Which organelle controls what goes in and out of a cell?
Cell Membrane
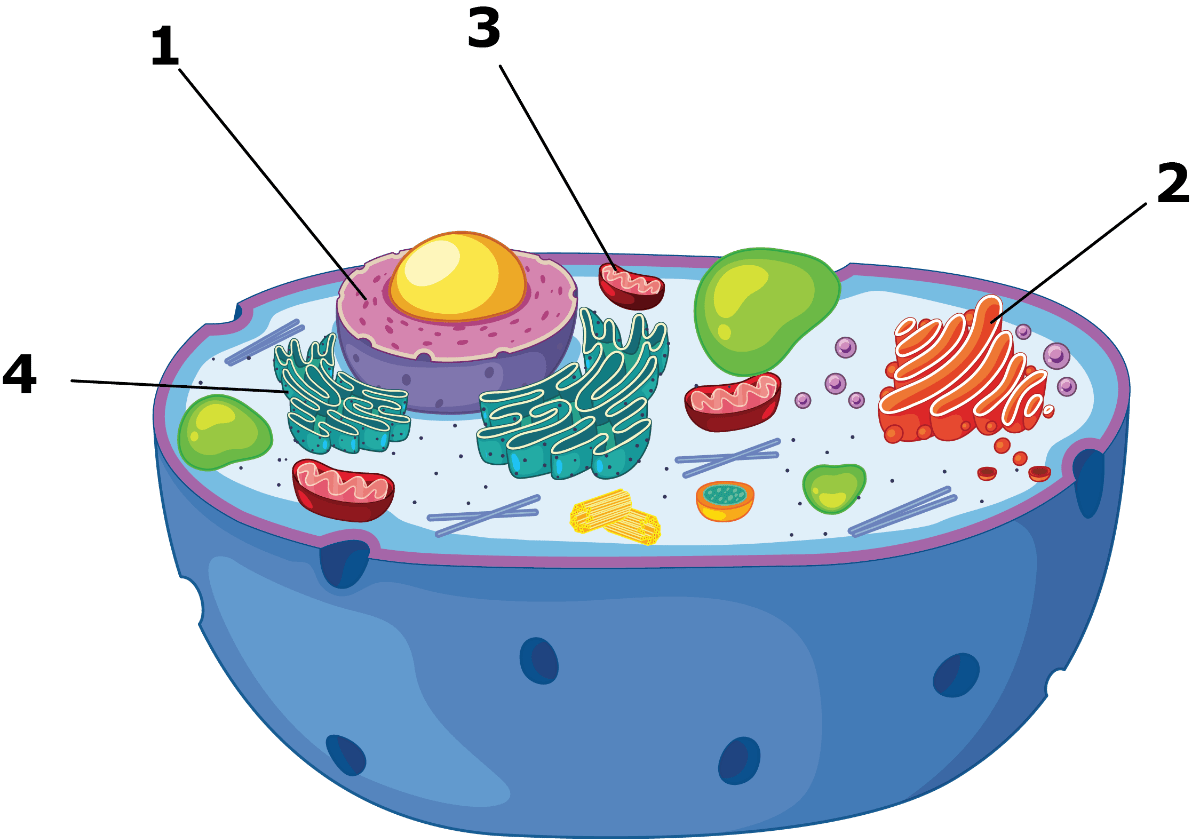
Which organelle is #4?
Rough ER
In which type of transport do molecules move from areas to high concentration to areas of low concentration?
Passive Transport
What do we call a virus that enters a bacteria cell?
Bacteriophage
Prokaryotes lack a _____ and _____-_____ _____.
Nucleus, Membrane-Bound Organelles
Which organelle provides energy for the cell?
Mitochondria
In which osmotic solution does the cell shrink in size?
Hypertonic
During which type of viral life cycle does the DNA of the host cell get taken over by the viral DNA?
Lytic
What are two structures plant cells have that animal cells don't?
