What are the four Macromolecules?
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
The first types or organisms to develop on earth were?
A) Prokaryotic
B) Eukaryotic
C) Epithelial
D) Cardiac
A) Prokaryotic
What crucial element did Earths early atmosphere lack completely, while today we have an abundance of it?
Oxygen
Early organisms on earth were...
A) Aerobic
B) Anaerobic
B) Anaerobic
This Macromolecule is used for short term energy
Carbohydrate
The Process in which plant cells produce energy.
Photosynthesis
Which of these statements are apart of the cell theory?
A) Cells absorb other cells for energy.
B) All cells are composed of identical parts.
C) All living things are made up of cells.
D) Cells reproduce via mating with female cells.
C) All living things are made up of cells.
This macromolecule is used for long term energy
Lipids
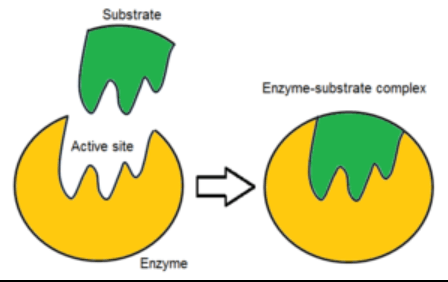
A Protein that reduces the activation energy a chemical reaction needs to go off?
Enzymes
This macromolecule forms our DNA and RNA
Nucleic Acids
The area where a substrate fits and locks into an enzyme in order to activate it?
Activation Site
This macromoelcue consist of specialized shapes that preform various functions in our bodies.
Proteins
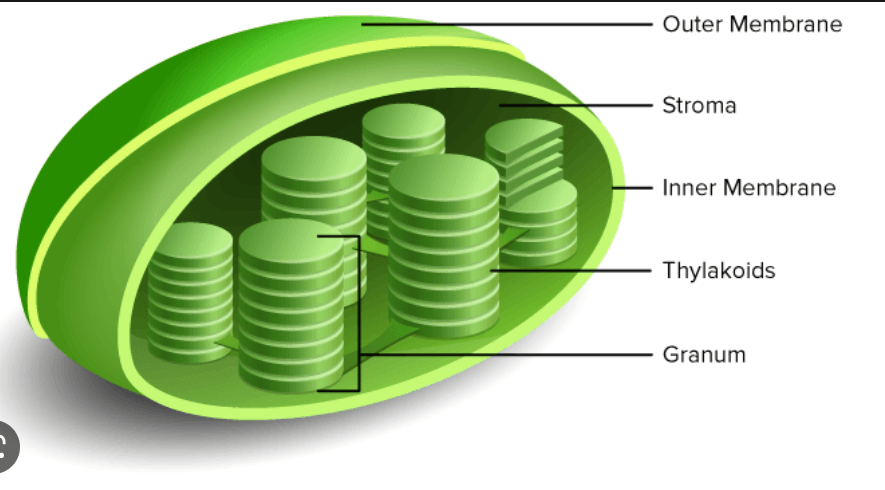
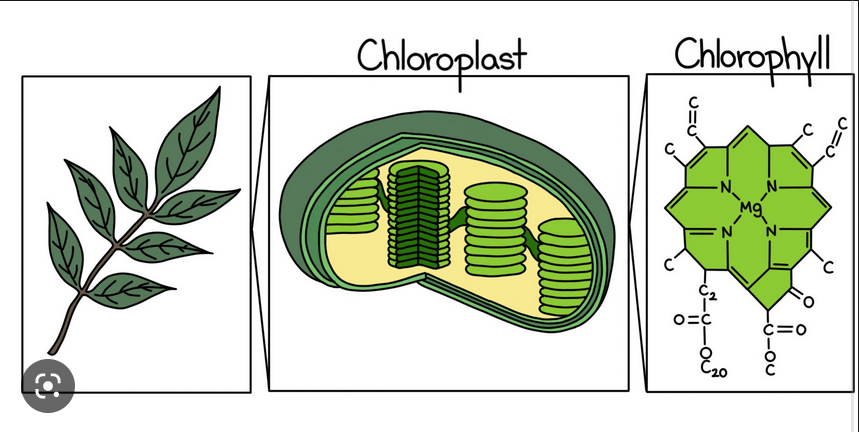
Organelle found in plant cells, a plastid that contains chlorophyll and in which photosynthesis takes place.
Chloroplast
The aqueous component of the cytoplasm of a cell, within which various organelles and particles are suspended.
Cytosol
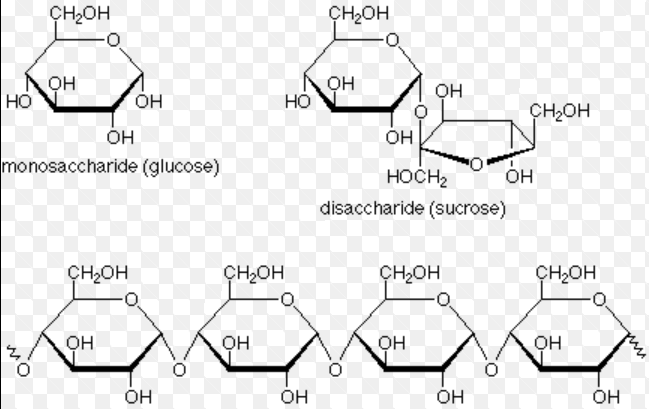
The three monomers of a carbohydrate?
Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, and Polysaccharides
What 4 elements primarily made up Earths earliest atmosphere?
