Places where carbon is stored in Earth and in Earth's atmosphere are called (page 1):
a) sinks
b) sources
c) reservoirs
Places where carbon is stored in Earth and in Earth's atmosphere are called reservoirs.
Sources and sinks are types of reservoirs.
What are 3 major source of greenhouse gases? (page 1)
burning fossil fuels, energy production, industry, coal/oil, agriculture...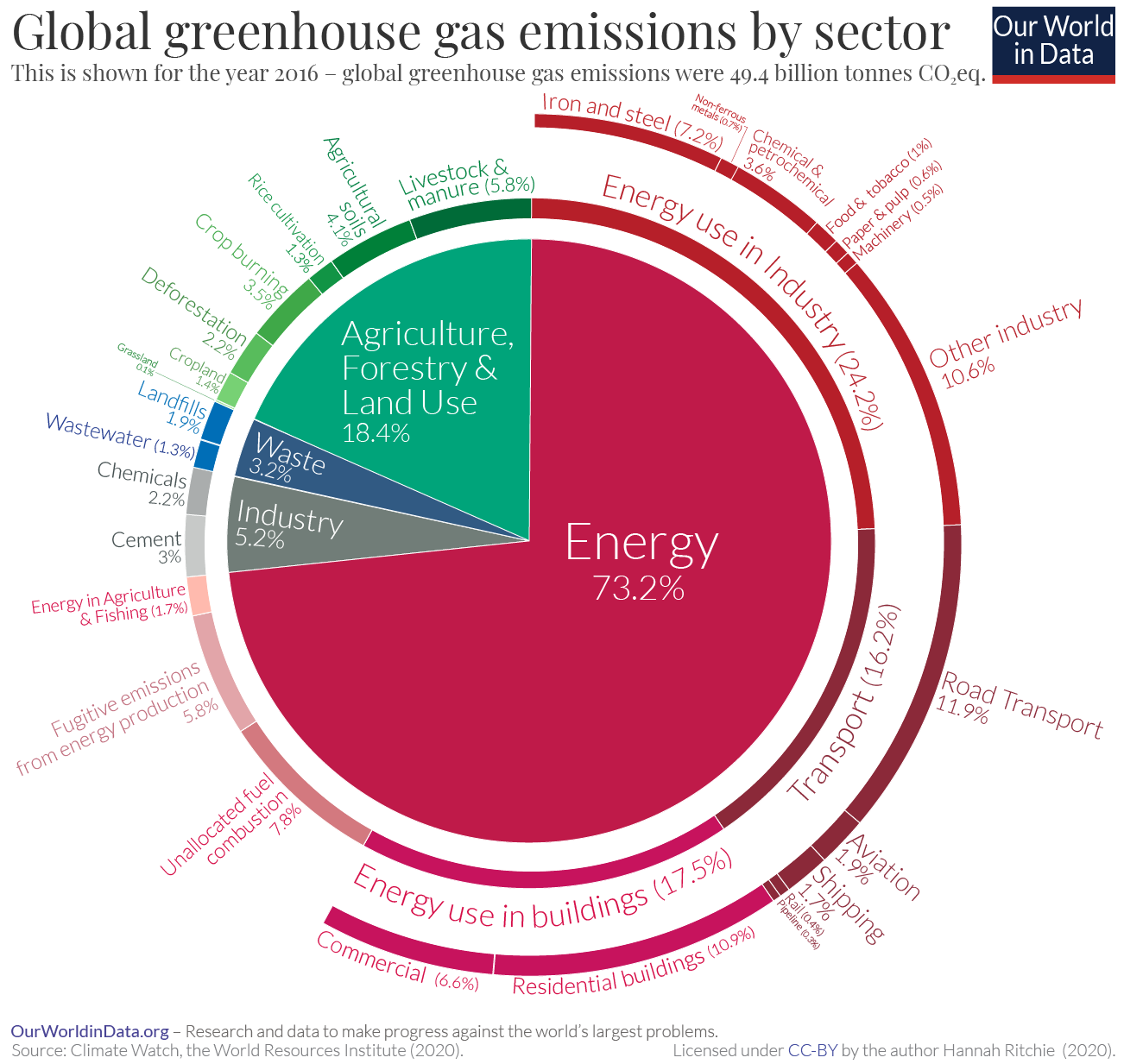
The chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
How many molecules of CO2 are required?
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
6 molecules of CO2. That's 6 Carbon atoms and 6x2=12 Oxygen atoms.
This is an example of (page 6)
a) commensalism
b) competition
c) predation
d) mutualism

