Any shaking of the ground measurable by seismic instruments, most are too gentle for people to feel
What is an earthquake?
Earthquakes are most common near the edges of these
What are tectonic boundaries?
A crack in a rock where movement has occurred
What is a fault?
An instrument that both detects and records earth waves
What is a seismograph?
An ocean wave caused by an earthquake
What is a tsunami?
An instrument that simply detects earth waves
What is a seismometer?
Some earthquakes can occur at other places where these exist, far from tectonic boundaries
What are faults?
A crack in rock where there is no visible movement along the surface
What is a joint?
The center of earthquake activity
What is the focus?
This type of earthquake magnitude scale is what geologists use to report to the public, there is no upper limit, but this scale doesn't work well for earthquakes stronger than a magnitude of 7
What is the Richter scale?
Modern seismologists believe that faults and earthquakes are caused by this
What are tectonic forces?
When plate sections move apart from each other
What are divergent boundaries?
Transform faults are also know as these
What are strike-slip faults?
The fastest body wave
What is a P wave?
A source of danger
What is a hazard?
This exists when two forces acting in opposite directions attempt to slide parts of the object past each other, it is the type of stress most significant in causing earthquakes.
What is shear?
When plates move toward each other
What are convergent boundaries?
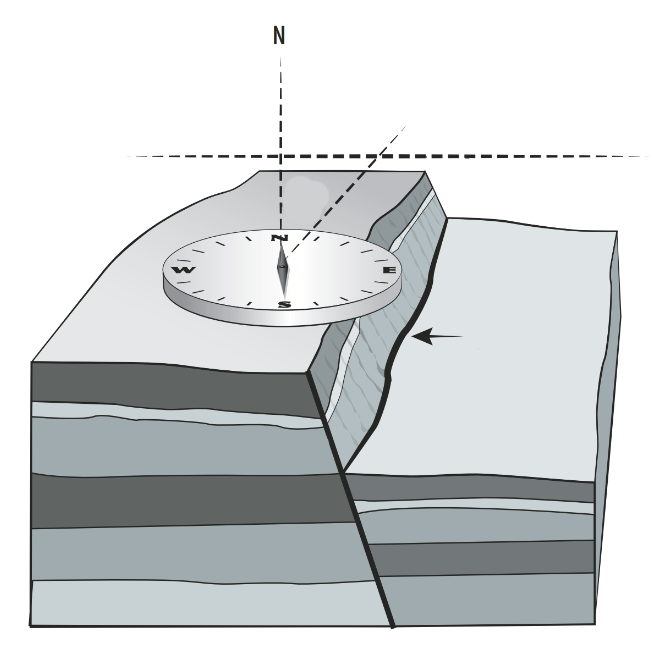
What is the fault (or fault line)?
These are the last waves to reach a seismic station, the two basic wave forms are Rayleigh waves and Love waves
What are surface waves?
The possibility of injury or death to people and damage to property, this can be reduced or eliminated
What is a risk?
This type of stress is a pulling motion. An example is the force that a rock climber exerts on the rope as he rappels down a cliff.
What is tension?
Subduction would most likely be occurring at this type of boundry
What is a convergent boundary?
The horizontal direction of a fault
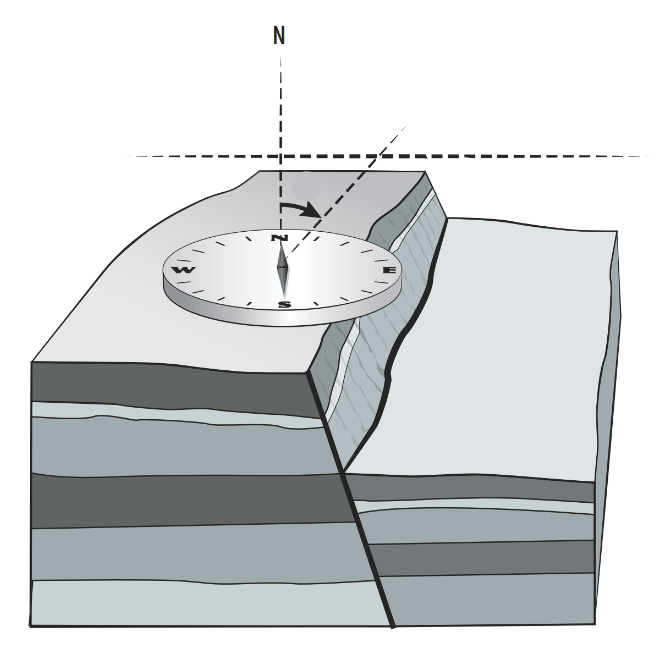
What is the strike?
The point on Earth's surface above the center of earthquake activity, seismologists need data from at least three seismic stations to pinpoint the location
What is the epicenter?
What is when buildings collapse?
- or -
What is when fires start due to broken gas mains or electrical wires?
These two properties of a material allow it to change shape without breaking under stress
What are ductility and elasticity?
Where plates slide past each other in opposite directions along long cracks in the crust
What are transform boundaries?
The angle of the fault face downward from the horizontal
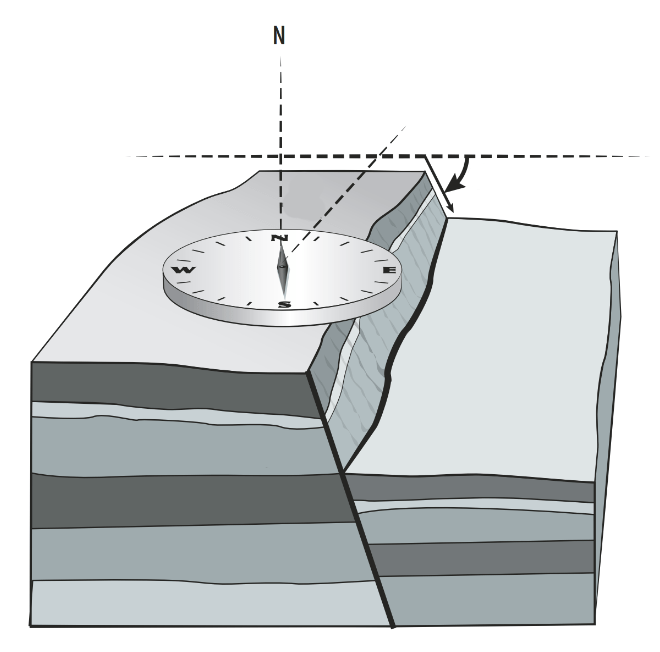
What is the dip?
This type of body wave cannot travel through the earth's core
What is an S wave?
If you move up one magnitude on the Richter scale (ex. from a 6.0 magnitude to a 7.0 magnitude), the larger earthquake has about this many times more energy
What is 32 (31.6)?