Water, Ammonia, Methane, and Nitrogen
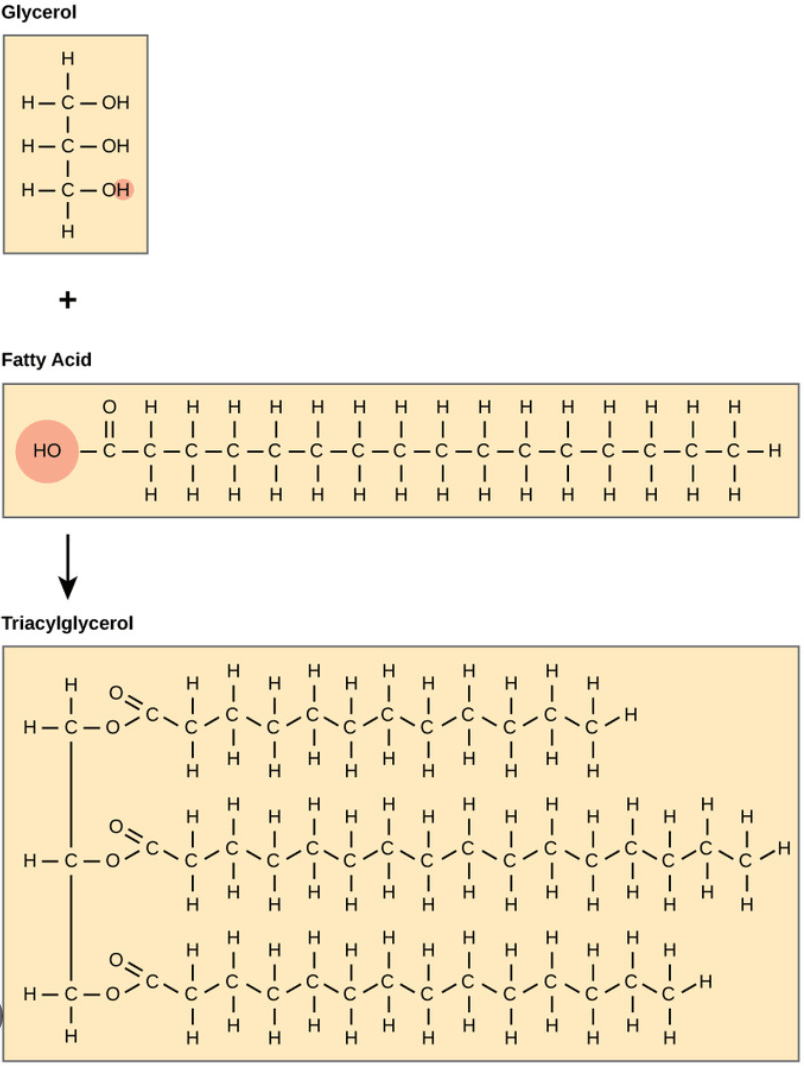
the two monomers of a lipid?
Glycerol and Fatty Acids
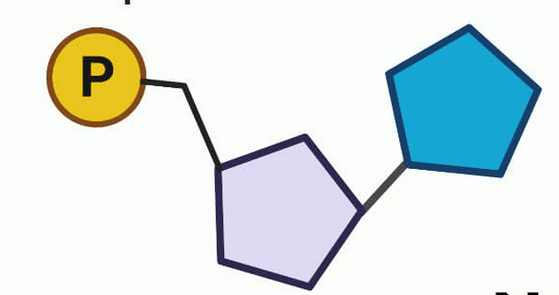
The monomer of a nucleic acid?
Nucleotide
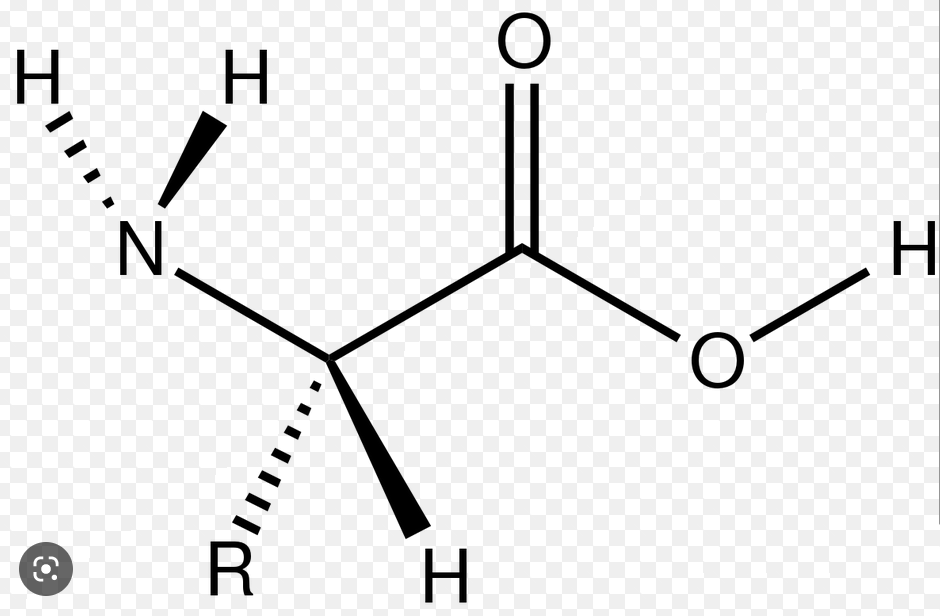
The monomer of a protein?
Amino Acids
A membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes.

