This is the mode of genetic transmission of hemophilia A & B.
What is X-linked recessive?
Hemophilia B (Christmas disease) is a bleeding disorder due to low factor IX. Usually, it is hereditary via X-linked recessive transmission. Concerns would be easy bruising, hemarthosis and/or excessive bleeding. Inital labs may show prolonged PTT, normal PT and platelet counts. Treatment is the replacement of Factor IX at a 100IU/kg dosing. The mnemonic to remember which factor is related to which one is Hemophilia A is "Factor Aight"
This is the neurotransmitter responsible for multiple pathways related to motivation and reward pathways in the brain.
What is dopamine?
D1 and D5 receptors have high density in the striatum, nucleus accumbens, olfactory bulb, and substantia nigra. These receptors are essential in regulating the reward system, motor activity, memory, and learning. D1 and D5 receptors, along with stimulating adenyl cyclase, also activate phospholipase C, which leads to the induction of intracellular calcium release and activation of protein kinase C. Protein kinase C is a calcium-dependent protein kinase. Calcium is also involved in modulating neurotransmitter release by exocytosis. D1 and D5 receptors are also involved in the kidney by inhibiting Na/K ATPase through PKA and PKC pathways. In the kidney, these receptors correlate with an increase in electrolyte excretion and renal vasodilation.
This is the recommended population to be screened for type 2 diabetes based on USPSTF guidelines.
Who are adults aged 35-70 years who are overweight or obese?
Screening for type 2 diabetes is recommended by the USPSTF in adults aged 35 to 70 years of age with BMIs > or = to 25 kg/m^2 or greater. It is a B grade recommendation.
This class of medications used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes has been associated with ketoacidosis.
What are SGLT-2 inhibitors?
SGLT2 inhibitors such as dapagliflozin have increasingly been shown to be associated with diabetic ketoacidosis under certain circumstances.
This is the treatment for poisoning caused by acetaminophen.
What is N-acetylcysteine?
N-acetylcystine is the mainstay of therapy for acute acetaminophen toxicity, and is almost 100% effective if given within the 1st eight hours after acetaminophen ingestion. It also can be used for conditions related to abnormal viscid or inspissated mucosal secretions. Utilization of NAC is either a 21-hour IV protocol or 72-hour oral protocol.
This is the treatment of choice for a patient with a history of allergic rhinitis who presents with bilateral red, itchy, and watery eyes.
What is topical antihistamines with mast cell-stabilizing activity?
Features suggestive of allergic conjunctivitis include bilateral involvement, pruritus, conjunctival hyperemia, watery discharge, blurry vision that improves with blinking, and a history of allergic rhinitis or atopy. Topical antihistamine drops with mast cell–stabilizing activity are the treatment of choice. However, if coexisting allergic rhinitis is present, intranasal steroids have shown evidence of improvement in ocular symptoms. Oral antihistamines may be used, especially in the presence of systemic symptoms, although they may worsen dry eye.
This inherited disease is the most common cause of congenital kidney disease and progression to ESRD.
What is autosomal dominal polycystic kidney disease?
ADPKD is the most common hereditary cause of kidney disease and is a frequent cause of end-stage renal disease. The most common extrarenal cystic complication is the formation of liver cysts, which are found in >90% of patients with ADPKD who are older than 35 years of age. Other locations for ADPKD-related cyst formation include the pancreas, spleen, and reproductive system, although these are not as common as hepatic cysts. The most severe complication of ADPKD is intracranial aneurysms, which are 2–4 times more prevalent in patients with ADPKD than in the general population but are not as common as liver cysts.
The class of medications is the first-line pharmacologic agent for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal delirium (delirium tremens).
What are benzodiazepines?
DTs are best initially treated with benzoiazepines. Typically these patient's should be managed inpatient in the ICU until their withdrawal symptoms subside. Along with that identification of comorbid conditions and supportive care with IV thiamine, agitation control and sleep hygiene are important.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends this population get AAA screening.
Who are men aged 65-75 who have ever smoked?
