Which of the following statements is true about the cell wall?
A) The cell wall is mainly composed of lipid
B) The cell wall is mainly composed of starch
C) The cell wall is mainly composed of protein
D) The cell wall is mainly composed of cellulose
D)

A molecule becomes more oxidized when it
A) gains a hydrogen (H+) ion
B) gains an electron
C) loses a hydrogen (H+) ion
D) loses an electron
E) changes shape
D)
In DNA technology, the term "vector" can refer to
A) the enzyme that cuts DNA into restriction fragments
B) the sticky end of a DNA fragment
C) an SNP marker
D) a plasmid to transfer DNA into a living cell
D) a plasmid to transfer DNA into a living cell
A is incorrect, because the enzyme that cuts DNA into restriction fragments is called a restriction enzyme/endonuclease.
The sticky end is a DNA fragment in which the terminal portion has a stretch of unpaired bases.


SNP marker -- idk,
"A single-nucleotide polymorphism is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population"

A dehydration reaction joins 2 glucose molecules to form maltose. The formula for glucose is C6H12O6.
What is the formula for maltose?
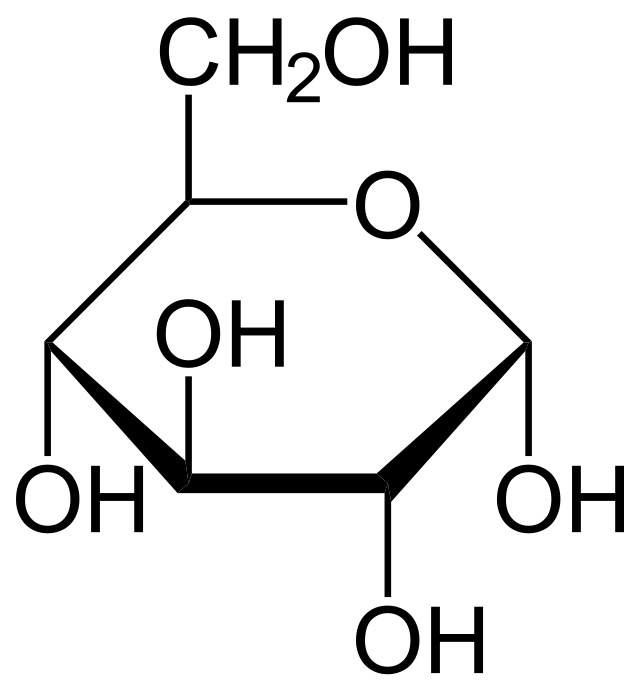
C12H22O11
2 glucose molecules = C12H24O12, but one H2O is lost during the dehydration reaction