Lysosome
The green pigment that plants use to make food during a process called photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll
Enzymes are specific shapes in order to control specifically what substrates can bind with them?
True or False
True
What Cell is this?
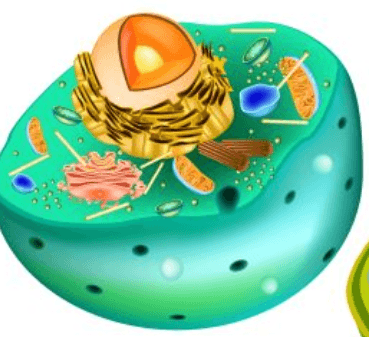
Animal Cell
These types of cells are larger and more complex, they contain organelles, and they can be both multicellular and unicellular, there DNA is contained in a nucleus.
Eukaryotes
What cell is this?
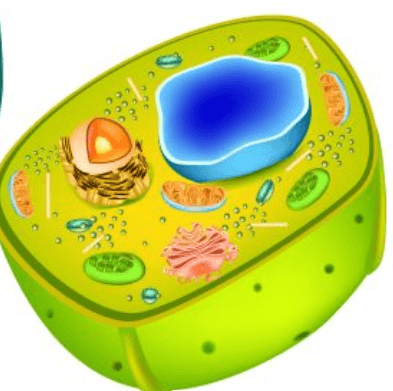
Plant Cell
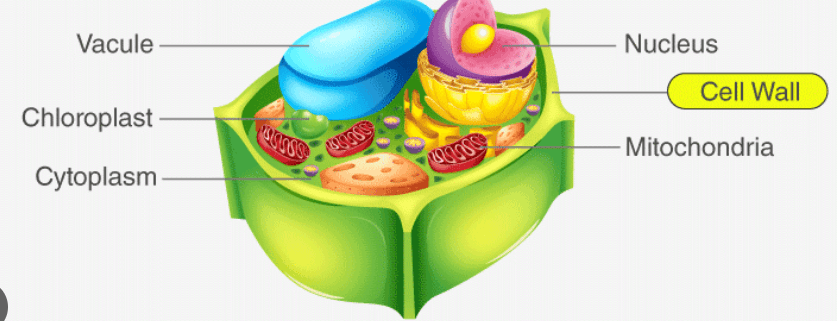
These cells are all unicellular, do not contain many if any organelles, and contain a nucleoid instead of a nucleus.
Prokaryotes
A rigid layer of polysaccharides lying outside the plasma membrane of the cells of plants, fungi, and bacteria. In the algae and higher plants it consists mainly of cellulose.
Cell Wall
True or False
Earth's early atmosphere lacked any oxygen and the environment had freezing temperatures.
False
What is the experiment shown below?
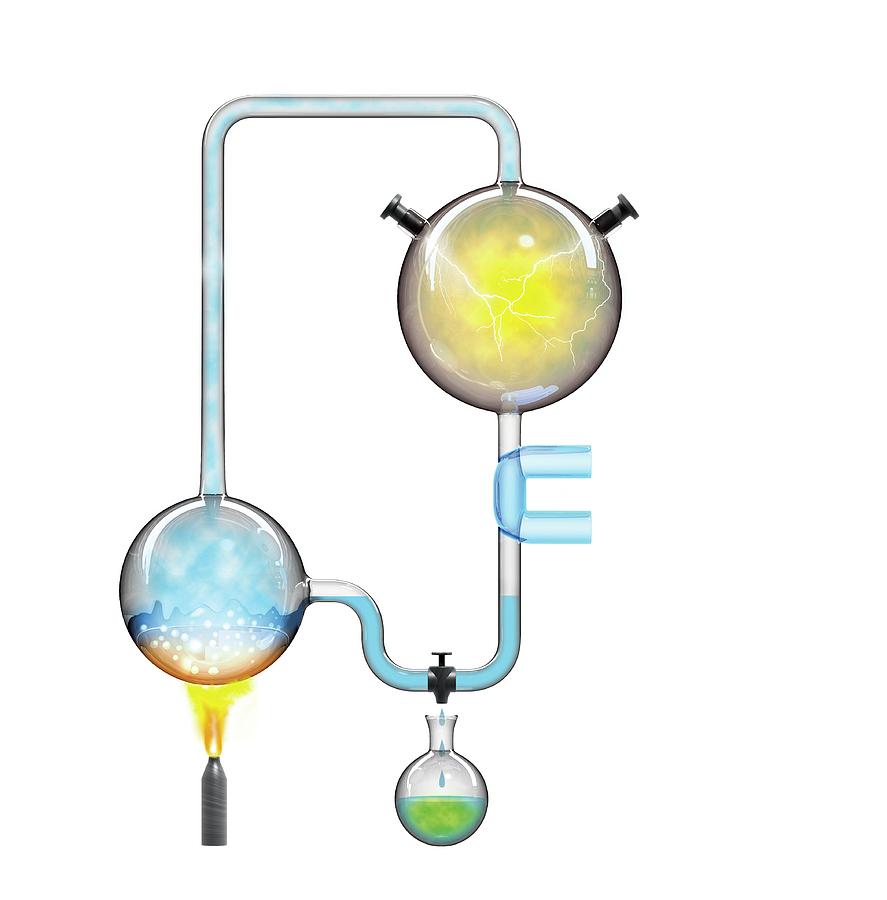
The Miller-Urey Experiment
What occurs at step 1 in the experiment?
