take a cell-fie
The closest relative of a mouse.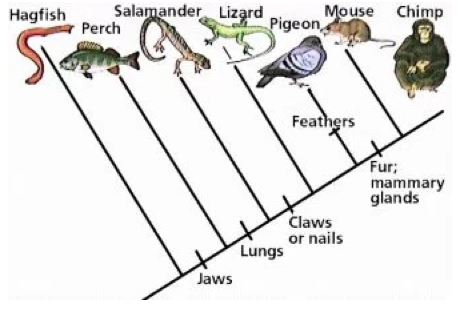
What is a chimpanzee?
The age of the Earth.
What is 4.6 billion years old?
The overall goal of cellular respiration.
What is to create ATP from the food we eat?
The smallest unit of life.
What is a cell?
These letters are often found at the end of an enzyme.
What is -ase?
The field of biology that identifies and classifies organisms.
What is taxonomy?
The building blocks (monomers) of proteins.
The colors absorbed by chlorophyll.
What is everything except green (but mainly blue, red and purple)?
The major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
What is having a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles?
These factors can cause an enzyme to denature.
What are extreme temperatures and extreme pH?
 The trophic role of the tawny owl.
The trophic role of the tawny owl.
What is a secondary consumer?
The term used to describe a part of the ecosystem that stores or contains carbon.
What is a carbon reservoir?
The light-independent reaction is also called this.
What is the Calvin Cycle?
The first person to name and describe a cell.
Who is Robert Hooke?
The process by which a cell gets rid of material by using vesicles.
What is exocytosis?
The two taxa used in binomial nomenclature.
What is genus & species?
What is by removing the 3rd phosphate?
The process of splitting a glucose molecule into 2 pyruvate molecules.
What is glycolysis?
This organelle is responsible for making proteins.
What is a ribosome?
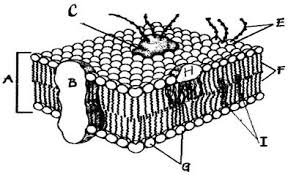 The structure labeled A in this diagram.
The structure labeled A in this diagram.
What is the phospholipid bilayer?
The term that describes a relationship in which one organism benefits, and the other is unaffected (neutral).
What is commensalism?
The 4 main elements in living things.
What are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen?
The chemical formula for glucose.
What is C6H12O6 ?
The organelle used to store sugar and water.
What is a vacuole?
The term used to describe the fact that some, but not all, molecules can cross the cell membrane.
What is semi-permeable?