An enzyme that thrives at a slightly acidic pH would function best at which of the following levels?
A. 3
B. 6
C. 8
D. 10
B
The shape of a protein is important because if the pH or temperature becomes too low or high, the protein will become _________ and lose its ability to function.
denatured
List the monomer for carbohydrates and provide one example of them.
simple sugars, glucose or something else.
glycerol, fatty acid tails.
How many of the following would be considered organic compounds? Specify which ones.
A. CH4
B. KCl
C. C6H12O6
D. H2O
E. NH3
Two, A and C.
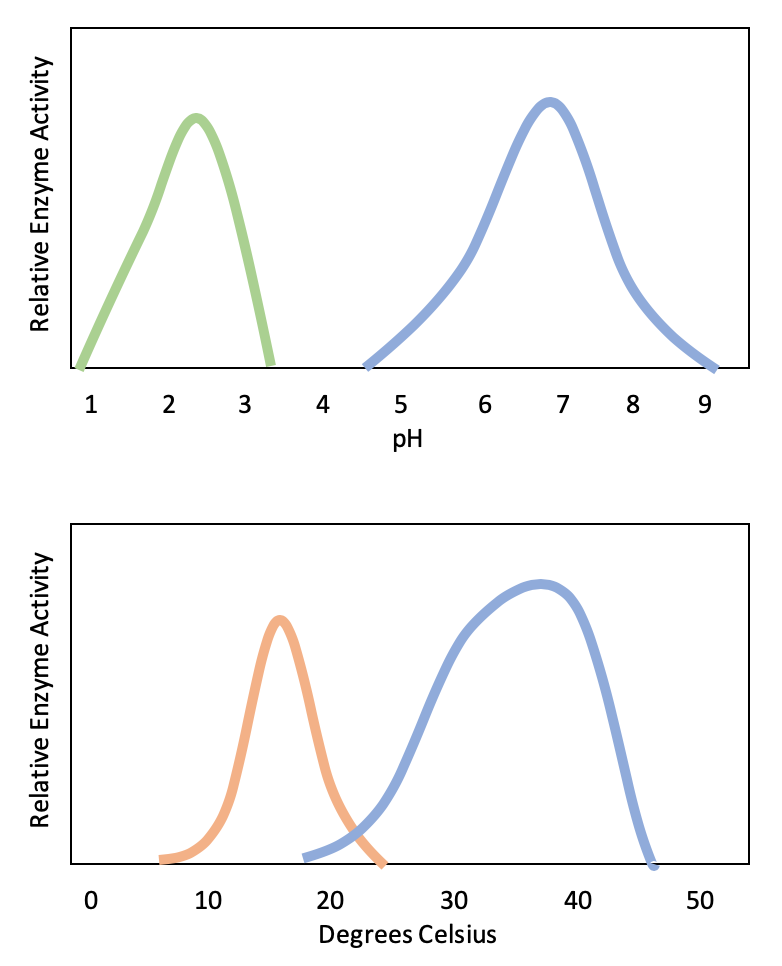
1. At what temperature do these enzymes have equal activity?
2. Which enzyme most likely works in the stomach?
1. 21 degrees celsius
2. greenase
A child is diagnosed with a condition where their body is not properly producing proteins. Which of the following may be symptoms? (potential multiple answers)
A. lack of insulation to internal organs
B. lack of antibody production
C. lack of cellulose in cell wall
D. less digestive enzyme production
B, D
Sucrose, more commonly known as _____ ______, is a ___________ meaning two simple sugars linked together.
table sugar, disaccharide.
What is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fat?
unsaturated fats contain a carbon-carbon double bond. Saturated fats contain all single bonds between carbon atoms.
Nucleic acids are the only macromolecule that contain this element.
Phosphorus
Enzymes are highly specific catalysts, meaning they ____ __ reactions by lowering the _________ _______.
speed up, activation energy.
The type of amino acid is based on the shape/formation of what group?
The R Group
Carbohydrates contain the elements ____, _____, and _____ in a _:_: _ ration.
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen. 1:2:1.
Lipids are __________ (polar/nonpolar) making them ____________ (soluble/not soluble) in water.
nonpolar, not soluble.
List the monomer for nucleic acids, an example of a nucleic acid polymer, and the function of nucleic acids.
nucleotides, DNA/RNA, encodes genetic information.
Create a simple illustration using a graph that shows how enzymes speed up reactions.
Anything showing an enzyme lowering the activation energy.

Proteins and nucleic acids are similar because the share the elements _______, ______, ______, and ______. Proteins and carbohydrates are similar because they can both be used for ________.
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen-structure/support.
In a process called glycogenesis- ________ (an energy storage for animals) is broken down into ______ so it is usable for energy. This is an example of a _______ (long chain) being broken down into its __________ (individual unit).
glycogen, glucose, polymer, monomer.
Explain why saturated fats are less healthy in terms of diet than unsaturated fats.
Saturated fats are solid at room temperature.
What are the things called that go into a chemical reaction and what are the things called that come out?
reactants, products.
Label each of the following letters and describe what is happening in each step.
A: active site
B:enzyme
C: substrate
D: enzyme-substrate complex
E: products
What are the three groups that make up the structure of an amino acid?
amino group, R group, carboxyl group.
Glycogen, starch, and cellulose are three important carbohydrate polymers. Explain each of their functions in living things.
Glycogen: energy storage in animals
Starch: energy storage in plants
Cellulose: structural support in the plant cell wall
Waxes, phospholipids, and triglycerides are three important classes of lipids? Explain the function of each in living things.
Waxes: water resistant outer covering
Phospholipids: formation of the cell membrane
Triglycerides: human body
Explain the difference between hydrolysis reactions and dehydration synthesis reactions and explain how they occur.
Hydrolysis breaks apart polymers into monomers, dehydration synthesis links monomers together into a polymer.