Which organelles contain DNA?
A) Nucleus
B) Vacuole
C) Mitochondria
D) Chloroplast
E) Ribosome
A, C, and D (nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplast)
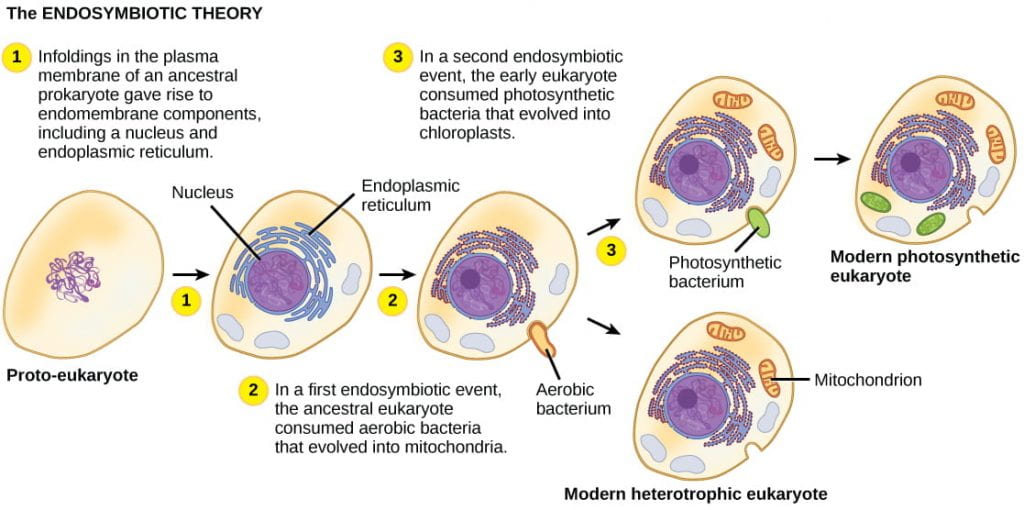
Evidence for the theory -- bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts are similar in size. Bacteria also have DNA and ribosomes similar to those of mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Host cells and bacteria formed endosymbiotic relationships long ago, when individual host cells took in aerobic (oxygen-using) and photosynthetic bacteria but did not destroy them.
In the overall process of glycolysis and cellular respiration, _ is oxidized and _ is reduced.
A) oxygen … ATP
B) glucose … ATP
C) carbon dioxide … water
D) glucose … oxygen
E) ATP … oxygen
D)
Meley homogenizes and centrifuges a sample of animal tissue, resulting in a pellet. She then pours off the supernatant (liquid above the pellet) into another tube and repeats the process several times, each time at a higher speed and for a longer time. Which cell component would she most likely find after the last centrifuge?
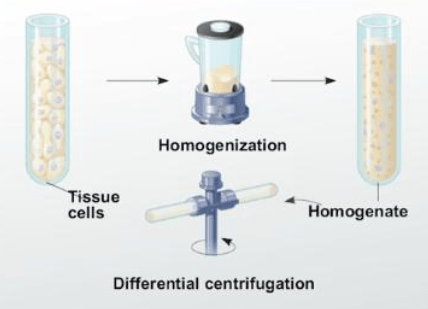
a) nuclei
b) mitochondria
c) chloroplasts
d) ribosomes
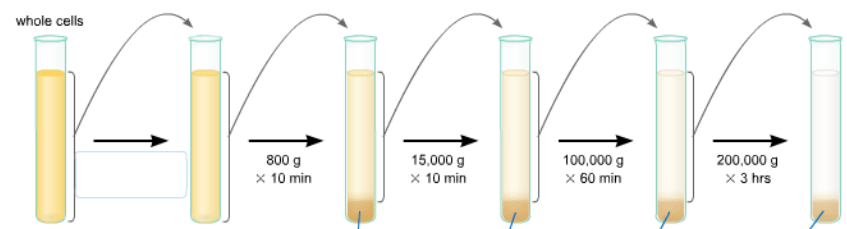
d) ribosomes
Cell fractionation is a technique used to separate cell components based on size and density.
At lower speeds, the pellet consists of larger components, and higher speeds result in a pellet with smaller components.

