What is the function of the nucleus?
What is to store genetic material (DNA)?
Name the four main types of macromolecules.
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What is an enzyme?
What is a protein that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions?
What are the main phases of the cell cycle?
What are interphase and mitotic phase?
What is the role of DNA helicase?
What is to unwind the DNA double helix?
What organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell?
What is the mitochondria?
What is the monomer of proteins?
Amino Acids
What is the active site of an enzyme?

What is the region where the substrate binds?
What occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle?
What is DNA replication?
What are the building blocks of DNA?
What are nucleotides?
What is the function of ribosomes?
What is to synthesize proteins?
Which macromolecule serves as the primary source of energy?
Carbohydrates
Name one factor that affects enzyme activity.
What is temperature, pH, or substrate concentration?
What is mitosis?
What is the process of cell division?
What enzyme is responsible for adding nucleotides during replication?
What is DNA polymerase?
What organelle is responsible for photosynthesis?
What is the chloroplast?
What role do lipids play in the body?
Energy storage, cell membranes, and hormone production.
What happens to an enzyme when it denatures?
What is it loses its shape and function?
Describe one key event in metaphase.
What is chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell?
What is the result of DNA replication?
What is two identical DNA molecules?
Describe the function of the golgi apparatus.
What is to package and deliver proteins and other nutrients in and around the cell?
What is the main function of nucleic acids?
What is to store and transmit genetic information?
How do enzymes lower activation energy?
What is by providing an alternative reaction pathway? 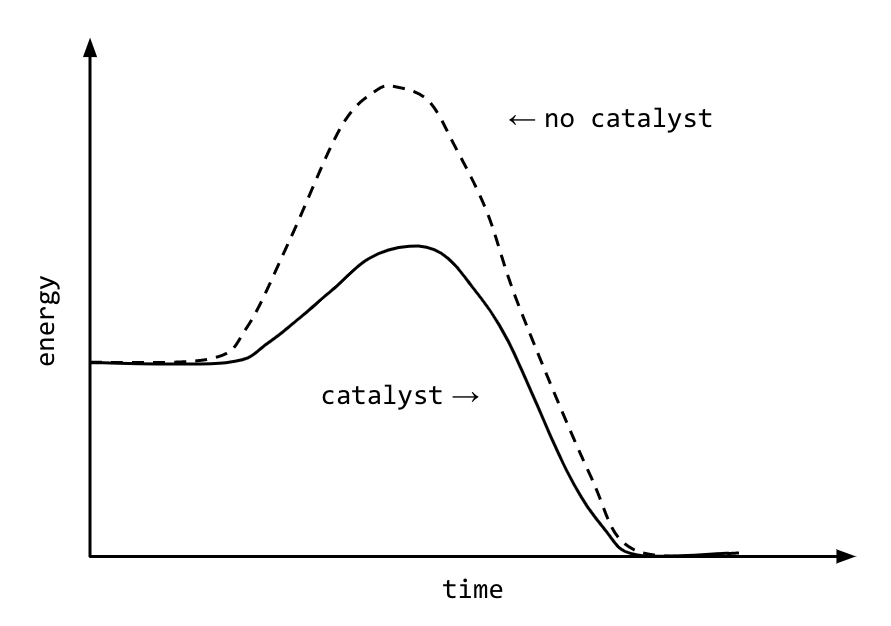
What is the purpose of checkpoints in the cell cycle?
What is to ensure proper cell division and DNA integrity?
Describe the difference between leading and lagging strands.
What is the leading strand is synthesized continuously, while the lagging strand is synthesized in fragments?