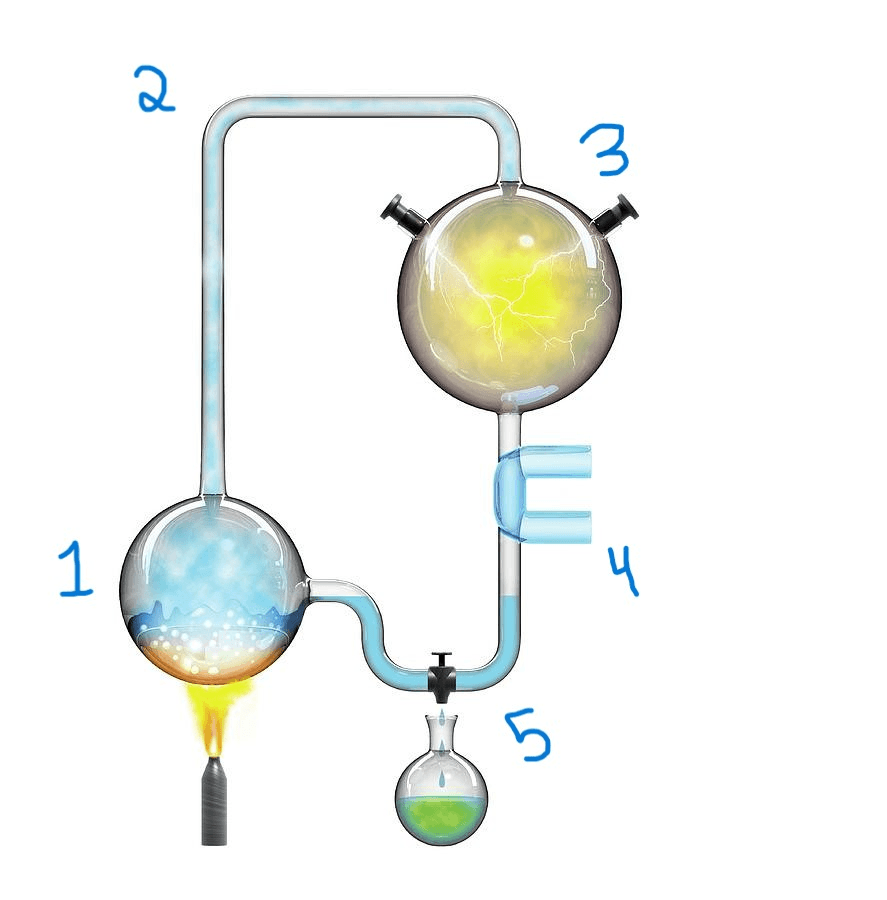
A) Water is heated, and water vapor is formed.
B) The Circulating gases are bombarded by sparks of electricity.
C) Cold water cools the chamber, causing droplets to form.D) Water is heated and water vapor forms.
D) Water is heated and water vapor forms.
What occurs at step 2 in the experiment?
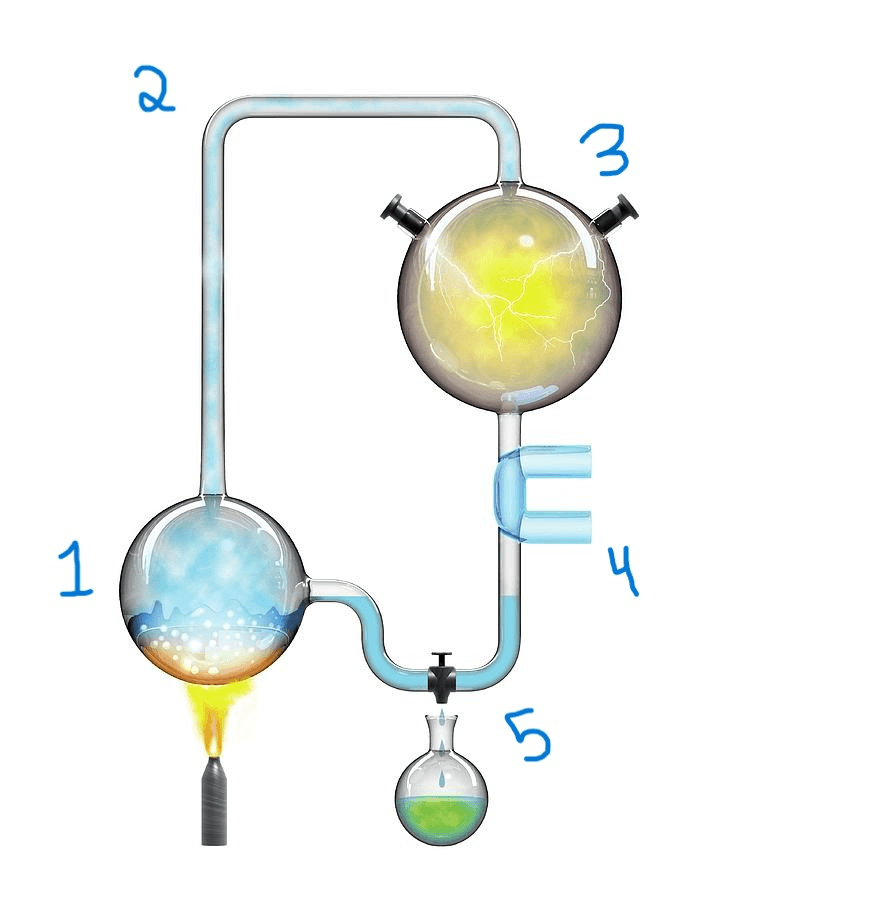 A) Water is heated, and water vapor is formed.
