Water (H2O) and ammonia (NH3) are both considered INORGANIC because both of the molecules are missing this element.
What is CARBON?
The building blocks of our biological macromolecules, called polymers, may be referred to as THESE. Amino acids are these in relation to proteins.
What are MONOMERS?
Monomers are bonded together to form these, another word for macromolecules. If amino acids are the monomers, proteins are the _________________.

What are POLYMERS?
This is the part of the enzyme that the substrate binds to.
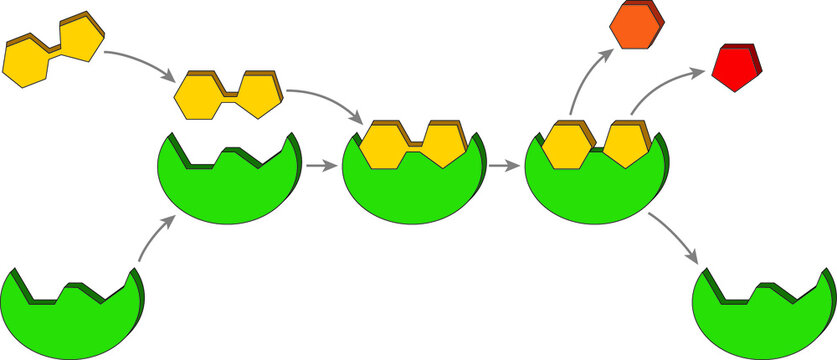
What is the ACTIVE SITE?
This THEORY describes the way enzymes and substrates fit together.
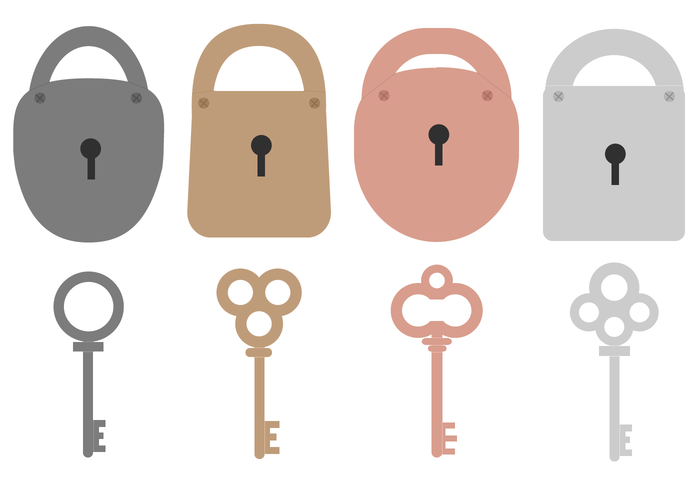
What is LOCK and KEY THEORY?
Glucose, a simple sugar, (C6H12O6) and methane (CH4) contain atoms of BOTH carbon and hydrogen making this molecule...
What is ORGANIC?
DNA and RNA, two types of nucleic acids, are built out of these subunits, or building blocks.
What are NUCLEOTIDES?
These molecules make up DNA and RNA. Their building blocks are nucleotides.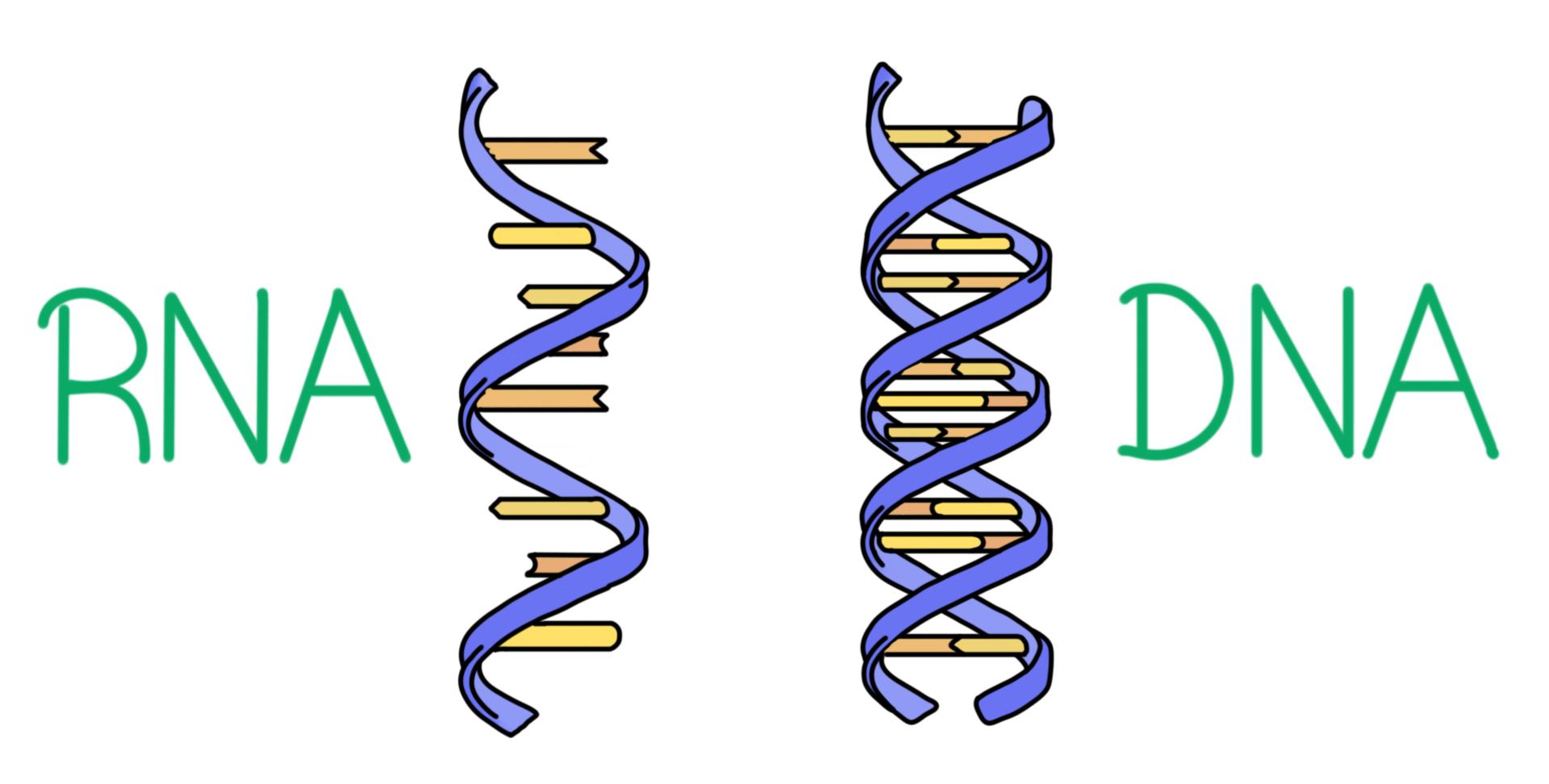
What are NUCLEIC ACIDS?
These TWO factors affect the rate of enzyme action. If these conditions are not optimal the enzyme can even be denatured!
What are TEMPERATURE and PH?
Enzymes catalyze, or control, all the chemical reactions that occur in our body, referred to as our metabolism. This is another name for enzymes (and the Regents exam will probably call them this)!
What is a BIOLOGICAL CATALYST?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids all contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, making all of these molecules __________________.
What is ORGANIC?
Lipids, fats and oils, are composed of these TWO types of building blocks.
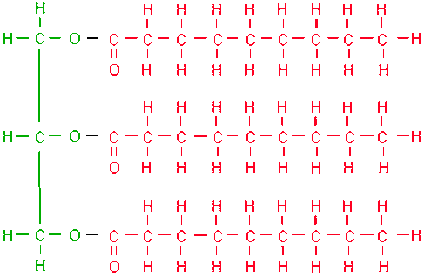
What are FATTY ACIDS and GLYCEROLS?
These molecules make up our cell membranes, are used for insulation, and serve as a source of stored energy. They are made of glycerols and fatty acids.
What are LIPIDS?
This word describes when an enzyme's molecular structure, and therefore its shape, is permanently changed and destroyed.