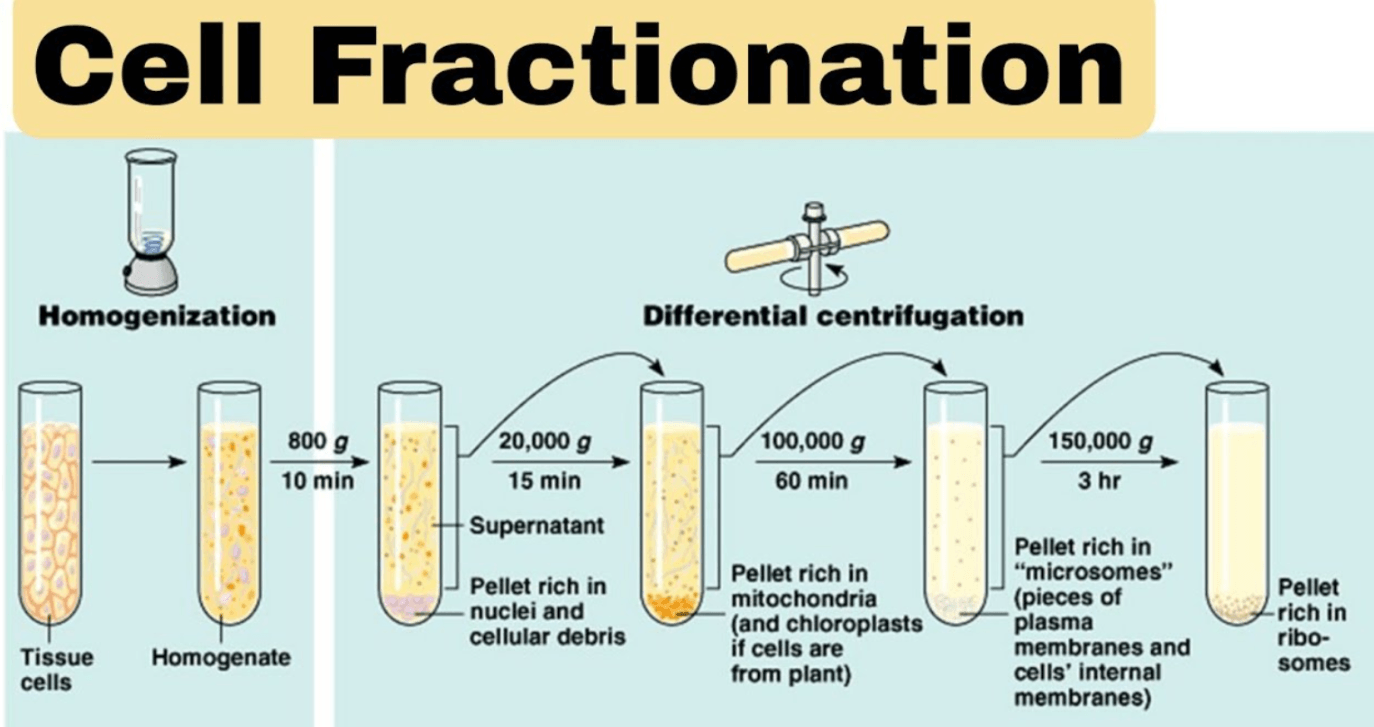
Aspartic acid and glutamic acid are acidic amino acids. In cellular pH (7.2), they have
a) positively charged side chains; hydrophobic
b) negatively charged side chains; hydrophobic
c) positively charged side chains; hydrophilic
d) negatively charged side chains; hydrophilic
e) no electrical charge in side chains
d) negatively charged side chains; hydrophilic
Aspartic acid and glutamic acid both have a carboxyl group, which usually dissociates at cellular pH. When it dissociates, it loses the hydrogen atom and has a -1 charge. The side chain is now negatively charged.

Polar side chains and electrically charged side chains are hydrophilic. This is because water is also a polar molecule.
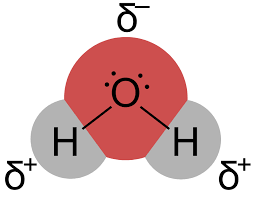
The oppositely charged ends attract each other, which is why polar and charged molecules are water-loving.
A researcher wants to film the movement of chromosomes during cell division. Which type of microscope should be chosen and why?
A) transmission electron microscope, because of its high magnifying power
B) transmission electron microscope, because of its high resolving power
C) light microscope, because of its high resolving power
D) light microscope, because the specimen is alive
E) scanning electron microscope, because of its ability to visualize the surface of subcellular objects
D)
Although the resolution of the light microscope is far less than with electron microscopes, light microscopy is the only technique that permits one to observe living cells.
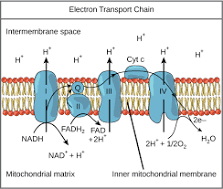
Most of the ATP produced in cellular respiration comes from which process?
A) substrate-level phosphorylation
B) the citric acid cycle
C) oxidative phosphorylation
D) reduction of NADH
E) glycolysis
C)
The picture below shows an apparatus used for DNA agarose gel electrophoresis. Which letter indicates the anode on the apparatus?
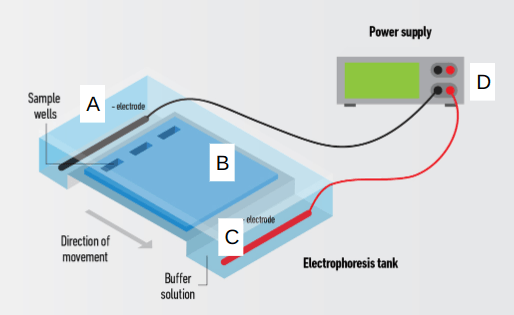
A)
B)
C)
D)
C) anode
A) cathode
B) agarose gel
D) power supply
The anode is positive (anode attracts anions), and the cathode is negative.
Gel electrophoresis is a method used to separate DNA according to molecular size (can also separate RNA and proteins). The molecules are pushed through the gel (which contains small pores) via an electrical field.
Smaller DNA fragments travel through the gel faster, while larger DNA fragments travel through the gel slower (harder time passing through the pores).
DNA is negative, so it is attracted to the positive charge (anode). Since the direction of movement is from A to C, A would be the cathode and C would be the anode.
Dawg is a dog🐶 who, as a pup, would quake at the sight of any tiny leaf🍁 that flew near her. One year later, she is a changed dog and will run🏃♀️ into the woods to chase a blowing leaf🍃. The learning mode in this scenario is
A) Classical conditioning
B) Habituation
C) Imprinting
D) Operant conditioning
E) Insight learning
B) Habituation
Habituation is a form of non-associative (does not need to be paired with another stimulus) learning in which a response to a stimulus decreases after repeated presentations of that stimulus.