A) Water is heated, and water vapor is formed.
B) A mixture of methane, ammonia, and hydrogen is added to the water vapor.
C) Cold water cools the chamber, causing droplets to form.
D) Water is heated and water vapor forms.
B) A mixture of methane, ammonia, and hydrogen is added to the water vapor.
What is occurring at step 4 in the experiment?
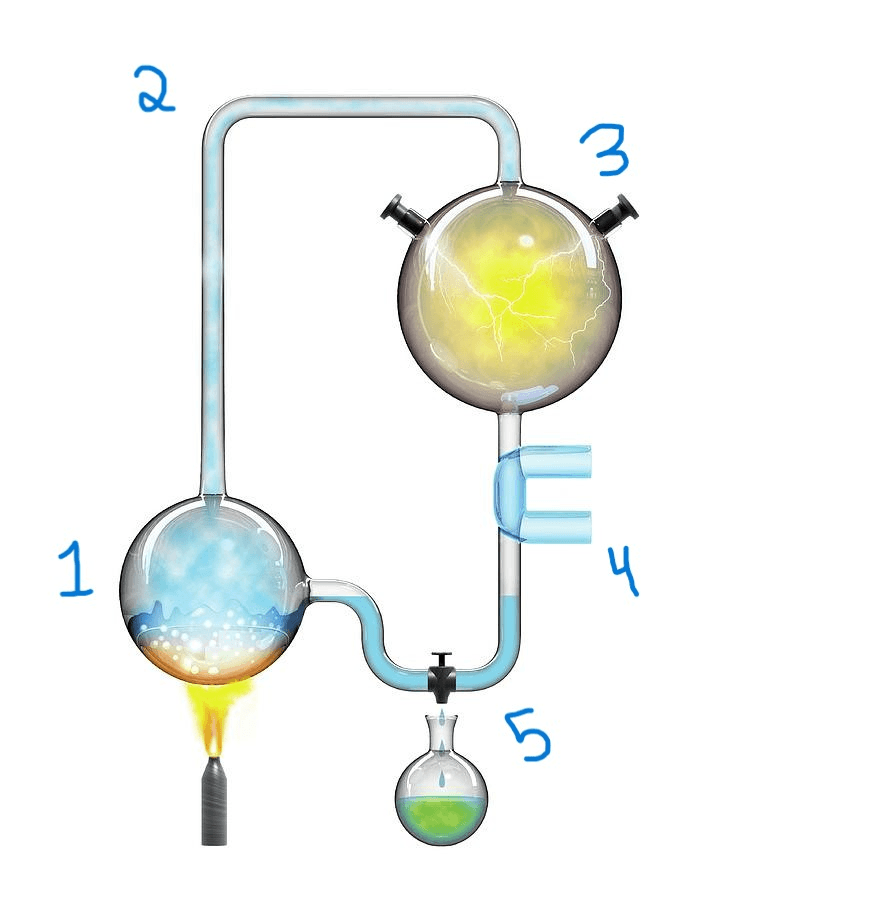
A) Water is heated, and water vapor is formed.
B) A mixture of methane, ammonia, and hydrogen is added to the water vapor.
C) Cold water cools the chamber, causing droplets to form.
D) Water is heated and water vapor forms.
C) Cold water cools the chamber, causing droplets to form.
What occurs in step 3 of this experiment?
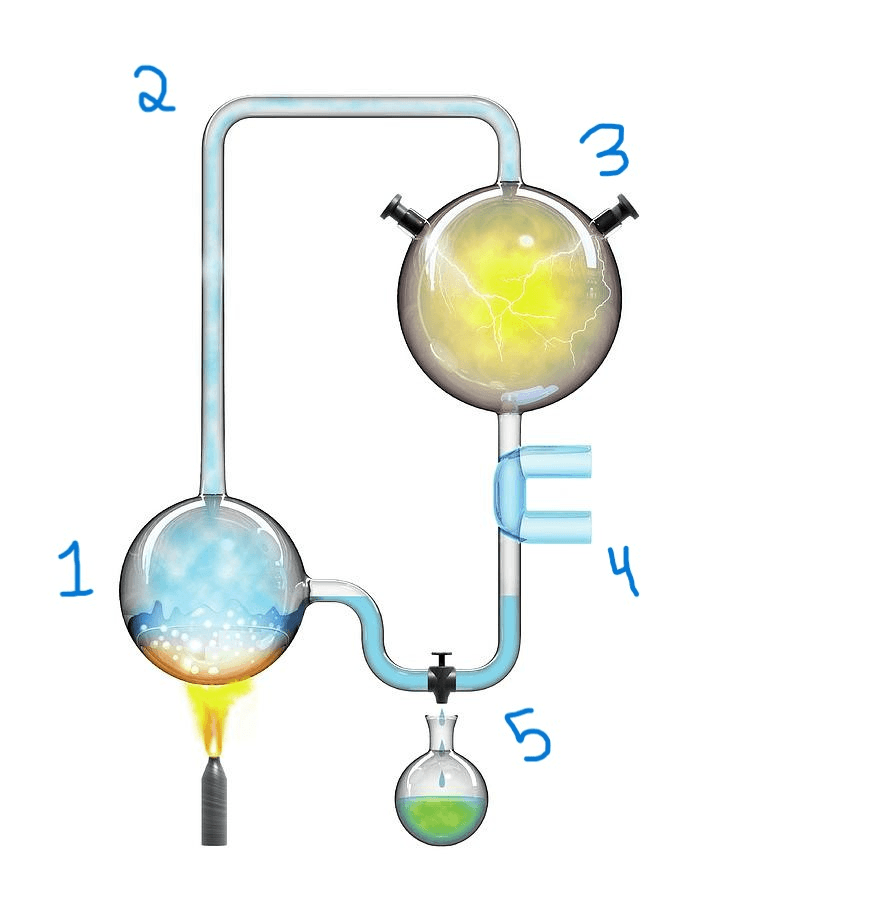
A) Water is heated, and water vapor is formed.