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends one-time screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) by ultrasonography in men age 65–75 who have ever smoked (Grade B recommendation). The USPSTF recommends against routine screening for AAA in women (Grade D recommendation). Do keep in mind 100 cigarettes in their life is typically considered the criteria of having ever smoked.
This is the recommended surgical treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes.
What is bariatric surgery?
Bariatric surgery is highly effective in treating obesity-related comorbidities, particularly diabetes mellitus (SOR A). It also reduces obesity-related mortality (SOR B) and results in greater weight loss than nonsurgical weight loss interventions (SOR A). Among the 3 major bariatric surgery procedures, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass leads to the greatest weight loss over the first 2 years.
This medication, used in the treatment of asthma, was given a black box warning in 2020 due to increased risk of suicidality.
What is montelukast (Singulair)?
In March 2020, the FDA upgraded its warning label for montelukast to a boxed warning (black box warning) based on the trends for all neuropsychiatric adverse events, including suicidality, associated with montelukast use reported in the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System database from the date of FDA approval in February 1998 through May 2019. The boxed warning does not indicate an increased risk of delirium, myocardial infarction, or venous thromboembolism.
This is the cause for this eye injury seen in the image below.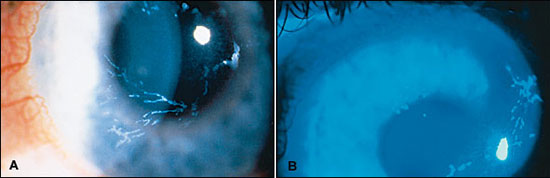
What is herpes simplex virus?
The herpes simplex virus can lead to dendritic ulcerations of the cornea that can cause eye pain, photophobia, visual blurring and watery eye discharge. Usually this infection is self-limited and mild and will heal without any form of treatment. Though it can become complicated and lead to secondary infections, perforation
This neurodegenerative disease (leading to chorea, tics, and dementia in younger patients) is caused by an autosomal dominantly inherited expanded CAG (cytosine-adenine-guanine)-trinucleotide repeat found within the gene of its namesake on chromosome 4.
What is Huntington Disease?
Huntington disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that leads to choreiformic movements, psychiatric manifestations and dementia. Diagnosis is clinic with observations of an expanded CAG trinucleotide repeat on the huntingtin gene of chromosome 4p. The transmission is autosomal dominant due to it caused aggregating protein changes to the neurons. Prognosis is supportive care. A key MRI finding is caudate atrophy.

These are the one of the two first-line medications for moderate to severe alcohol use disorder.
What are naltrexone and acamprosate?
Pharmacotherapy for AUD is underused in primary care; barriers to its use include physician knowledge and comfort. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved three medications for AUD (naltrexone, acamprosate, and disulfiram). The American Psychiatric Association recommends naltrexone and acamprosate as first-line agents for moderate to severe AUD. Although disulfiram is FDA approved, there is no solid evidence that it helps patients maintain abstinence from alcohol.
This is the USPSTF recommended dose of aspirin use daily for the prevention of preeclampsia for those who are at high risk.
What is 81 mg/day of aspirin?
The USPSTF recommended 81mg of aspirin daily for the prevention of preeclampsia for those who are high risk. High risk is defined as those with:
- A history of preeclampsia
- Multifetal gestation
- Chronic hypertension
- Pregestational type 1 or 2 diabetes
- Kidney disease
- Autoimmune disease
- Multiple moderate risk factors (>= 2) (nulliparous, obese, FMHx preeclampsia, black persons, low SES, AMA)
These four diagnostic tests (and their parameters) can be utilized to diagnose a patient with diabetes.
1.) Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test of >= 126 mg/dL in asymptomatic or symptomatic patients.
2.) HbA1C test of >= 6.5% in asymptomatic of symptomatic patients
3.) 75 gram, 2-hr Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) with level >= 200mg/dL
4.) Random plasma glucose (RPG) test of >= 200mg/dL with classical symptoms of hyperglycemia.
As per the ADA guidelines of interpretation of DM diagnostic tests. Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is confirmed with either the presence of unequivocal hyperglycemia (RBG >=200 with symptoms) or requires two abnormal test result findings of the same sample or two separate test samples.
