This structure exists within plant cells but NOT within animal cells.
Cell Wall; Chloroplasts
Quadruple Jeopardy: These are the 3 stages of the cell cycle that are often combined into 1 phase known as "interphase".
G1, S, G2
Quadruple Jeopardy: Exocytosis and Endocytosis are both examples of this type of cell transport.
Active Transport
Name the four types of biomolecules.
lipids, carbs, nucleic acids, and proteins
This molecule is the "currency" for energy in all cells performing respiration.
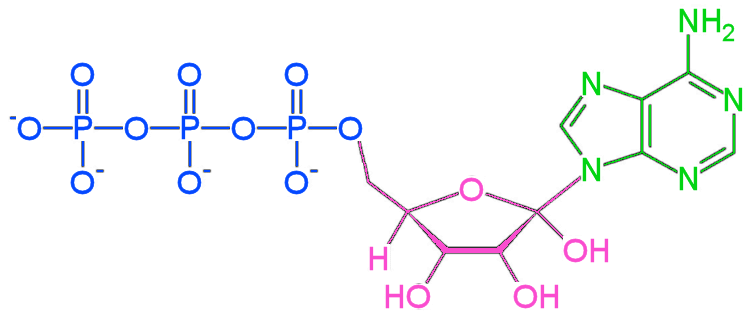
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
This organelle houses the genetic information known as DNA within eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus/Nucleolus
A complete copy of DNA is created during this stage of the cell cycle.
S (synthesis)
This is the direction of the concentration gradient.
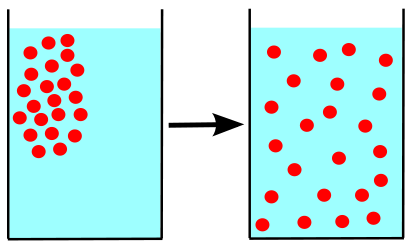
high to low
This biomolecule provides long-term energy and heat insulation.
lipids
Double Jeopardy: These are the two stages of photosynthesis.
light-dependent stage, Calvin Cycle
This organelle is attached all over the rough side of the endoplasmic reticulum, producing proteins.
ribosomes
Triple Jeopardy: What happens during cytokinesis?
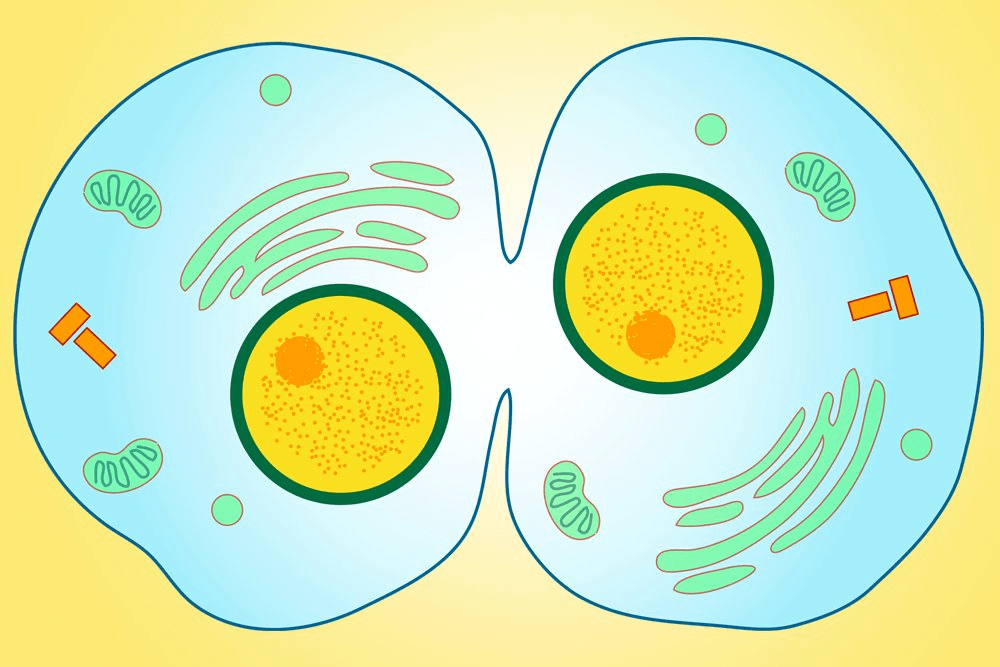
Cytoplasm splits to create 2 daughter cells.
This term is defined as the process of maintaining balance within a cell via self-regulation.
Homeostasis
This term is another word for "building blocks", and is the smallest unit of a biomolecule.
monomer
Double Jeopardy: These are the products of respiration.
carbon dioxide, water, and heat/ATP
Triple Jeopardy: This type of cell does not possess many complex organelles, even missing a nucleus for its DNA.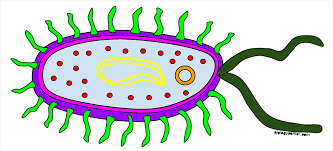
prokaryote
Double Jeopardy: This phase of mitosis consists of chromatids being pulled apart.