B) A mixture of methane, ammonia, and hydrogen is added to the water vapor.
C) Gases are bombarded with sparks of electricity.
D) Water is heated and water vapor forms.
C) Gases are bombarded with sparks of electricity.
This organelle stores water, is found in Plant cells.
Vacuoles
French chemist Louis Pasteur made two flask of nutrient broth. One broth was open and the other was closed to the open air. Over time only the open flask experienced bacterial growth. This proved that...
A) Cells are created when air comes into contact with a nutritional base.
B) All cells are airborne.
C) All cells must come from previously existing cells.
D) With enough nutrients, cells can be grown anywhere.
C) All cells must come from previously existing cells.
Name this Macromolecule?
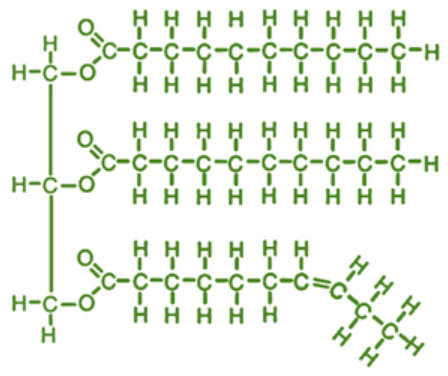
Lipid
Name this Macromolecule?
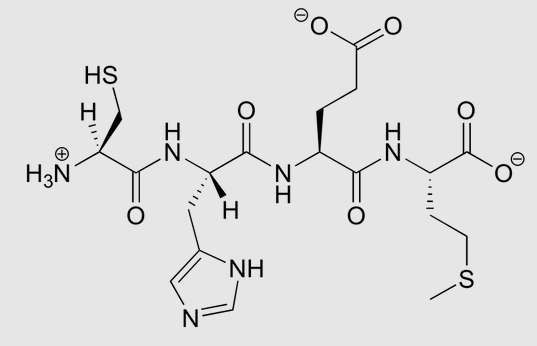
Protein
Name this Macromolecule?
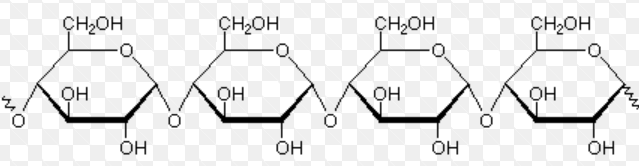
Carbohydrate
Name this Macromolecule?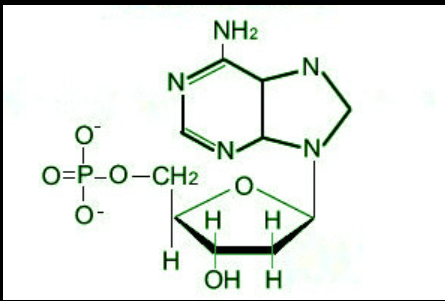
Nucleic Acid
Name this Macromolecule?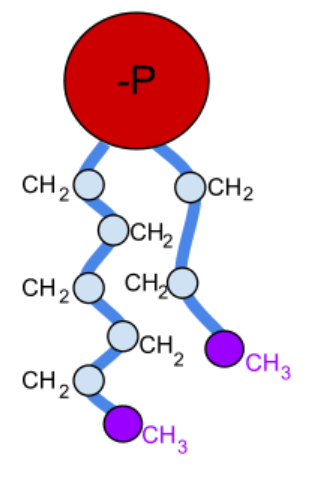
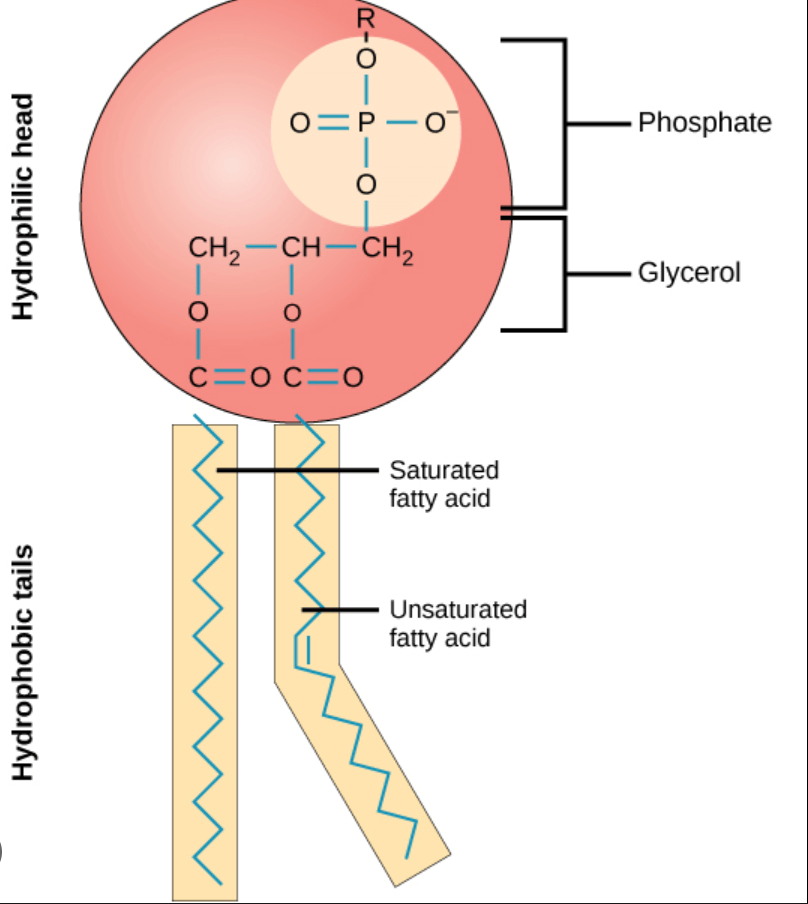
Phospholipid
List all levels of organization from smallest to largest.
