Forms of an element with a different number of neutrons and thus contain a different mass number.
Isotopes
Proteins that enhance correct protein folding and prevent inappropriate binding.
Chaperonins or chaperones.
What is Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids
Usually single stranded, contains a ribose sugar and have complimentary base pairs; Adenine, Guanine, Uracil, Cytosine
RNA
Molecules that have the same chemical formula but different arrangement of atoms
What is isomers
How many valence shells does oxygen have and how many bonds can oxygen make?
Oxygen has two valence shells and can make two bonds.
An electron is transferred between atoms, creating positive and negative ions that attract on another.
What is Ionic bond
Name the monomer that is associated with each polymer
What is amino acids, monosaccharide, nucleotide
What are the names of the pyrimidines (single ring structures)
Cytosine (C), uracil (U), thymine (T)

Two molecules that are covalently bonded together to form a larger molecule.
What is Condensation (dehydration) reactions
This type of bond describes the equal sharing of electron pairs. Give an example of a covalent bond.
Covalent bond. ex. Peptide bond
This describes the amount of energy needed to change water from liquid to gas; helps to moderate climate and ocean temperature; heat energy must be absorbed from environment (sweating)
High specific-heat and heat of vaporization
This macromolecule is associate with steroids, cholesterol, oils, waxes and fats
Lipids
What are the names of the purines (two ring structures)
Adenine and guanine 
A sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain what be described as having what type of structure
What is Primary Structure
What type of bond binds proteins?
peptide bonds
Interactions of nonpolar substances in the presence of polar substances (especially water)
Hydrophobic interaction
This macromolecule is associated with cellulose, glycogen, chitin, starch. Name the molecule and at least one organism that contains either of this molecules.
What is carbohydrates. lobsters and other crustaceans contain exoskeletons made up of chitin (a polysaccharide found) in their shell.
Polymers of nucleotides are linked by this type of bonk/linkage.
This term describes loss of function resulting from a
change in 2°, 3° or 4° structure; reversible or
irreversible. Name this phenomenon and state at least two of four known denaturing agents
What is denaturation. Denature agents; High temperature, ▲pH, polar substances, non-polar substances
Arrange the correct bond/linkage with the appropriate macromolecule
Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic acids, Carbohydrates
Phosphodiester bonds
Ester bonds (ester linkage)
Glycosidic bond (glycosidic linkage)
Peptide bond
Phosphodiester bonds- Nucleic Acids
Ester bonds (ester linkage) lipids
Glycosidic linkage- carbohydrate
Peptide bond- Proteins
The tendency of atoms to form stable molecules resulting in 8 electrons in their outermost shells.
The Octet Rule
Contains polar (hydrophilic) and non-polar (hydrophobic) regions and give an example of a component of the cell that this term would describe.
Amphipathic; phospholipids
What is the difference between a nucleoside and a nucleotide.
Nitrogenous base + Sugar (carbohydrate) = nucleoside
Nitrogenous base + Sugar (carbohydrate) + phosphate = nucleotide
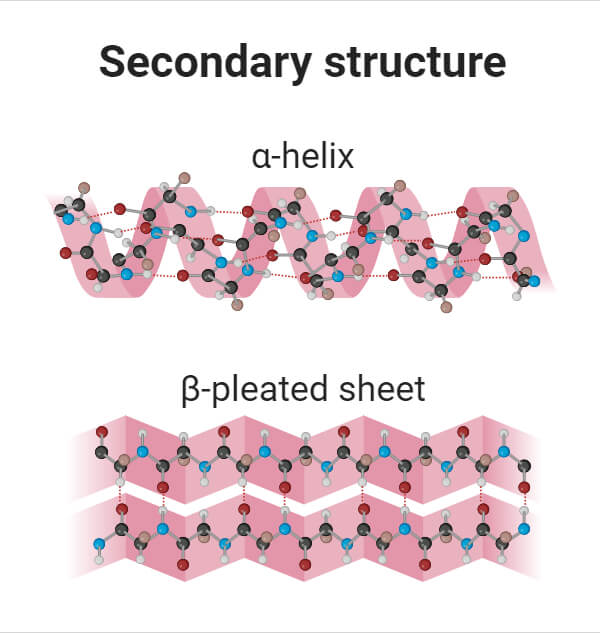
This structure is associated with alpha helix (coil) and beta pleated sheets, both of which are stabilized by hydrogen bonds
Secondary structure (2°)