Poisoning by this class of medications presents with confusion, hyperthermia, flushed skin, tachycardia, mydriasis, constipation, urinary retention, and dry skin.
What are anticholinergics?
This constellation of symptoms in the appropriate setting of drug ingestion are concerning for anticholinergic toxicity. The types of substances to be concerned with are antipsychotics, TCAs, antihistamines, Jimson Weed and deadly nightshade. Treatment is supportive care via cooling measures, BZDs, and physostigmine.

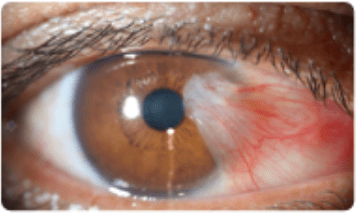
This pathology is most commonly associated with the eye exam finding seen in the image below.

What is syphilis?
Argyll Robertson pupils describe the physical exam findings associated with advanced stages of syphilis. Characterized by bilateral small pupils that fail to constrict in response to bright light but exhibit constriction during near vision tasks, Argyll Robertson pupils are a diagnostic marker for tertiary syphilis.
These two genes are the most important genetic risk factors for a patient developing celiac disease.
What are HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8?
Though blood screening via IgA tissue transglutaminase and genetic testing of HLA-DQ2/8 provide clinicians with a generalized question or concern, they are both non-diagnostic. Either secondary follow-up blood testing with IgA endomysial antibodies or direct visual pathology via an EGD are the best next steps after a positive IgA tissue transglutaminase screening with symptoms.
This stimulant drug is the least likely to have a false-positive finding on a urine drug screening.
What is cocaine?
Cocaine is a stimulant with a short duration of action, typically 30-60 minutes. The drug itself is very unlikely to have a false-positive result on urine drug screens due to the major metabolite, benzoylecogonine, that lasts 2-3 days after use. This metabolite is highly specific to cocaine and does not have similar false positives like methamphetamines, which can cross-react with decongestants and appetite suppressants or have reduced excretions with ingestion of large amounts of bicarbonates.
This is the USPSTF grade for screening of lipid disorders in children and adolescents 20-years of age or younger.
What is Grade I?
The USPSTF concluded that there is insufficient evidence for or against screening for lipid disorders in children and adolescents less than 20-years of age or younger. The AAP does recommend a one-time lipid screening between the ages of 9 and 11-years-old AND between 17-21-years-old, or for those with a high individual risk at the ages of 2, 4 and 6.
These are the ideal treatment options for antihyperglycemic control in a patient with a history of type 2 diabetes and newly diagnosed end-stage renal disease.
What are GLP-1 RA and insulins?
GLP-1 RAs and insulins are the only current recommendations for treatment for ESRD. Insulins are preferred due to the breadth of evidence in support of their utilization in ESRD versus GLP-1s that are still requiring further investigation, but seem safe Acarbose may also be safe due to the mechanism of action being outside the need for renal utilization, however typically the preferred option would be insulins. SGLT2-Is may also be safe, however further large studies need to be evaluated.
This class of antibiotics was issued a warning for systemic versions of the medication can increase the occurrence of aortic dissections and ruptures.
What are fluoroquinolones?
In 2018 the FDA issued a warning statement about systemic fluoroquinolones increasing the occurrence of aortic dissections and ruptures. The drugs in the group thus should be avoided in those with existing aortic aneurysms or in those at increased risk of developing an aneurysm (Marfan, EDS, PVD and hypertension), unless no other option is possible.
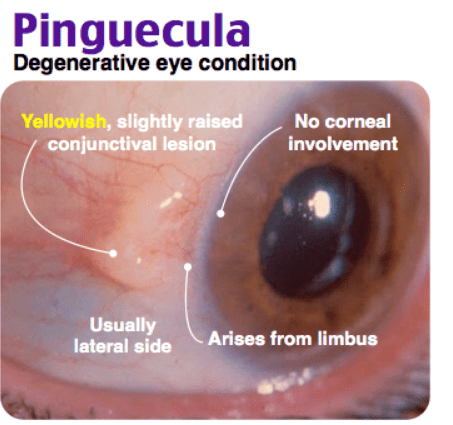
This is the most common risk factor for the disorder in this image below.