Which feature do prokaryotes and eukaryotes have in common?
A) mitochondria, ribosomes, cytoplasm
B) ribosomes, nucleus, plasma membrane
C) nucleus, plasma membrane, ribosomes
D) ribosomes, plasma membrane, cytoplasm
E) mitochondria, cytoplasm, plasma membrane
D)
How many molecules of ATP are gained by substrate-level phosphorylation from the complete breakdown of a single molecule of glucose in the presence of oxygen?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 32
b) 2
Plants are more readily manipulated by genetic engineering than animals because
A) recombinant genes can be inserted into plant cells by microinjection
B) a somatic plant cell can grow into a complete plant
C) more vectors are available for transferring recombinant DNA into plant cells
D) plant genes do not contain introns
B) a somatic plant cell can grow into a complete plant
A somatic cell is a cell in a multicellular organism other than reproductive cells (germ cell, gamete, or gametocyte). A somatic cell contributes to forming the body of an organism.
Stem cells are cells that can divide into multiple kinds of other cells (they're not limited to dividing into their own type). Stem cells are categorized based on their potency, or the diversity of cell types they can become as they differentiate. Totipotent stem cells can divide into all cell types in an organism. A totipotent cell has the potential to divide until it creates an entire, complete organism. Pluripotent stem cells can divide into most cell types in an organism, but cannot develop into an entire organism on their own.
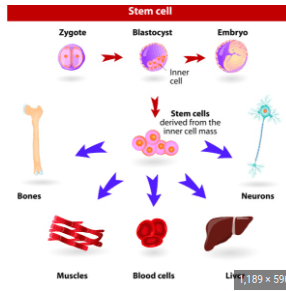
Somatic plant cells are totipotent, meaning they can grow into a complete plant. Cells in animals show totipotency only during the earlier stages of embryonic development. Thus plants are more readily manipulated by genetic engineering than animals.
A is incorrect because microinjections can be used to directly transfer genes in both plant and animal cells.
The number of cloning vectors present for transferring rDNA (recombinant DNA) into plant and animal cells does not vary much.
Plant cells are eukaryotic. All eukaryotic cells have coding (exons) and non-coding (introns) regions in their DNA. During the formation of a functional mRNA, the introns are spliced off so that they do not interfere with the process of protein formation by translation of the mRNA.
In a genetic code with 3 nucleic acids per codon, what would hypothetically be the maximum number of amino acids that could be encoded?
A) 60
B) 61
C) 62
D) 63
D) 63
The number of potential triplets is 64. Subtracting for a necessary stop codon, organisms could code for up to 63 different amino acids.

