Define endothermic and exothermic
endo - heat taken up (+ deltaH)
exo - heat released (- deltaH)
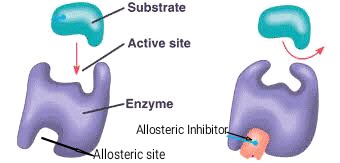
What is an allosteric site?
site other than the enzyme's active site
Which type of filament moves cells via muscle contraction or cell crawling
actin
Glycolysis creates __ ATP and __NADH and ___ Pyruvate
Does entropy increase or decrease in this equation?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O
What factors affect reaction rates for an enzyme
temperature, concentration, pH
Proteins to be imported into the nucleus contain a ____________ on the ___ - terminal
nuclear localization sequence (NLS) on C-terminal
Where does the citric acid cycle occur?
mitochondria
How do we know a reaction is spontaneous
delta G (Gibbs free energy) is negative
Why does enzyme curve eventually reach a plateau?
The enzyme is saturated with substrate
How are adjacent cells held together (4 ways)?
Tight junctions, Desmosomes, Gap junctions, Plasmodesmata (plants only)
The committed step of glycolysis creates what molecule?
fructose 6-phosphate → fructose 1,6- bisphosphate
What is the high energy state between breaking old bonds and forming new bonds
transition state
Describe what an anabolic pathway does
synthesize molecules and requires energy
What is the function of the endomembrane system?
Protein sorting, packaging, shipping, and recycling
Includes nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, the ER, and Golgi apparatus, as well as the plasma membrane
In FAD --> FADH2, is FAD oxidized or reduced?
Reduced
Draw an energy diagram for an exergonic reaction
Where change in free energy is negative
/endergonic-vs-exergonic-609258_final-2904b2c359574dfcb65a9fca2d54179a.png)
Explain competitive vs non-competitive inhibition
competitive - binds to same site
non-competitive - binds to a different site (AKA allosteric inhibition)
What are the 3 ways lysosomes recycle proteins?
receptor-mediated endocytosis, phagocytosis aka "cell eating," and autophagy ("self-eating")
List the three types of organisms (variants of cellular respiration) and what they do
Obligate anaerobes: rely entirely on anaerobic; O2 is poisonous
Facultative anaerobes: can use O2 when available but can survive using fermentation when O2 is absent
Obligate aerobes: organisms that require O2 to grow