What is DENATURED?
In this type of reaction, simpler building blocks are combined to form a more complex product
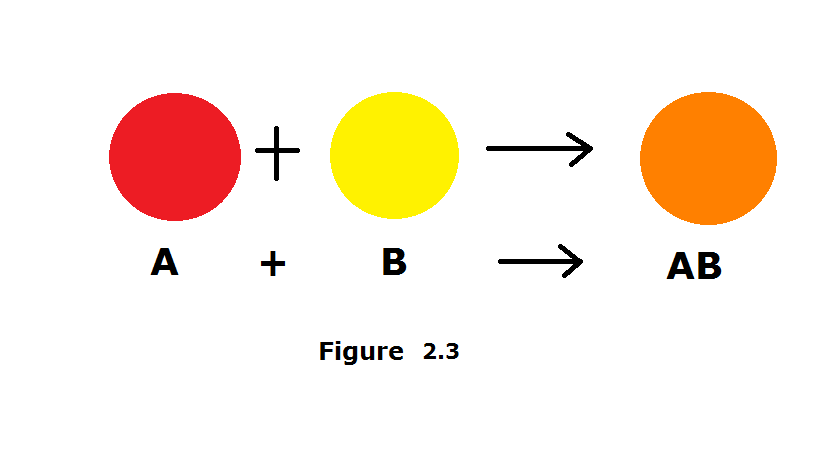
What is SYNTHESIS?
Carbon dioxide, or CO2, is an INORGANIC molecule because it lacks atoms of this element.
What is HYDROGEN?
If a carbohydrate was exposed to a carbohydrate-digesting enzyme, these monomers (building blocks) would be the products.

What are MONOSACCHARIDES, or SIMPLE SUGARS?
All of the molecules in the image fall into this category of macromolecule, including simple sugars and starches. These molecules are used for energy.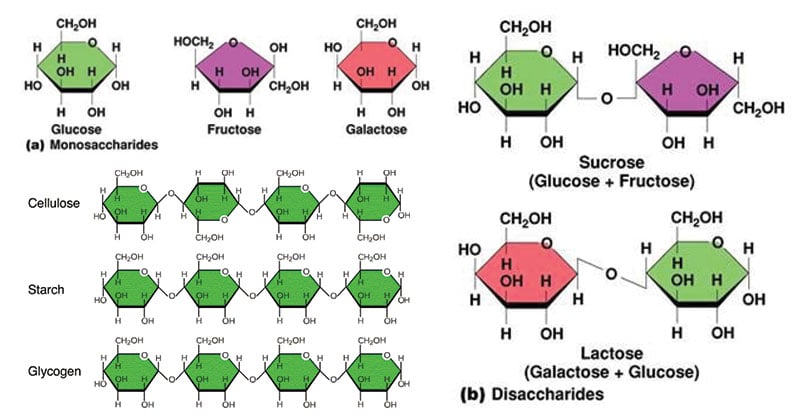
What are CARBOHYDRATES?
This is the substance enzymes bind to and acts on.

What is the SUBSTRATE?
This type of reaction occurs frequently in our digestive system! In this type of reaction a complex molecule is broken down into its simpler subunits.

What is DIGESTION?
This molecule is ____________.

What is ORGANIC?
These are the monomers, or building blocks, of proteins. "Protein shakes" are full of these.

What are AMINO ACIDS?
There are four main types of these macromolecules in our bodies: hormones, enzymes, antibodies and receptors. The shape of these molecules determines their function!

What are PROTEINS?
Temperature affects enzyme action. What is the optimal temperature for sucrase?

What is 37 DEGREES CELSIUS?
What is the optimal pH for ENZYME A?
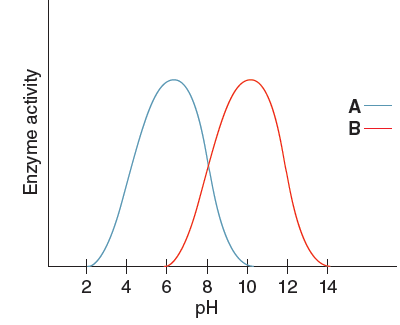
What is a pH of 6?
