A proton DONOR and increases the concentration of H⁺ ions in a solution
What is an acid?
Carries cholesterol from the cells to the liver to be broken down and eliminated
What is a high density lipoprotein (HDL)?
The special sequences at the end of chromosomal DNA that lengthen the parental strand and preserve DNA
What is a telomere?
An exception to the central dogma
What are retroviruses?
This organization level of eukaryotic chromosome is coiled around 8 core histone subunits
What is a nucleosome?
A type of molecule that has positive and negative poles
What is a dipole?
The two main types of secondary protein structures
What is are 𝛂-helixes and 𝜷-pleated sheets?
The discontinuous fragments in the lagging strand
What are okazaki fragments?
The direction that RNA polymerase moves along the template strand and the synthesizes in
What is the 3’ to 5’ direction and the 5’ to 3’ direction?
The type of mutation that is non-inheritable and occur in non-gamete cells; only passed on to the daughter cells of the original cell that sustained the mutation
What is a somatic mutation?
A geometric isomer that is on the opposite side of the carbon double bond
What is a trans geometric isomer?
The bond that keeps together multiple monosaccharides to form a polysaccharide
This protein prevents the separated DNA strands from rejoining by binding to the separate strands and stabilizing them
What are single-strand DNA-binding (SSB) proteins
The site where the growing polypeptide chain is held
This is what lac z codes for which then breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose
What is 𝜷-galactosidase?
Hyperventilation reduces CO2, making the blood too basic. Breathing into a paper bag helps restore CO2 and balance blood pH
What is respiratory alkalosis?
A site separate from the active site with causes a conformational change of the active enzyme and prevents binding to the substrate
What is allosteric inhibition?
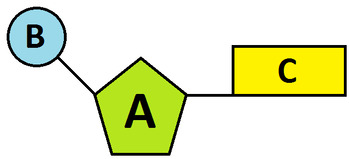
What is a five carbon sugar (A), a phosphate group (B), and a nitrogenous base (C)?
The start (1) and stop codons (3)
This example of a repressible regulator, in the presence of its effector, binds to the operator and prevents transcription
What is the trp operon?

What is an alpha carbon, a carboxylic acid group, an amino group, a side chain, and a hydrogen?
Contains no overall electrical charge but contains separate parts which are positively and negatively charged
The compliment to this sequence: 5’-AGTCCGAAT-3’
What is 3'-UCAGGCUUA-5'?
The three post-transcriptional modifications needed for pre-mRNA to leave the nucleus without being degraded
What is a 5' guanine cap, a 3' Poly(A) tail, and RNA splicing?
Euchromatin is loose and has enhanced gene regulation because of the addition of acetyl groups (-), reduces the positive charge on histones
What is histone acetylation?