This type of cell is Multicellular and does not have a cell wall
What is an animal cell?
This is responsible for converting glucose into energy for the cells.
What is the mitochondria?
Control center of the cell
What is the nucleus?
The chromosomes align at the center of the cell.
What happens in metaphase?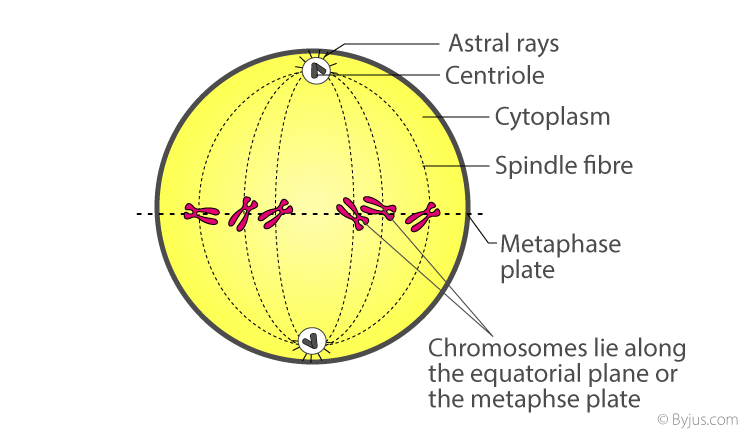
Viruses need this to reproduce for them
What is a host cell?
This type of cell is Multicellular, has a cell wall, a central vacuole, and has Chloroplasts
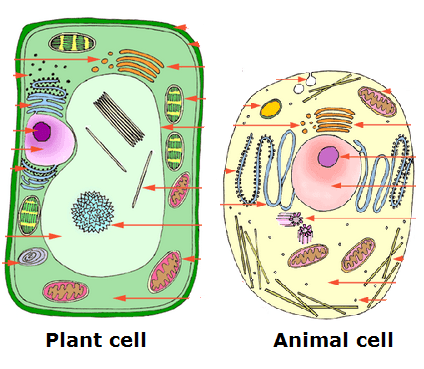 What is a plant cell?
What is a plant cell?
Mechanism involved in maintaining homeostasis that requires energy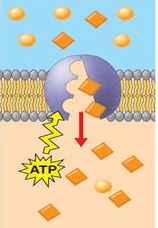
What is active transport?
Makes energy for the cell
What is the mitochondria?
The chromatin condense into visible chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the mitotic spindle begins to form
What is prophase?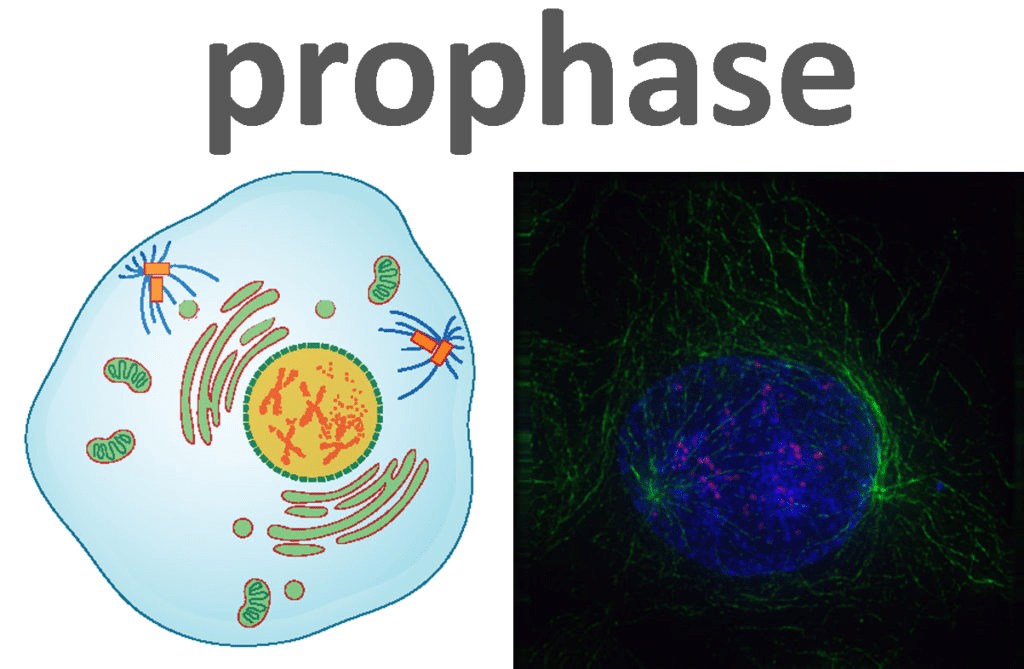
This is the order of organization levels from simple to complex
What is Cell, Tissue, Organs, Organ Systems, and Organisms?
This type of cell is unicellular and has a flagella to help it move
What is bacteria?
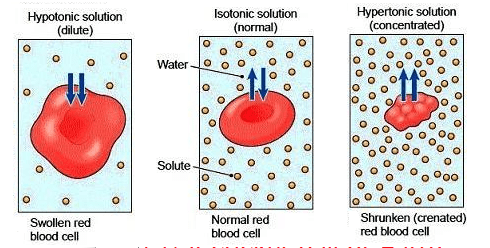
The movement of water from a high concentration to low concentration
What is osmosis?