Atom, Molecule, Cell, Tissue, Organs, Organ System, and Organism
A microscopic network of protein filaments and tubules in the cytoplasm of many living cells, giving them shape and coherence.
Cytoskeleton
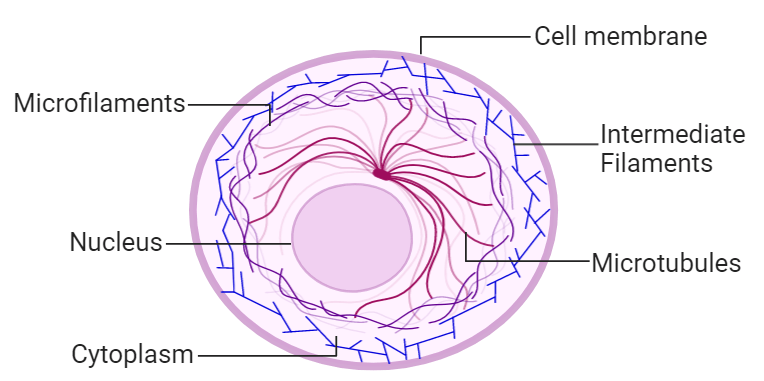
What is the role(s) of the nucleus?
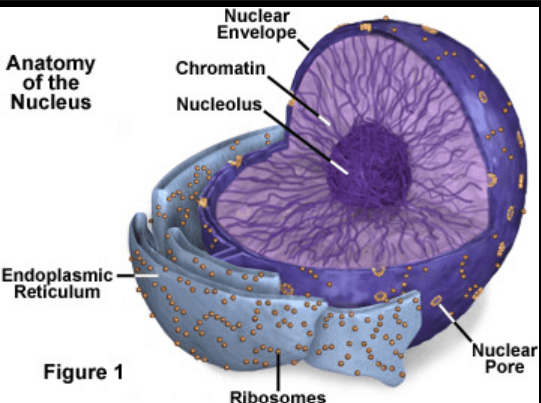
Controls and regulates the activities of the cell. Carries genes and hereditary information.
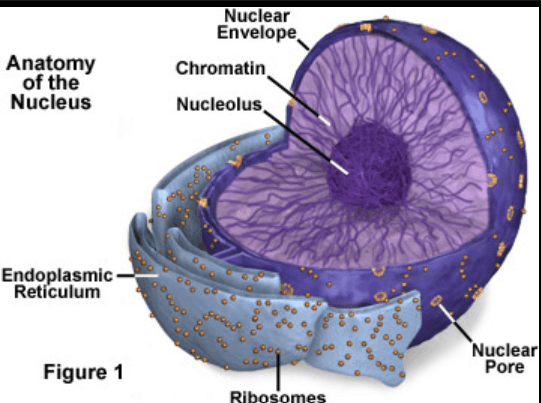
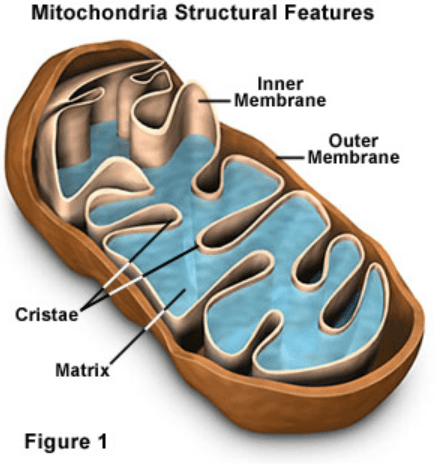
What organelle contains its own DNA and produces ATP for the cell to use.
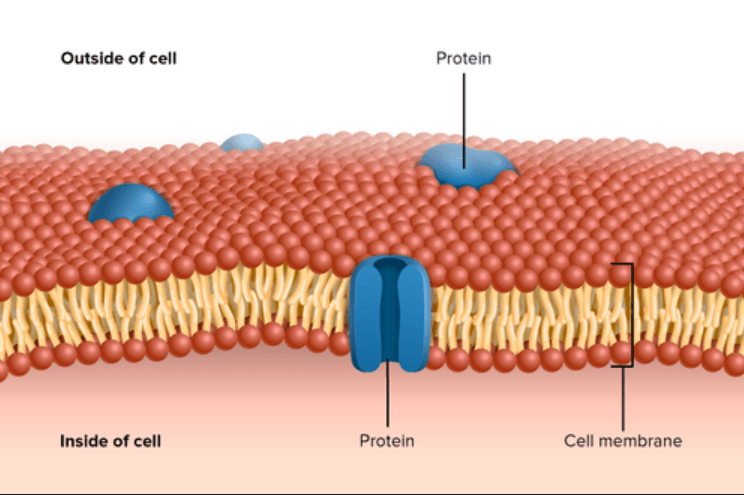
A selectively permeable barrier that regulates what can and cannot enter the cell.