What is sunlight exposure?
This pathology below is a pterygium. It is most commonly associated with a history of excessive sunlight exposure. It is described as a triangular-shaped growth on the medial side of the cornea, if it does not invade the cornea it is called a pinguecula. It usually does not require treatment unless if presents with symptoms (usually dry eye or irritation) or it leads to vision changes if it invades the pupil.
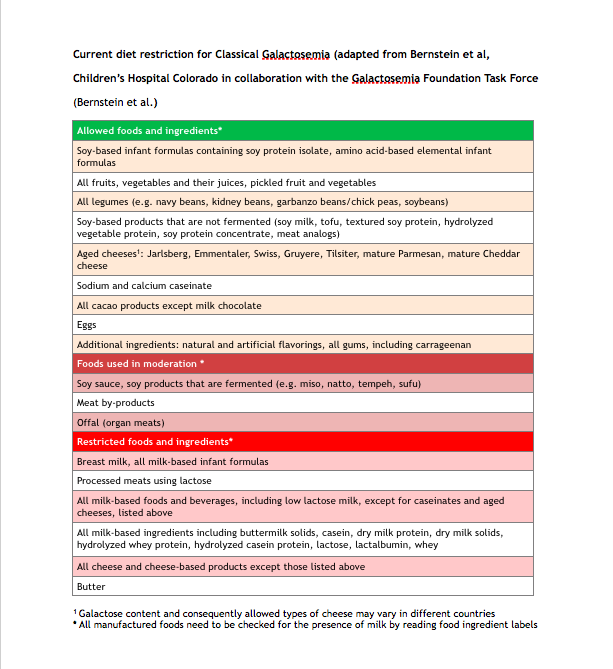
This is the type of formula (i.e. hypoallergenic, goat's milk) to give to newborns with the autosomal recessive disease galactosemia.
What is soy-based formula?
Galactosemia is an autosomal recessive disease that is part of our routine newborn screening in the hospital. It leads to a deficiency in the enzyme (galactose-1-phospahte uridyltransferase [GALT]) that metabolizes galactose. Thus, to provide them with carbohydrates, they must avoid foods containing galactose (i.e. dairy). Symptoms are broad and life-threatening including jaundice, liver damage, seizures, and organ failure if not treated appropriately.
This is the daily numerical threshold of morphine milligram equivalents (MME) that the CDC recommends to provide a patient with a prescription of naloxone.
What is 50?
To mitigate opioid harm, the evidence shows the risk of opioid overdose increases at the threshold of 50 MME/day. Thus it is recommended to provide a prescription of naloxone (Narcan) for any patient at that threshold. A general avoidance should be less than 90 MME/day due to substantially higher risk of overdose.
This medication should be continued with patients on hospice care with a history of type 1 diabetes, to prevent hyperglycemia and ketosis.
What is long-acting insulin?
The goal of diabetes mellitus management in end-of-life care transitions from a primary goal of preventing long-term complications to preventing short-term symptoms and acute complications related to hyperglycemia. As such, no specific blood glucose value is recommended in such patients.
The needs of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes differ in this situation. Patients with type 1 diabetes require insulin to prevent hyperglycemia and ketosis even if they are eating minimally or not at all. Long-acting insulin such as glargine insulin is most appropriate to prevent these complications. Doses may be adjusted to prevent hypoglycemia, but should not be discontinued. Short-acting insulin may be used as needed but is less important than long-acting insulin in the final weeks and days of life when patients are eating very little.
Patients with a long history of diabetes may be used to aiming for tight control of glucose and find it difficult to accept more lenient glucose goals with fewer daily injections. Some patients may choose to continue to aim for tight glucose control despite being counseled about the lack of benefit for such an approach. Patients may also find that they feel worse with higher blood glucose levels (fatigue, urinary frequency) and prefer to aim for tighter glycemic control for this purpose. Patients with type 2 diabetes at the end of life may aim for blood glucose levels as high as the 300s if they do not feel unwell at this level of hyperglycemia. Medications with a risk for hypoglycemia should be discontinued first in patients with low oral intake.