Site of photosynthesis
What is the chloroplast?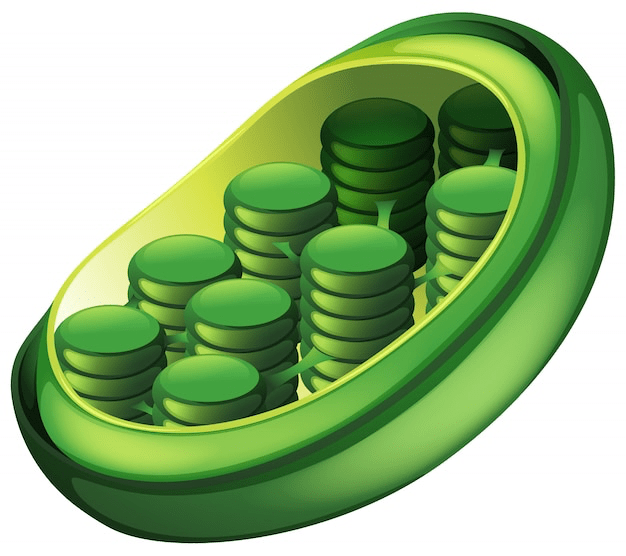
The sister chromatids separate and are pulled toward opposite poles of the cell
What is anaphase?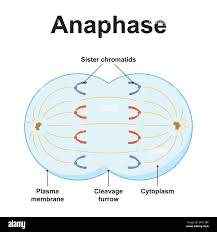
The concentration of solute inside the cell and outside the cell is the same
What is isotonic?
This can be uni or multicellular, has a nucleus, and is found in plants, animals, and fungi
What is a Eukaryote?
Which activity occurs in the S phase?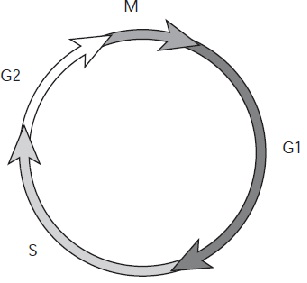
What is the Replication of DNA?
Site of protein synthesis
What is the ribosome?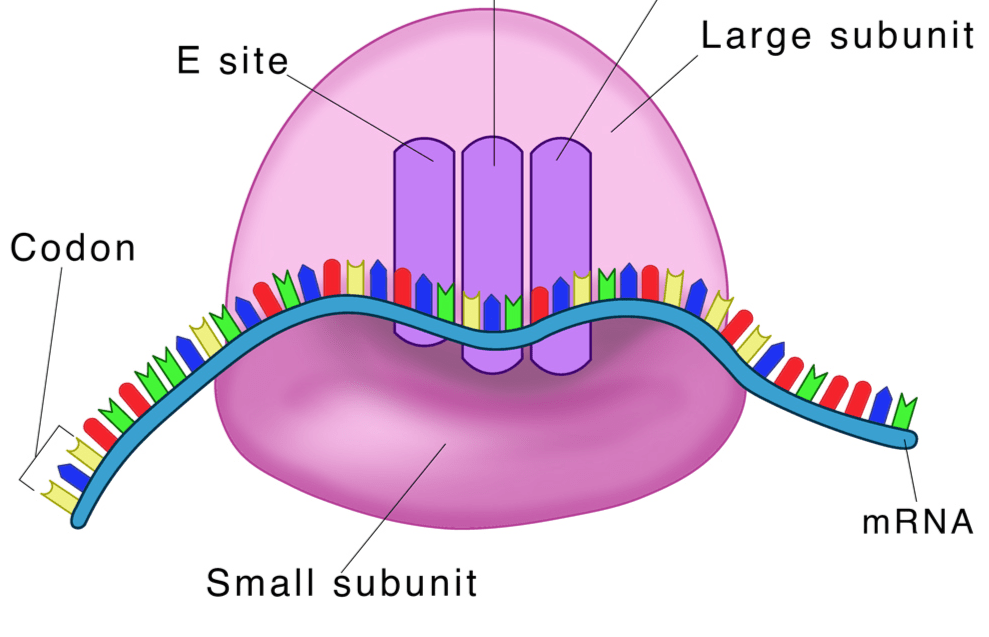
The cytoplasm divides, resulting in 2 identical cells.
What is cytokinesis?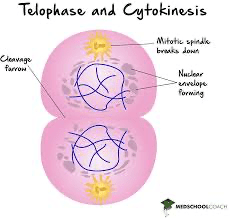
Cells will shrink in this concentration of solution
What is hypertonic?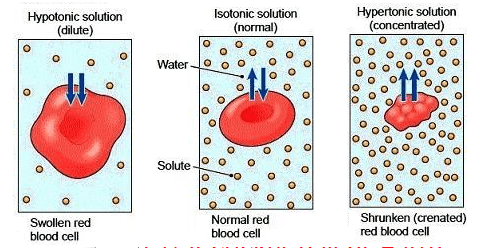
Unicellular organism lacking a membrane bound nucleus, other organelles, and is very small in comparison to other kinds of cells
What is a Prokaryote?
This type of transport across the membrane requires energy as pictured in illustration D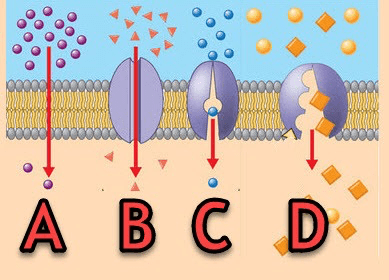
What is Active transport?
Controls what enters/exits the cell
What is the cell membrane/lipid bilayer?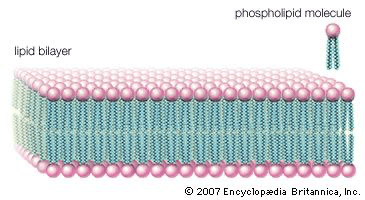
The chromosomes reach the poles, and new nuclear membranes form around them.
What is telophase?
What is Hypotonic?