Define adhesion. Give an example.
Water's ability to stick to different substances.
Ex. Meniscus, Capillary action
All macromolecules have these elements.
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
What kind of cell is shown?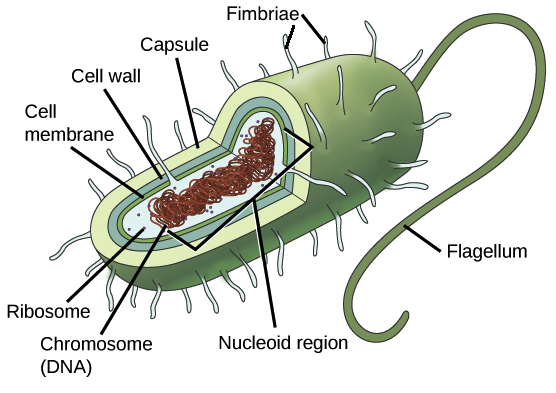
Prokaryotic
What is the difference between passive and active transport?
Active - requires energy
Passive - does not require energy
Light microscopes use _____, while electron microscopes use _____.
Light, electrons
Water is the universal _____.
What are the 4 macromolecules and what do they do?
Carbs - Provide immediate energy
Lipids - Store energy
Proteins - Enzymes, transport channels, structure
Nucleic acids - Store and transport genetic material
This organelle is the _____ and is responsible for _____.
Mitochondria, cellular respiration/releasing energy
The first kind of organisms were _____ and _____.
Which microscope can view living organisms?
Light
What does high heat capacity mean?
Water requires a lot of heat to raise the temperature. This is important to keep homeostasis.
The smallest unit of any macromolecule is known as a _____. List each for all 4 macros.
Monomer
Carbs - Monosaccharides
Lipids - Fatty acids
Proteins - Amino acids
Nucleic acids - Nucleotides
What organelle is responsible for protein synthesis? Where can it be found?
Ribosomes. On the rough ER or in the cytoplasm.
Name the 3 components of the Cell Theory.
The cell is the basic unit of life.
All living things are made up of cells.
Cells come from preexisting cells.
Scanning electron microscopes (absorb/reflect) electrons, creating an image of _____.
Oxygen and hydrogen in a water molecule have this type of bond.
Covalent
Enzymes are a type of _____. What do they do?
Protein. Speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy.
Name 3 structures plant cells have that animal cells do not.
What is structure 1? It is used in which type(s) of transport?
Protein
Passive - channel proteins
Earth's early atmosphere was mostly composed of _____, and _____, and didn't have _____.
H2O, nitrogen, O2
Water forms these types of bonds with other water molecules because of water's polarity.
Hydrogen bonds
Name each structure.
1. Carb
2. Lipid
3. Nucleic acid
4. Protein
Name four similarities between eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells.
DNA, cell membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm
Explain the Miller-Urey experiment.
Simulation of early earth's atmosphere attempting to support the hypothesis that organic material can form under the right conditions. Specifically amino acids.
Draw endosymbiosis.
anaerobic prokaryote engulfs aerobic prokaryote -> eukaryotes (animals)
new aerobic eukaryote engulfs photosynthetic prokaryote -> eukaryotes (plants)