These are 2 essential steps in the management of DKA and HHS prior to insulin administration.
Fluids, Fluids, Fluids, electrolyte replacement.
According to GOLD guidelines, this is the specific duration of systemic corticosteroid therapy for inpatient AECOPD.
What is 5 days?
This is a likely cause of hemolytic anemia when blood smear demonstrates Heinz bodies and bite cells.
What is G6PD deficiency?
This was the cause of hematuria in Kody's CPC.
Bladder-invasive prostate cancer
This maneuver is the definitive treatment for posterior canal BPPV.
What is the Epley maneuver?
This is the expected pH finding in a patient with HHS.
What is a near-normal or mildly elevated pH (no significant acidosis)?
Two devices that can deliver O2 between 6 & 15 LPM.
Venturi mask
Non-rebreather mask
(heated high-flow NC can also accommodate that range and up to 90L/min)
These are 3 contraindications to NPPV.
What are: indication for emergent intubation, facial trauma, airway obstruction, inability to protect airway, anticipated prolonged duration of NIP support, UGIB, recurrent/anticipated emesis
These are the two approaches for prostate biopsy.
What are transperineal (TP) and transrectal (TRUS)?
This result on head impulse test is consistent with central cause of vertigo.
Normal, appropriate tracking eye movements with abrupt head impulse.
In DKA, this is the arterial pH below which bicarbonate should be infused.
pH < 6.9
pH ≥ 6.9, no bicarb
These are 2 etiologies for decreased DLCO.
What are ILD, pulm resection, CTEPH?
These are 2 conditions with demonstrated mortality benefit with NPPV.
What are:
Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure
Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
Neuromuscular/chest wall causes of Respiratory Failure, Postoperative respiratory failure after abdominal, thoracic, and cardiac surgery, Respiratory failure in immunocompromised patients
This is the most common cause of elevated PSA in men with age > 50.
What is BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia)?
Two tests with Class I recommendation for every patient with suspected (pre)syncope.
What are orthostatic vitals and ECG?
In a patient with DKA, this is a characteristic of leukocytosis that is suggestive of infection.
What is WBC > 25,000 or > 10% bands?
This is the more likely cause of hypercapnia in patient's with COPD receiving excessive oxygen therapy.
Supplemental O2 inducing/worsening V/Q mismatch and undermining pulmonary vascular auto-regulation (perfusing unventilated lung). (Haldane effect may also be at play)
This specific type of anemia is characterized by spherocytes on peripheral smear and a positive direct Coombs test.
What is autoimmune hemolytic anemia?
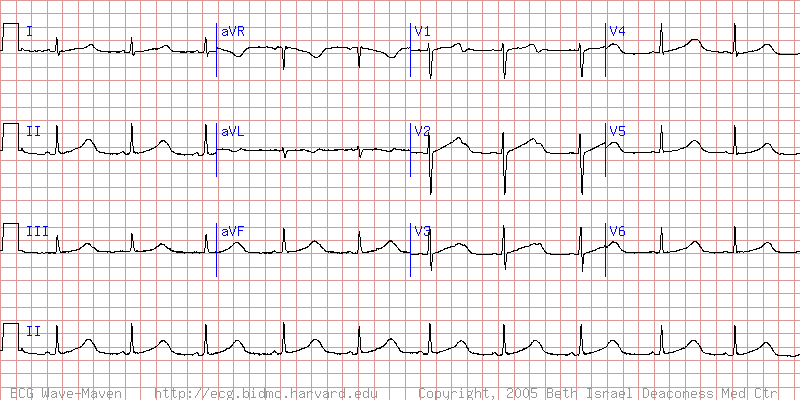 This is the most likely cause of syncope in a patient with this ECG.
This is the most likely cause of syncope in a patient with this ECG.
What is long QT syndrome possibly Torsades?
