List 3 obligate anaerobes
1. Actinomycetes Israelii
2. Clostridium tetani
3. Clostridium Botulinum
4. Clostridium dificile
5. Clostridium perfringens
Name a Beta Lactam and explain its general mechanism of action
Penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenams, etc.
MOA: broadly, they inhibit penicillin binding proteins, and prevent them from building the cell wall in gram positive species.
Is Hashimoto's thyroiditis more common in males or females?
Females! 7x more common
Name 2 bacteria that interfere with SNARE proteins.
1. C. botulinum
2. C. tetani
What's my favorite professional sports team

Describe the two C. difficile enterotoxins
Toxin A: disrupts cytoskeletons and tight junctions, leading to fluid permeability and diarrhea.
Toxin B: depolymerizes actin filaments, leading to more cell death and tissue damage.
+50 bonus: explain why amoxicillin is frequently given with clavulanate.
strep pyogenes pharyngitis, H. influenza, Borrelia Burgdorferi.
Bonus: clavulanate is a beta lactamase inhibitor, so it increases the spectrum of amoxicillin.
Name one systemic symptom of rheumatoid arthritis.
Popliteal cyst, serositis, subcutaneous nodules, scleritis/uveitis, Sjögren's syndrome, osteoporosis
Explain what happens in each of the following (50 pts per correct answer):
Conjugation
Transformation
Transduction
Transposition
Conjugation: Bacteria to bacteria plasmid transfer via pilus
Transformation: bacteria picks up DNA off of the ground
Transduction: incorporation of new DNA via bacteriophage
Transposition: Bacteria's own DNA jumps around
Where did I study abroad
Costa Rica
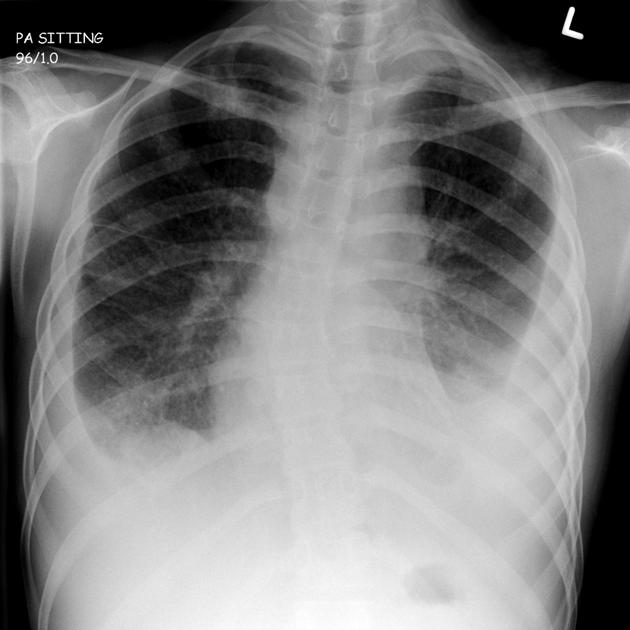
Hints available for -50 pts each.
Primary tuberculosis
Why be cautious with a patient on other drugs when prescribing a macrolide to treat an infection?
(2 correct answers, just need one)
1. Macrolides can inhibit a PGP efflux pump that is needed to expel certain other drugs. This can lead to a toxic buildup of other drugs.
2. Macrolides inhibit Cytochrome p540.
Ixodes tick!
Egg starts on ground, grows into a larvae.
Larvae feed on first host (rodents), and pick up Borrelia spirochete. Larvae drops back to the ground and turns into a nymph.
Nymph feeds on second/terminal host. This is usually what we're bitten by.
OR, adult can go to reservoir (deer), and then to second/terminal host (us). Less common.
Describe the MOA for daptomycin.
Bonus (+100): what pathology can you not use daptomycin for and why?
Generally, it inserts into the cell wall and opsonizes it. This leads to depolarization and cell death.
BONUS: cannot use dapto for pneumonia! It gets inactivated by the surfactant.
What's my least favorite immunoglobulin
IgE
Name the species!