Of the cellular compartments listed below, which has the lowest pH?
A. Mitochondrial matrix
B. Endoplasmic reticulum
C. Lysosome
D. Cytoplasm
E. Nucleus
C)
Reactions involved in the light-dependent phase of photosynthesis may be found in
A) grana lamellae only
B) stroma lamellae only
C) inner surface of the thylakoids only
D) inner and outer surface of the thylakoids
E) outer membrane of the chloroplast envelope
D) inner and outer surface of the thylakoids
*explanation*
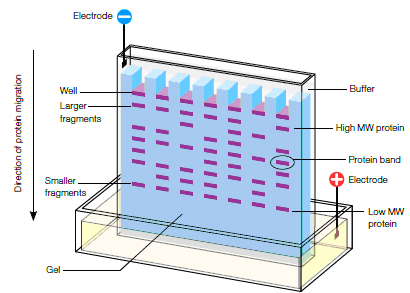
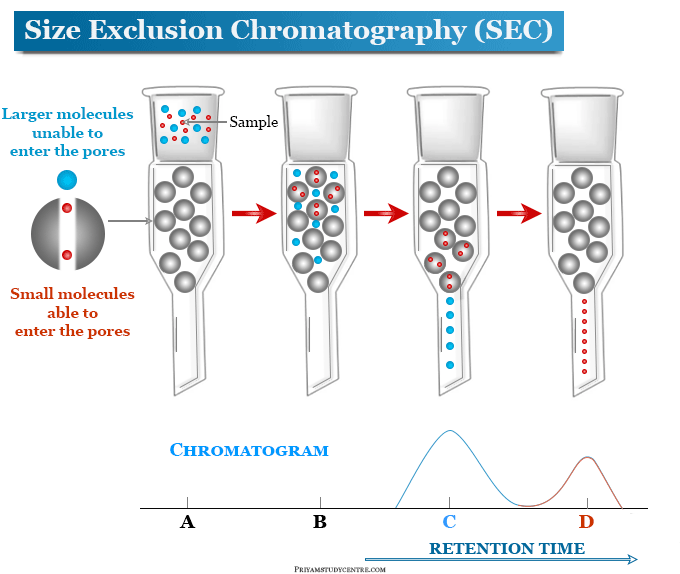
Which two of the following techniques can be used to estimate the molecular weight of a protein?
A) Isoelectric focusing
B) Electrophoresis
C) Size exclusion gel chromatography
D) Ion-exchange chromatography
E) Affinity chromatography
B+C
Electrophoresis uses an electric current to move molecules through a gel or other matrix. High MW molecules are closer to the starting point.
Size exclusion gel chromatography filters molecules through a gel, which consists of beads with pores of specific sizes. Molecules that are too big cannot pass through the pores and instead flow through the space around the pores (quicker flow). Smaller molecules enter the pores and are slowed down (slower flow).
VS electrophoresis where big molecules move slower while small molecules move quicker.
Isoelectric focusing, ion-exchange chromatography, and affinity chromatography separate molecules by charge (as the names imply).

In mammals, circadian rhythms are coordinated by clustered neurons in this part of the brain.
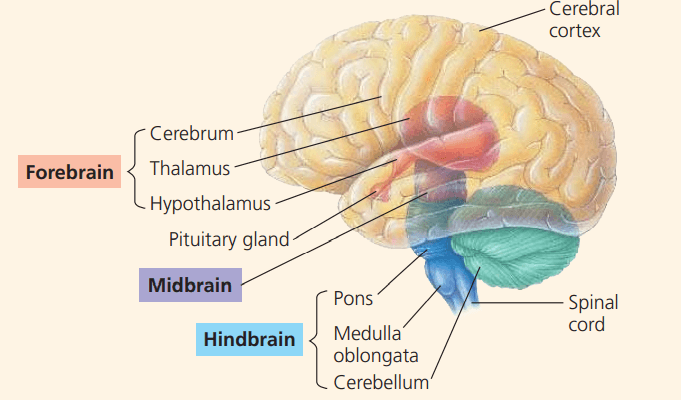
Hypothalamus
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is a cluster of neurons in the hypothalamus (responsible for homeostasis and basic survival behaviors) that synchronizes the biological clock in cells throughout the body to the cycles of day/night.