The first step of DNA fingerprinting/profiling
DNA extraction
Transgenic organism
A segment of DNA that carries the instructions for building proteins.
What is a gene?
Transcribe the following DNA sequence:
ATGCATGGC
UACGUACCG
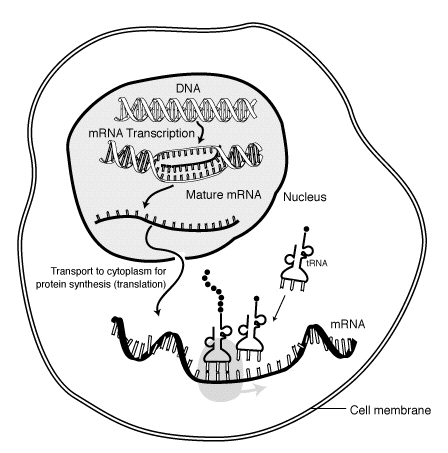
Translation takes place when the mRNA leaves the nucleus, goes into the cytoplasm and heads to a __________.
Ribosome

What are substances or agents that cause mutations called?
mutagens
Makes millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA segment
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
A circular piece of DNA naturally found in bacteria, often used as a vector to deliver genes into host cells.
Plasmid
 What is the backbone of the DNA strand made up of? (2 molecules)
What is the backbone of the DNA strand made up of? (2 molecules)
deoxyribose sugar and phosphate
What are the two steps of Protein Synthesis called, IN ORDER.
Transcription, Translation

What is the monomer of a protein?
amino acid
 When bases are inserted or deleted it causes a ___________. This causes the bases to move to the left or right depending on the type of mutation.
When bases are inserted or deleted it causes a ___________. This causes the bases to move to the left or right depending on the type of mutation.
frameshift
Non-coding regions of DNA with repeats around 3-7 base pairs in length.
What are Short Tandem Repeats (STRs)?
In CRISPR gene editing, this molecule directs the editing machinery to a specific DNA sequence by matching its bases to the target.
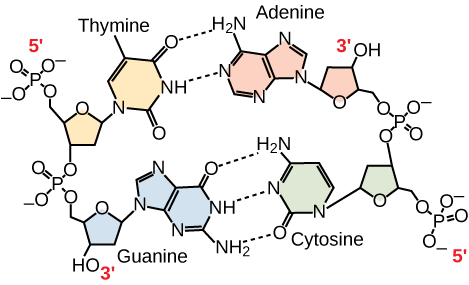 The type of bond that holds bases together in the double helix.
The type of bond that holds bases together in the double helix.
Hydrogen Bonds
In order to release the amino acid from tRNA, the ________ on the mRNA and the __________ on the tRNA must connect.
codons, anti-codons

During Transcription, what enzyme reads the DNA template strand and converts it to mRNA?
RNA Polymerase
True/False: a mutation always changes an organism's phenotype
False - a mutation is a change in the base-pair sequence and it may or may not cause a change in a trait
During gel electrophoresis, explain the two factors that affect the movement of the DNA through the gel.
1. Electricity - DNA is negatively charged, so all fragments move toward the positive electrode.
2. Size of the DNA fragments - smaller fragments fit through the pores more easily, so they move faster and therefore farther.
In the CRISPR system, this enzyme acts as molecular scissors, cutting DNA at the location specified by the guide RNA.
What is Cas9?
What DNA is included in the genome of an animal cell?
nuclear DNA
mitochondrial DNA
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-680790233-5897f4fb5f9b5874eed4b5b2.jpg)
In translation the mRNA strand binds to the ribosome and brings in tRNA, what is being made?
polypeptide
 What mRNA codon(s) would translate to Serine?
What mRNA codon(s) would translate to Serine?
UCU
UCC
UCA
UCG
What type of mutation can be inherited?
Gametic mutation
5 applications of DNA Fingerprinting
1. Forensics
2. Paternity testing
3. Identify human remains
4. Identify genetically modified organisms
5. Determine evolutionary relationships among organisms
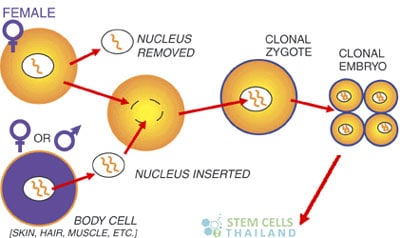
In reproductive cloning, the nucleus from a body (somatic) cell is transferred into an egg cell that has had its own nucleus removed in a process called____.
Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT)
There has been a mix-up in the maternity ward of a hospital. Using DNA fingerprinting, how could you determine which baby belonged to which parents?
Each baby will have half of their DNA banding pattern from the mother and half from the father.
What are these 3 types of RNA and what do they do?
A. rRNA: builds the structure of the ribosome and helps to form the peptide bonds that hold amino acids together.
B. tRNA: brings amino acids to the ribosome.
C. mRNA: brings the genetic information from the nucleus to the cytoplasm/ribosome
What are the 3 amino acids associated with the following DNA sequence?
TAC TGT AAA 
AUG: Met - Start
ACA: Thr
UUU: Phe
Describe three possible results from a base substitution.
1. No effect on the protein (silent mutation).
2. Protein is the wrong shape due to one different amino acid.
3. Protein is too small (short polypeptide) due to a premature stop codon.