This is an example of predation.
In the food web, what 3 organisms are producers/autotrophs? (page 5)
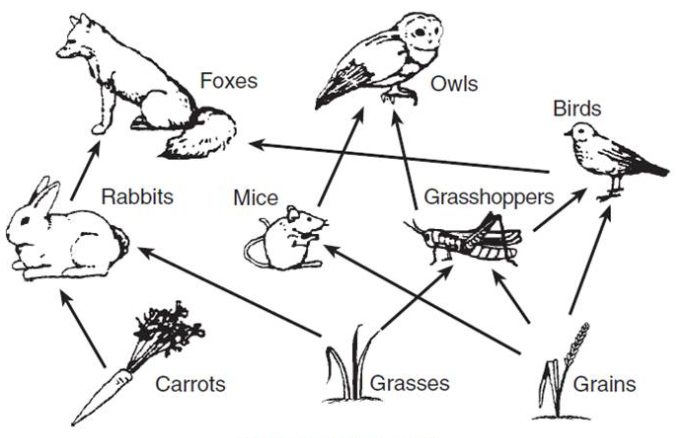

Carrots, grasses, and grains are producers/autotrophs because they make their own food through photosynthesis.
A major cause of global warming is carbon moving from the _______________ reservoir to the ______________ reservoir (page 1)
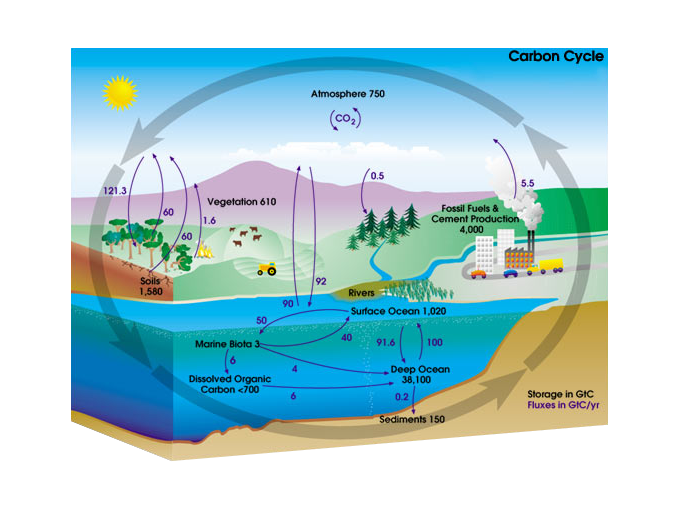
A major cause of global warming is carbon moving from the fossil fuel reservoir to the atmosphere reservoir (page 1)
What are 4 major kinds of greenhouse gases? (page 1)
CO2 (carbon dioxide), fluorinated gases, nitrous oxide, methane
What 3 types of organisms photosynthesize? (page 3)
-plants
-algae
-some bacteria (cyanobacteria)
Define a density-dependent limiting factor (page 6)
Density-dependent limiting factors depend on the population density (how many individuals live in a certain area).
Usually, high populations with a lot of individuals living close to each other are affected by density-dependent limiting factors.
Food availability is an example of a density-dependent limiting factor.
What would happen to the population of rabbits and the population of carrots if foxes were hunted to extinction? (page 5)

The rabbit population would increase because their only predator would be gone. The population of carrots would decrease because there are more rabbits in the ecosystem to eat them.
When we burn fossil fuels to create electricity, the fossil fuel reservoir loses more carbon than it gains. This makes it a (page 1):
a) source
b) sink
When we burn fossil fuels to create electricity, the fossil fuel reservoir loses more carbon than it gains. This makes it a source.
Sources are reservoirs that lose more carbon than they gain.
What would Earth be like if there were no greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere? (page 2)
Very cold! The heat re-emitted by Earth would all travel into space, and the planet would be, on average, -20 degrees Celsius (-4 degrees Fahrenheit)
Match each input of photosynthesis with the part of the plant that absorbs it (page 2):
1) CO2
2) light energy
3) H2O
Match each input of photosynthesis with the part of the plant that absorbs it (page 2):
1) CO2 is absorbed through the stomata
2) light energy is absorbed by the chloroplasts
3) H2O is absorbed by the roots
How is parasitism different from predation? (page 6)

The predator kills the prey immediately; the parasite lives on or inside the host’s body.

