What is anything that takes up space and has mass?
Matter
What are the beginning parts of a chemical reaction?
Reactants
Which type of organic compound has peptide bonds?
Proteins
What is a pure substance made of two or more chemically combined elements?
Compound
What is a pure substance that is made of only one kind of atom?
Element
What does a catalyst do to a reactions activation energy?
Lowers it
What is the primary function of carbohydrates?
Fuel source
What is the simplest form of energy for life?
Glucose
Why are valence electrons important?
What is a substrate?
Which organic compound is insoluble in water?
Lipids
If the thermal energy of an organism's particles increases, what else increases?
Temperature
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
Cation - has more protons than electrons
Anion - has less protons than electrons
What is the difference between cohesion and adhesion of water?
Cohesion - the attraction of water particles to each other
Adhesion - the ability of water to attract other substances to it
A base with a nitrogen in it
Phosphate gropu
Sugar
What is the difference between a solvent and a solute?
Solvent - the substance doing the dissolving
Solute - the substance being dissolved
Draw a water molecule.
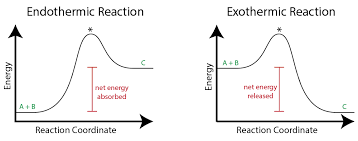
Draw graphs for exothermic and endothermic reactions.
What are the four substances connected to the central carbon atom of an amino acid?
Amine group (NH2)
Carboxylic acid group (COOH)
Hydrogen
R-group
How does an enzyme work?
An enzyme helps a chemical reaction occur quickly by lowering its activation energy. It has a spot, called the active site, where a molecule can attach to. The enzyme uses the active to hold the substrate in place while a chemical reaction takes place.