This term describes diverticular inflammation associated with an abscess, phlegmon, fistula, perforation, or stricture.
What is complicated diverticulitis?
Reversal agent for unfractionated heparin
Protamine sulfate
Limited cases of this superficial staphylococcal infection can be managed with this treatment

Topical mupirocin
(also would accept topical retapamulin)
This diagnosis should be suspected in a patient with binocular diplopia, especially if ptosis that improves with application of an ice pack to the eye lid is also present
Ocular myasthenia gravis
(diplopia in myasthenia is typically variable, worsening with sustained gaze or fatigue, and may be accompanied by ptosis that worsens throughout the day)
In the episode "Walking Small", Plankton teaches SpongeBob to be assertive. But, in reality, this is all part of Plankton's plot to turn this beach into a new Chum Bucket location.

Goo Lagoon

What is the recommended first-line treatment for uncomplicated diverticulitis
Pain control and liquid diet
(Will accept "conservative management", "observation", etc. as long as antibiotics aren't in the answer)
For patients on warfarin experiencing life-threatening bleeding, these two preferred agents should be administered.
1. Vitamin K
2. 4-factor PCC
FFP can be used for warfarin reversal, but PCC is preferred for its rapid reversal of INR, rapid infusion, and lower risk of volume overload.
This is a streptococcal infection of the epidermis, upper dermis, and superficial lympatics
Erysipelas
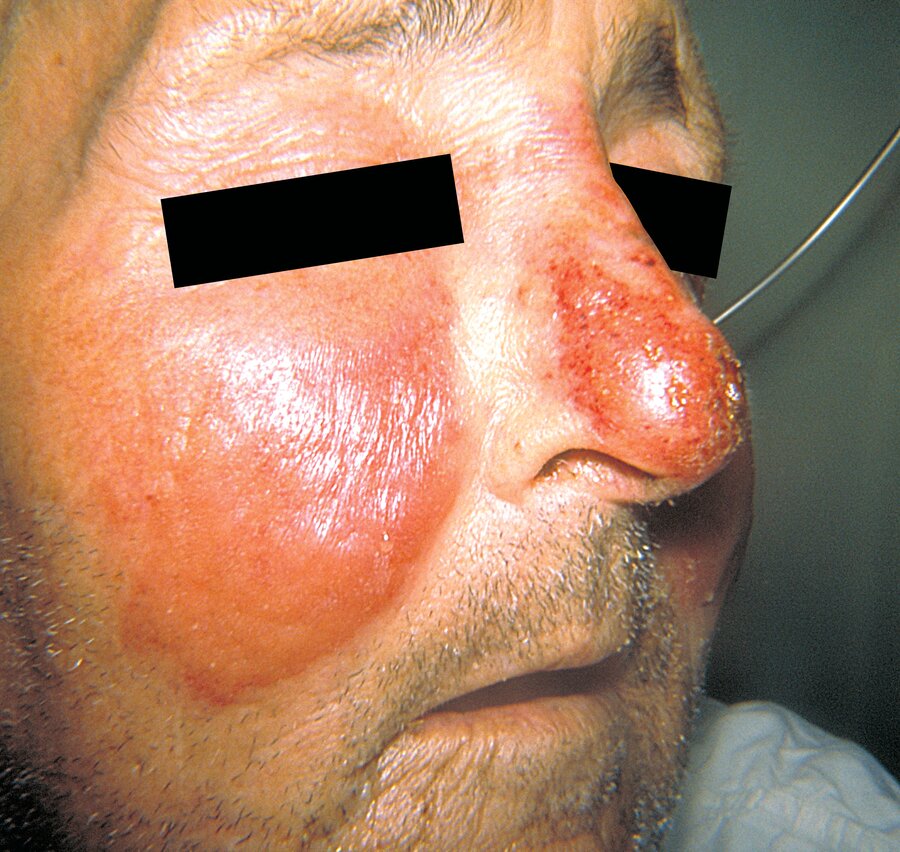
(Distinct from cellulitis, which is less well-demarcated and involves the deeper dermis and subcutaneous fat)
A patient appears to have an isolated cranial nerve III palsy with an unreactive pupil. Noncontrast CTH is negative for hemorrhage. What test should be performed next and what are you assessing for?
CTA/MRA brain assessing for intracranial aneurysm
This weapon unfortunately backfired on Spongebob and Patrick when they attempted to use it to stop the evil villain Man Ray

The Orb of Confusion

What is the recommended diagnostic test for acute diverticulitis?
A contrast-enhanced abdominal and pelvic computed tomography (CT) scan.
This reversal agent for factor Xa inhibitors (eg, apixaban) was recently withdrawn from the US market in Dec 2025 due postmarketing safety data on thromboembolic events, including serious and fatal outcomes.
Andexanet alfa
(4f-PCC is now the preferred reversal agent)
Treatment of an uncomplicated cutaneous abscess is more likely to succeed if both of these measures are taken together (if your answer includes a drug, you must be specific)
1. Incision & drainage
2. Antibiotics with empiric MRSA coverage such as TMP-SMX or doxycycline
(IV antibiotics not an acceptable answer for an uncomplicated abscess)
What laboratory testing should be performed in a 60-year-old patient with recent-onset diplopia and headache?
Inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP)
(to rule out giant cell arteritis)
The Alaskan bull worm

Provide three options for an appropriate oral antibiotic regimen for a patient with acute diverticulitis who requires them.
1. Ciprofloxacin + metronidazole
2. Levofloxacin + metronidazole
3. TMP-SMX + metronidazole
4. Amoxicillin-clavulanate
This is the reversal agent for dabigatran
Idarucizumab
This bacterial pathogen primarily associated with dogs can cause cellulitis and sepsis, particularly in patients with asplenia/hyposplenism
Capnocytophaga canimorsus
Most likely diagnosis in a patient presenting for diplopia and this appearance on eye exam.

Graves' disease
(other acceptable answers: thyroid eye disease, Graves' orbitopathy or ophthalmopathy)
This is the name of the pet who is sure to win the Great Snail Race thanks to his nerves of steel. Well, at least according to his owner, Patrick.
Rocky

For a patient with acute diverticulitis complicated by an abscess, what is the size threshold at which antibiotic therapy alone significantly more likely to fail?
>4 cm
Although no specific reversal agent exists for fondaparinux, these two agents may provide some reversal if needed for bleeding/emergency surgery.
1. Recombinant factor VIIa
2. PCC
This condition is a subtype of necrotizing soft tissue infection typically associated with contamination of trauma-associated wounds
Clostridial myonecrosis (traumatic gas gangrene)
This rare cause of diplopia is characterized by painful ophthalmoplegia and granulomatous inflammation of the cavernous sinus
Tolosa-Hunt syndrome
SpongeBob brags to Patrick about having received this number of gold stars in Mrs. Puff's boating school class.

74