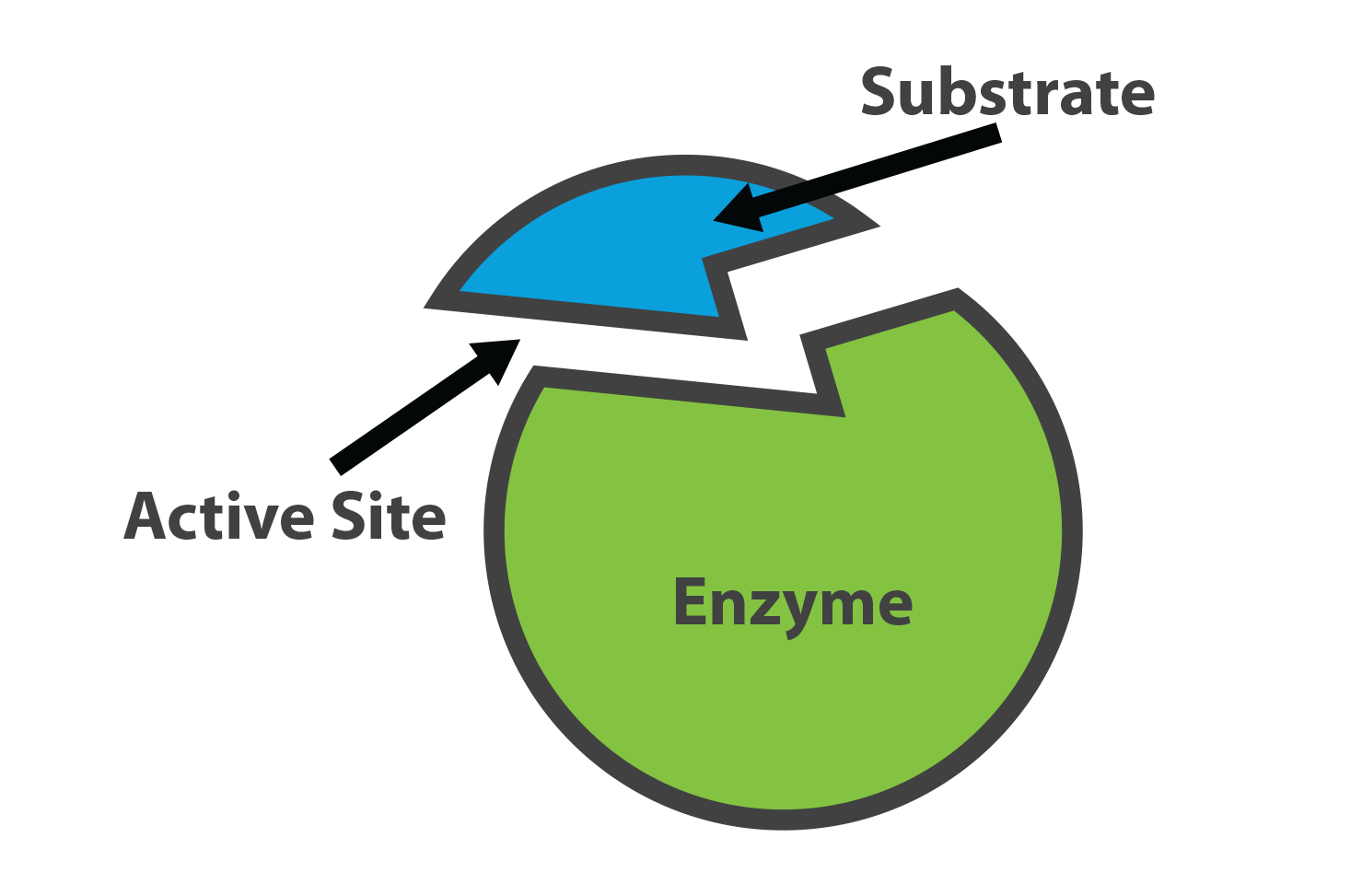
Reduces activation energy of a reaction to help speed it up!
Define producer in Biology
An organism that can make and store energy using resources from its surrounding environment (photosynthesis: sunlight, CO2, water--->glucose, O2)
Simple cells that make up single celled organisms such as bacteria and archaea; DNA is not contained within the nucleus
Prokaryotic cells
During meiosis, reproductive cells called gametes are produced (i.e. eggs, sperm, pollen, etc). These cells are call ______ cells because they contain only one copy of each chromosome (in humans 23).
haploid
Chyme leaves the stomach and enters what part of the digestive system next?
The small intestine (this is where nutrients are absorbed)
Name one form that carbon can be found in during the carbon cycle.
Glucose (C6H12O6), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4)
A relationship between two organisms where one benefits and the other derives no benefit or harm (neutral).
Commensalism
Homeostasis is the ability of the body or cell to maintain _________ as it deals with external changes.
Equilibrium
Organisms who have two identical alleles for a particular gene are called?
Homozygous
What is the purpose of the epiglottis?
To lay over the trachea when swallowing food to avoid choking and allowing food to pass down the esophagus towards the stomach.
The building blocks for nucleic acids are called nucleotides, give an example of a nucleotide (or the letter abbreviation for one).
Adenine- A
Thymine- T (DNA only)
Guanine- G
Cytosine- C
Uracil-U (RNA only)
In ecology, how do we define carrying capacity for a species?
The largest number of individuals for a particular species that an environment can support. Usually stopped by a "limiting factor."
The function of the ribosome, an organelle found within a cell is to make what?
Protein! (by using messenger RNA (transcribed in the nucleus) to translate RNA into specific amino acids that link together to for the 3D protein molecule)
When the phenotype is a blend of both the parent's alleles we call this?
Incomplete Dominance