Gram negative bacili*. Acid labile and transmitted through fecal-oral route. Has a unique Toxin Coregulated Pili.
Vibrio Cholera
What is Grey Baby Syndrome, and what (rarely used) antibiotic can cause it?
GBS: grey skin, hypotonia, hypothermia, and shock in a newborn. Due to a toxic buildup of Chloramphenicol that damages the liver proteins needed to metabolize it.
What's the first-line treatment for RA?
What's it's mechanism (the NBME answer)?
How does Leucovorin affect this treatment?
BONUS (you automatically win): what's the actual mechanism of this drug for RA that Matt carefully researched and presented to the class?
Methotrexate
Inhibits DHF reductase, blocking pyrimidine synthesis. This reduces the amount of inflammatory cell presence, reducing RA symptoms.
Leucovorin acts here as a folate replacement to alleviate the side effects of methotrexate.
BONUS: inhibition of AICAR, which builds up adenosine inside the cell. Adenosine gets pumped out and binds to A2A on neutrophils, reducing their inflammatory function.
Are patients with Chronic Granulomatous Deficiency more susceptible to catalase positive or catalase negative bacteria? Explain why.
Catalase Positive!
CGD patients have phagocytes that are unable to use the enzyme NADPH oxidase, so they cannot do the respiratory burst to kill pathogens.
All aerobic pathogens will create some H202 to some degree, but catalase positive organisms will be able to reduce that. Catalase negative organisms can't, and the phagocytes can use that H202.
What's my middle name
Alexander
A 21-year-old woman who is a college student is brought to the emergency department 2 hours after the onset of fever, chills, severe headache, and confusion. Her temperature is 39°C (102.2°F), respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg. Physical examination shows numerous petechial lesions over the upper and lower extremities. There is resistance to neck flexion. Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid shows numerous leukocytes and gram-negative diplococci. Administration of which of the following vaccines is most likely to have prevented this patient’s condition?
(A) Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine
(B) Meningococcal conjugate vaccine, 4-valent
(C) Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, 7-valent
(D) Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, 23-valent
(E) Varicella vaccine
B! She has Neisseria meningiditis
A 45-year-old man presents to the clinic with a 5-day history of fever, malaise, and a productive cough with greenish sputum. He has a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and has had multiple exacerbations in the past year. On physical examination, his temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, heart rate is 105 beats per minute, and respiratory rate is 22 breaths per minute. Auscultation reveals decreased breath sounds and crackles in the right lower lung field. A chest X-ray shows a right lower lobe infiltrate. Sputum Gram stain shows Gram-negative rods.
Which of the following antibiotics is the most appropriate initial therapy?
A. Amoxicillin
B. Azithromycin
C. Ciprofloxacin
D. Vancomycin
E. Clindamycin
C. Ciprofloxacin to treat Pseudomonas infection!
A 4-month-old infant is brought to the emergency department by his parents because of poor feeding, constipation, and weak cry for the past 2 days. On examination, the infant appears lethargic with poor muscle tone. Physical examination reveals a floppy baby with diminished deep tendon reflexes. The mother mentions that she has been feeding the baby homemade honey as a natural remedy for his constipation.
Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of the infant's condition?
A. Inhibition of acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction
B. Demyelination of peripheral nerves
C. Autoimmune destruction of acetylcholine receptors
D. Spread of spirochetes that causes systemic inflammation that has worsening symptoms in 3 distinct stages.
E. Blockade of calcium channels
D. Lyme disease!!
JK it's A.
A 35-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. He has had persistent left upper quadrant abdominal pain for 3 weeks despite therapy with omeprazole. Upper esophagogastroduodenoscopy shows an active duodenal ulcer. In addition, he now has dehydration secondary to intense diarrhea. Which of the following is the most likely causal organism of his diarrhea?
(A) Campylobacter jejuni
(B) Clostridium difficile
(C) Helicobacter pylori
(D) Proteus vulgaris
(E) Salmonella typhi
B. C. diff! PPIs actually increase the risk for C Diff infection.
What's my favorite smell?