Cell Wall, Chloroplast
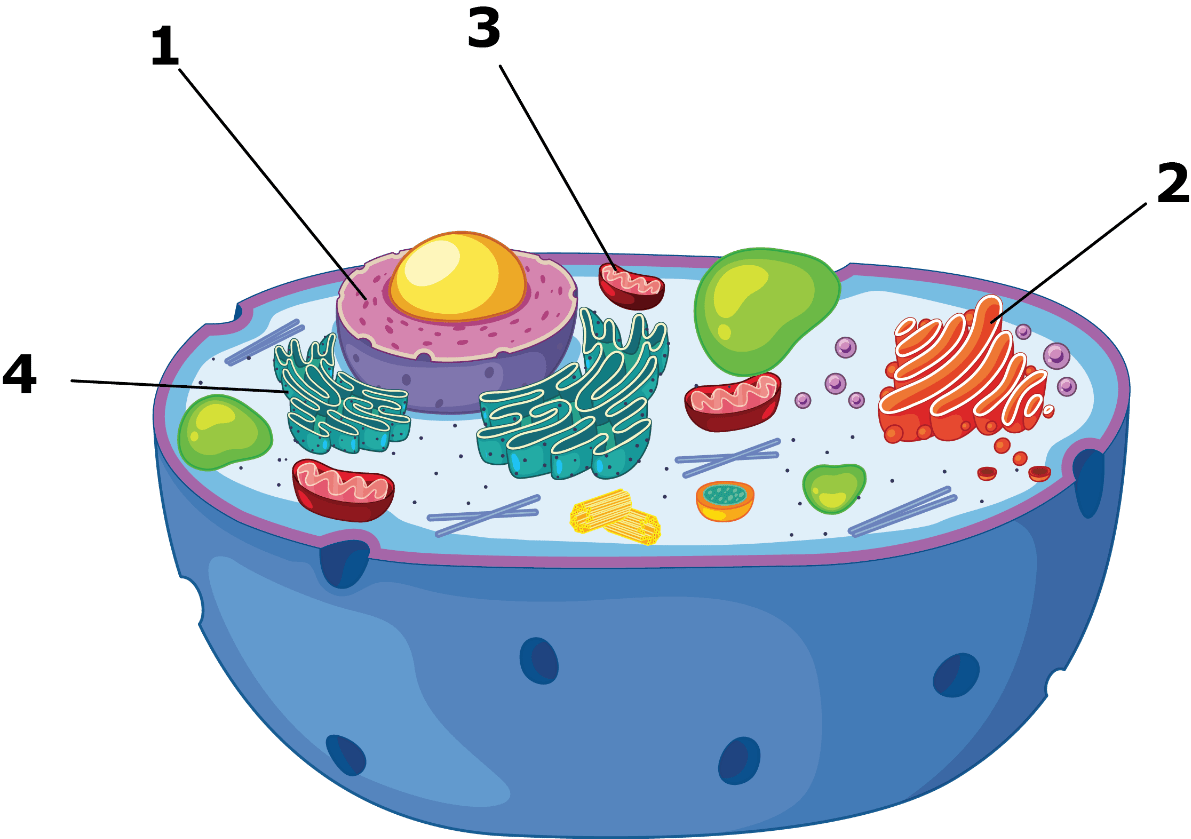
Which organelle is #2?
Golgi Complex
_____ is the movement of molecules down a concentration gradient, while _____ _____ is the movement of molecules down a concentration gradient with the help of special proteins channels.
Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion
During which type of viral life cycle is the host cell membrane dissolved by viral enzymes?
Lytic
How do plant and animal cell vacuoles differ?
Plant cells have one large central vacuole.
Which organelle controls all cell activities?
Nucleus
What is the source of energy that drives active transport?
ATP
During which type of viral life cycle does a "trigger" such as stress can cause the virus to activate?
Lysogenic
Which four structures can be found in all types of cells?
Genetic Material (DNA & RNA), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Cell Membrane
Which organelle is responsible for protein synthesis?
Ribosomes
In active transport, what is moved across a cell membrane using transport proteins?
Ions
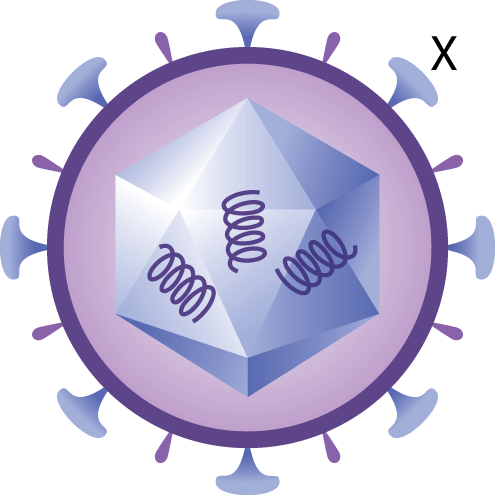
The function of the structure labeled "X" in the figure above is most likely allowing the virus to do what to a cell?
Anchor/Attach