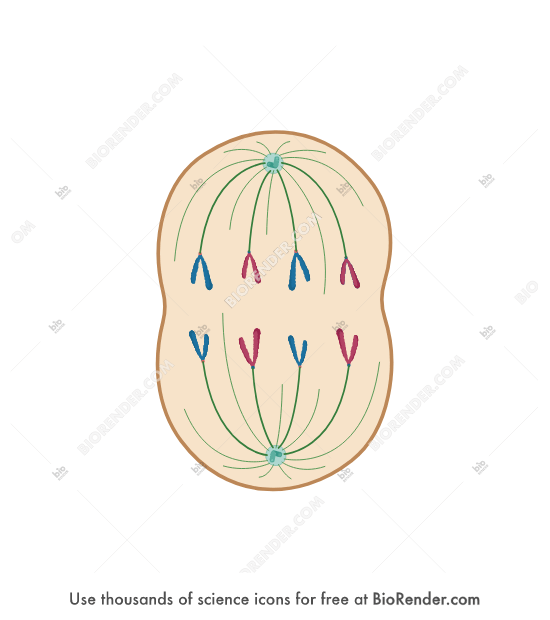
Anaphase
This describes an environment in which there is more water on the outside of the cell than the inside, forcing the cell to absorb water.
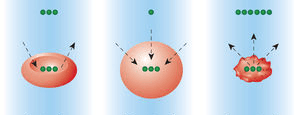
hypotonic
DNA belongs to this family of biomolecules.
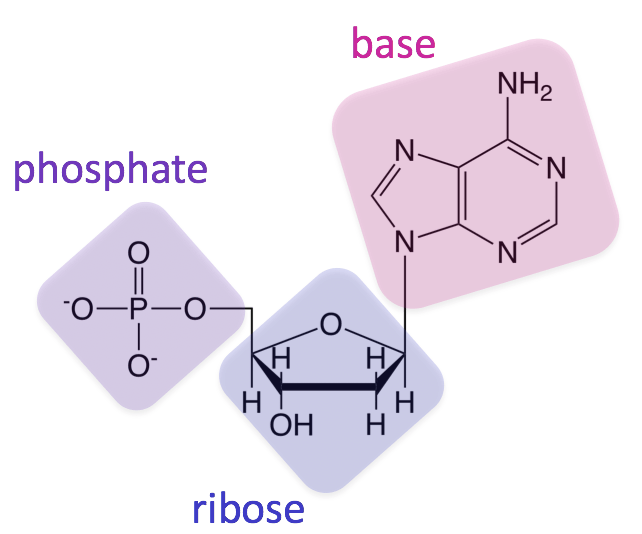
nucleic acid
This type of respiration requires oxygen.
Aerobic respiration
Double Jeopardy: This organelle is known as the "powerhouse" of energy for the cell.
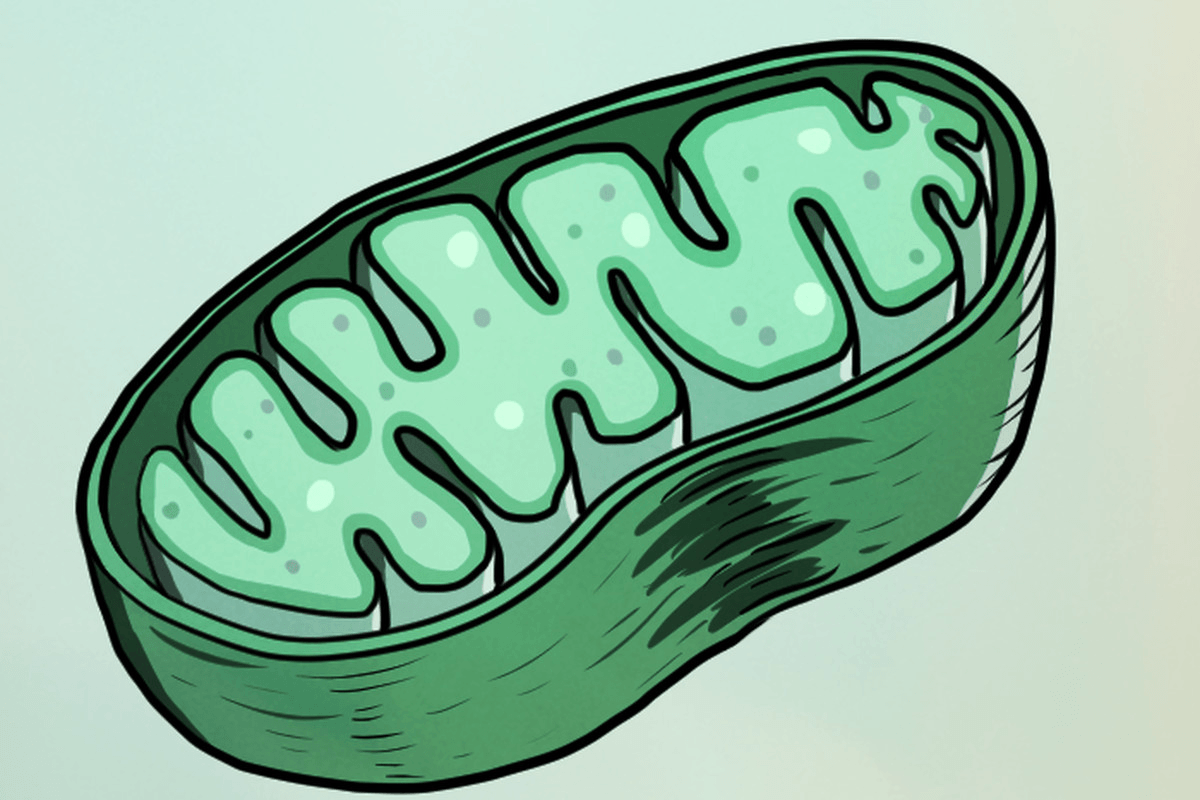

mitochondria
Quadruple Jeopardy: This term describes uncontrolled growth and division of cells.
Cancer
Triple Jeopardy: What is the difference between passive transport and active transport?
Active requires energy; passive does not.
This biomolecule functions to provide short-term energy through saccharides.
carbohydrates
Triple Jeopardy: Which energy process gains more reactant due to burning of fossil fuels?
photosynthesis