Cell Membrane
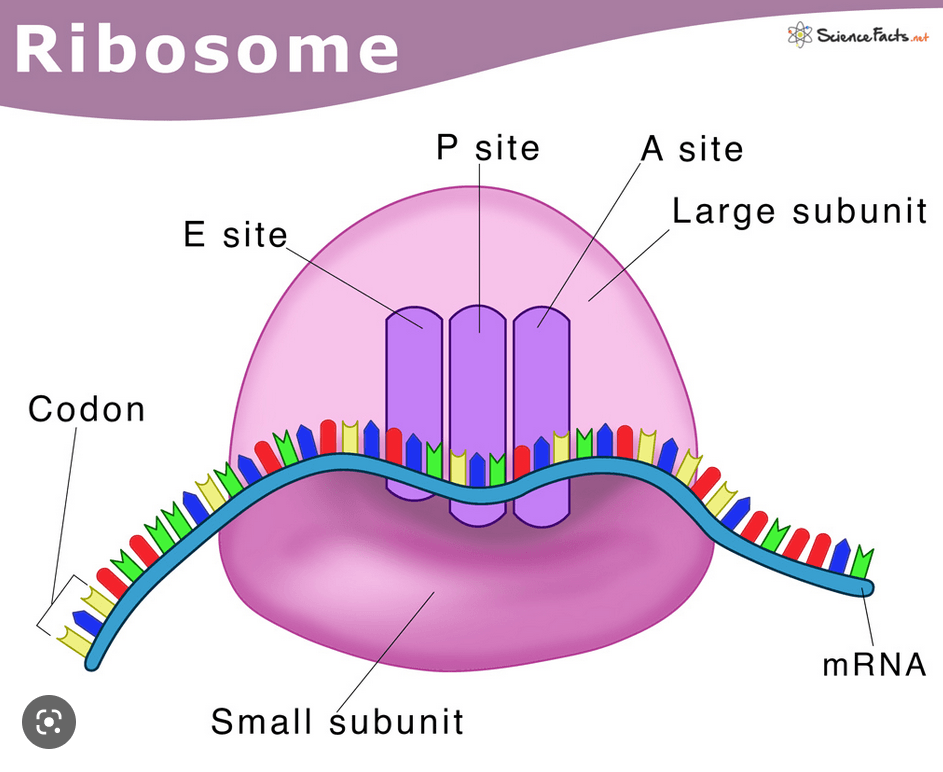
The site of protein synthesis in the cell and also can be found embedded in the Rough ER.
Ribosome
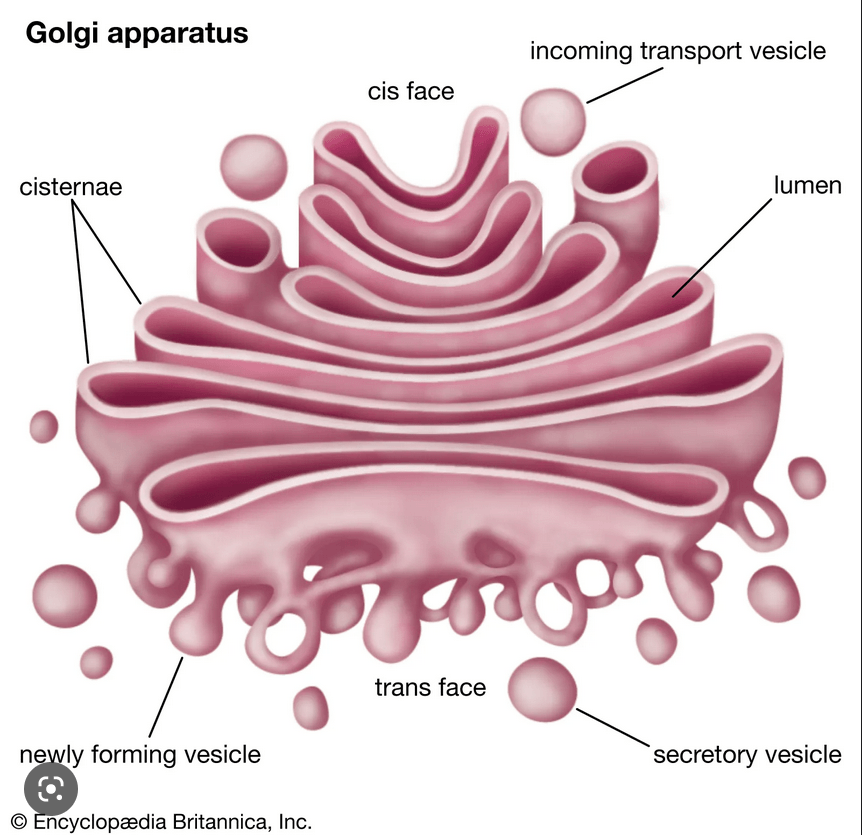
Folded membranes within the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells, involved in secretion and intracellular transport.
Golgi Apparatus
Some eukaryotic cell organelles, such as mitochondria and plastids, evolved from free-living prokaryotes.
Endosymbiotic Theory
In a phospholipid, which part is hydrophilic and which part is hydrophobic?
Hydrophilic: Head
Hydrophobic: Tail