Tight blood pressure control is also less important in patients at the end of life. Blood pressure medications may be continued if a patient desires to do so, is able to take them orally, and is not hypotensive. For this patient, blood pressure medication is less important than insulin. Atorvastatin will not benefit this patient and may be discontinued.
This is the American Diabetes Association's recommendation on the utilization on non-nutritive sweeteners (i.e. aspartame, sucralose, stevia, saccharin).
What is acceptable use?
Non-nutritive sweeteners contain few or no calories. According to the American Diabetes Association, non-nutritive sweeteners may be acceptable to use instead of nutritive sweeteners such as sucrose. They should be used in moderation if they are used.
The use of non-nutritive sweeteners can help to reduce overall intake of carbohydrates and calories. They do not significantly affect glycemic control. Research is inconsistent regarding the effects of non-nutritive sweeteners on weight loss, but most systematic reviews and meta-analyses demonstrate a benefit. There is no recommendation to avoid sucralose or aspartame in patients with type 2 diabetes.
This toxidrome can be precipitated with the utilization of dextromethorphan in somebody who is already at risk due to history of other medications that utilize a similar mechanism of action to dextromethorphan.
What is serotonin syndrome?
Symptoms of serotonin syndrome range from mild to life-threatening and typically appear minutes to hours after ingestion of serotonergic medications. SSRIs are the most commonly associated class of medication due to their widespread use. The Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria are the most commonly used diagnostic tool. History of serotonergic medication use, signs of inducible clonus, agitation, and diaphoresis, as well as hyperthermia are all symptoms leading to serotonin syndrome. The addition of dextromethorphan would likely lead to this as it is available OTC and works by inhibiting serotonin re-uptake. Malignant hyperthermia on the other hand generally appears over a longer period of time and does not typically induce clonus. There are few, if any, choices for medication therapy of concomitant attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and depression that do not increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, so patients on these regimens should be educated about the symptoms of serotonin syndrome and common causative agents.

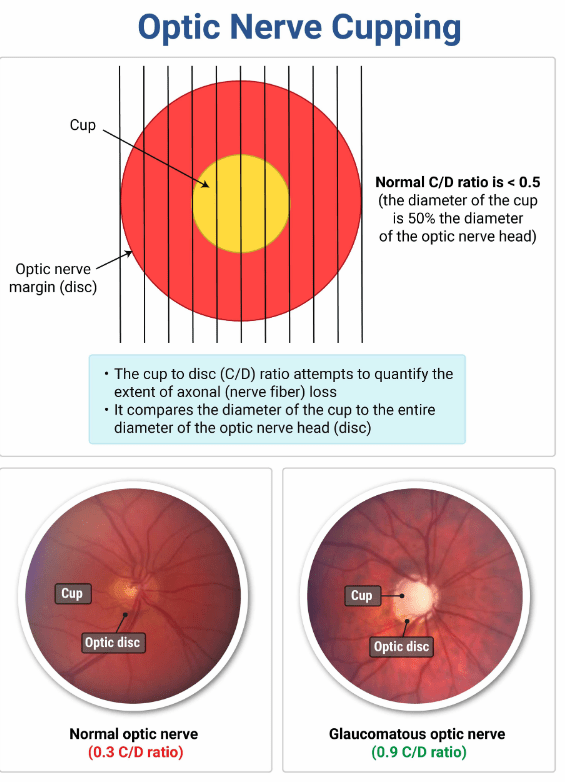
This is the fundoscopic finding that is commonly associated with glaucoma.
What is an increased cup to disc ratio?
Glaucoma is defined as a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve. It is often, but not always, accompanied by increased intraocular pressure. An increased cup to disc ratio (cupping) is an abnormality that is associated with glaucoma. This has been defined as a ratio >0.3–0.5. Retinal vessel changes are not associated with glaucoma. Papilledema is a swelling of the optic disc that is generally caused by increased intracranial pressure.