The ECG demonstrates sinus rhythm with a very prolonged QT interval of 0.6 second. Note broad T waves with notching (or possibly U waves) in the precordial leads. Patients with long QT syndrome at increased risk for torsade de pointes, syncope, and SCD. Patients at high risk of recurrent syncope or sudden death need an ICD.
These are two activities that commonly precede situational or vagotonic (not vasovagal) syncope.
What are micturition, defecation, tussation, deglutition?
This is the initial insulin bolus dose typically given intravenously in DKA patients.
What is 0.1 units/kg IV bolus?
These are two medications that, under the right circumstances, may be provided to help a patient tolerate NPPV.
What are dexmedetomidine, low dose benzodiazepine, or low dose opioids.
This is a brief explanation of how to calculate a reticulocyte index.
Correcting abs retic ct for the hematocrit and expected maturation provides a more accurate assessment of the BM ability to mount an appropriate response to anemia and differentiate a production vs destruction/loss etiology.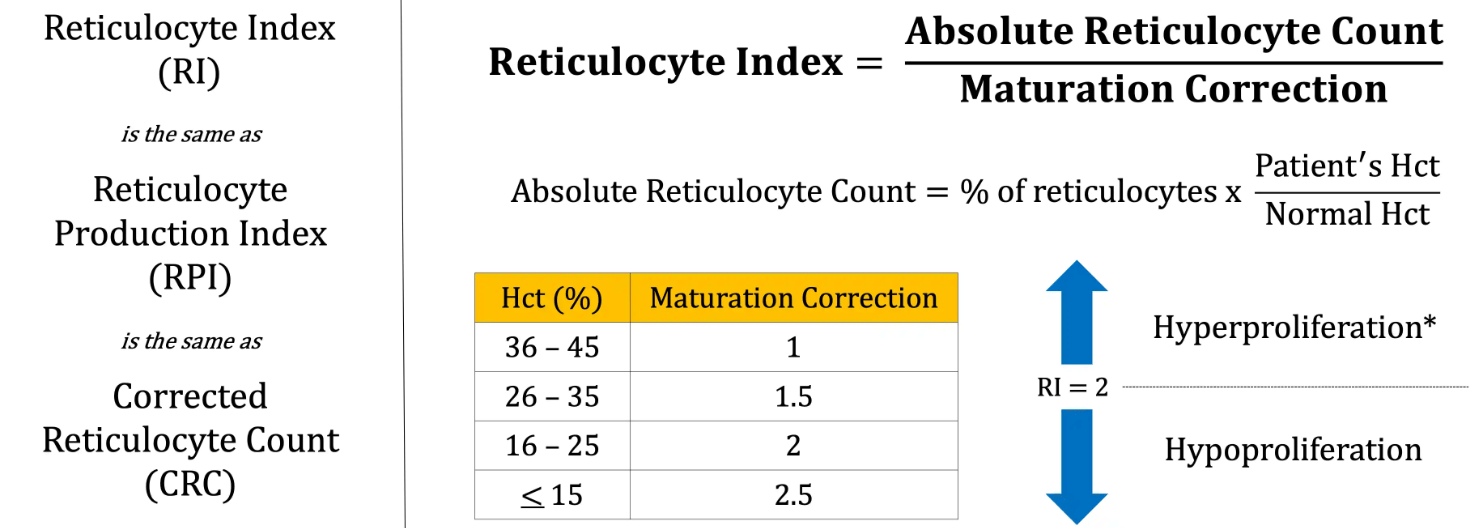
In the initial staging prostate adenocarcinoma, a PSA level exceeding 20 ng/mL, a Gleason Grade Group of 4 or higher, or a clinical T-stage of T3 or T4, universally mandates these two specific imaging modalities to evaluate for distant metastatic disease before proceeding with definitive local therapy.
What are a bone scan and a CT scan of the abdomen/pelvis (or MRI)?
For a patient with recurrent, unexplained syncope and no clear cardiac structural disease, this device is indicated for long-term rhythm monitoring to detect elusive arrhythmias.
What is an ILR?