In the trophic pyramid, what trophic level are the snakes? (page 5)
Snakes are secondary consumers. Trophic pyramids are labeled from the bottom up, starting with "producers", then "primary consumers," "secondary consumers," and, if necessary, "tertiary consumers" and "quaternary consumers"
Photosynthesis moves carbon from the ____________________ reservoir to the ____________________ reservoir(s) (page 1)
Photosynthesis moves carbon from the atmosphere reservoir to the vegetation and surface ocean reservoir(s)
Describe the trend in CO2 concentration and temperature:
As CO2 concentration _____________ over time, temperature ___________________.
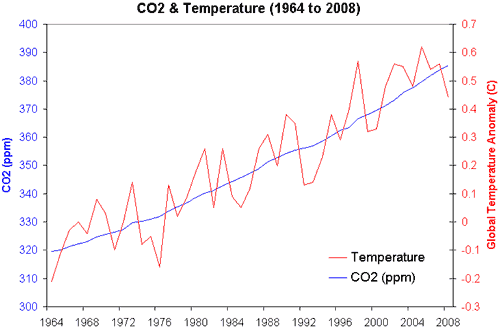
Describe the trend in CO2 concentration and temperature:
As CO2 concentration increases over time, temperature increases.

List the 2 outputs of the photosynthesis equation and where they go (page 2):
1)
2)
BONUS 50 points: name the third molecule that moves out of the stomata with one of the outputs of photosynthesis
List the 2 outputs of the photosynthesis equation and where they go (page 2):
- O2 (oxygen) is emitted by the stomata
-glucose / sugars / starch / carbohydrates stay in the plant and are used as chemical energy and as part of the plant's body
BONUS 3) Water (H2O) is NOT an output of photosynthesis, but does exit the plant through the stomata
Define carrying capacity and identify what the carrying capacity is for this population (page 7)

Carrying capacity is the maximum number of individuals a place can support over a long period of time. In this example, it is approximately 1.5-1.6 million individuals.
Approximately what percent of energy is passed up from one trophic level to the next? (page 4)
10%. The "10% rule" also applies to population size at each trophic level, and total biomass at each trophic level. (page 4)
In order to fight global warming, we need to (page 1):
prevent emissions of greenhouse gasses into the __________________
AND
remove carbon from the _____________ and store or sequester it in other ___________________.
In order to fight global warming, we need to (page 1):
prevent emissions of greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere
AND
remove carbon from the atmosphere and store or sequester it in other reservoirs.
Could there be "too much" CO2 in the atmosphere for plants to use? (page 3)

Yes! Plants can only absorb CO2 as fast as their stomata allow. Plants with fewer stomata on their leaves, or with closed stomata, absorb CO2 more slowly. As you can see on the graph, the plant has a "maximum speed" for photosynthesis at about 120 units. Adding more CO2 does not result in the plant photosynthesizing faster.
Why might a plant close its stomata? When stomata are closed, what is the effect on the plant's ability to photosynthesize? (page 3)
A plant might close its stomata to prevent water loss
When stomata are closed, plants cannot absorb CO2. They can do photosynthesis until they run out of CO2 inside their leaves.
What two other types of organisms MUST exist in this ecosystem? (page 8) OPTIONS:
OPTIONS:
-another herbivore -decomposers (bacteria/fungi)
-a tertiary consumer -producers/autotrophs
BONUS 50 points: What kind of relationship do the foxes and rabbits have?

The system must have decomposers (bacteria/fungi) and producers/autotrophs
BONUS: the foxes and rabbits are in a predator-prey relationship
Why does only 10% of the energy at a certain trophic level pass up to the next level?
Organisms use (lose) energy while they are live in the forms of motion and heat.