2 day old male, Full term, home birth, did not receive any medications at time of or after delivery, exclusively breastfed presents with:
-blood in stool, scattered petechiae over the abdomen and blood oozing from the umbilical cord.
Treatment?
What is Vitamin K!
2 hours after delivery, a neonate born at 39 wks has a choking episode while breastfeeding and is gagging on oral secretions. An OG tube is placed and CXR is obtained. Prenatal hx/delivery were uncomplicated other than significant polyhydramnios.
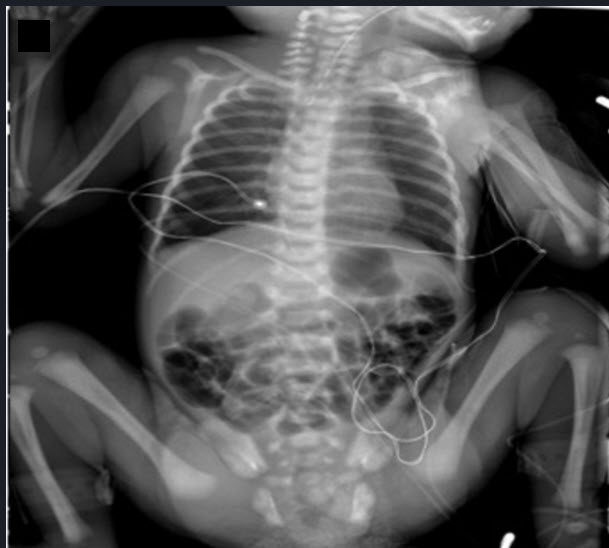
Of the following, evaluation of this neonate will MOST likely include
A. computed tomography of the chest
B. echocardiography
C. esophagoscopy
D. upper gastrointestinal tract contrast study
What is B. Echocardiography
v a C te r l
Tracheoesophageal fistula or esophageal atresia should be considered in a newborn with choking episodes, increased oral secretions, and a prenatal history of polyhydramnios.
- In addition to a thorough physical examination, diagnostic evaluation for neonates with TEF/EA should include echocardiography, renal ultrasonography, and spinal ultrasonography. While vertebral anomalies may be seen on plain radiography, spinal ultrasonography should be performed to rule out a tethered spinal cord.
Female infant born at 38w2d.
- At 1 min: neonate has acrocyanosis, HR 90 bpm, breathing spontaneously, weak cry on stimulation, and flexion of her extremities.
- At 5 min, she continues to have acrocyanosis, HR 140 bpm, she has a strong cry, and she is moving all extremities.
Of the following, this neonate’s APGAR scores are:
A. 5, 8
B. 6, 8
C. 5, 9
D. 6, 9
What is D. 6 and 9
1-minute Apgar score of 6 (1 point each for heart rate <100 beats/min, weak cry, flexion of extremities, and acrocyanosis; and 2 points for breathing spontaneously)
5-minute Apgar score of 9 (2 points each for heart rate >100 beats/min, strong cry, crying with stimulation, and moving extremities, and 1 point for acrocyanosis).
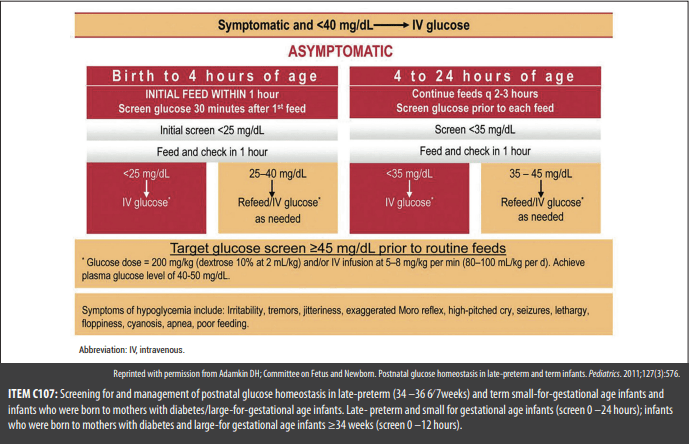
30 mins after birth, a neonate has a POC glucose level of 52 mg/dL. Repeat POC glucose level at 1 hr after birth is 35 mg/dL. He was born at 40w0d with a BW of 3.98 kg (largeeee). The neonate’s mother does not have a history of diabetes, and her GTT result during pregnancy was normal. The BW's of her other 4 children were all above 3.8 kg. The neonate is asymptomatic and has normal PE findings.
Of the following, the BEST next step in this neonate’s management is to
A. administer 10% dextrose IV
B. administer 25% dextrose PO
C. repeat the POC glucose level in 1 hr
D. send blood to the laboratory for a plasma glucose level
What is: D. send blood to the lab for a confirmatory plasma glucose level (asymptomatic!)
Blood glucose levels measured using POC glucose meters are less accurate than plasma glucose levels measured in the laboratory, especially in the low blood glucose range. Because the neonate is asymptomatic, the best next step in management is to send blood to the laboratory for a confirmatory plasma glucose level.
A pediatrician is called to an urgent cesarean delivery at 38w0d due to fetal bradycardia. The 36 yo mom's first prenatal visit was at 37 wks, when u/s showed severe oligohydramnios; the fetal kidneys could not be visualized. The findings were discussed with mom, and she was scheduled to see the MFM specialist but went into labor before the appt. The clinician arrives for the delivery and prepares for resuscitation. There was no opportunity to talk to the mom before delivery about the fetus’ condition and plans for care.
Of the following, the BEST next management step after delivery will most likely be:
A. administration of intravenous antibiotics
B. endotracheal intubation for positive-pressure ventilation
C. performance of renal ultrasonography
D. umbilical line placement for intravenous glucose
What is B. ET intubation for PPV
A newborn is examined 4 hrs after birth in the normal newborn nursery. She was born at 39w0d, uncomplicated vaginal delivery. On PE, the neonate has a soft boggy swelling over the occipital area that crosses suture lines with bruising and scattered petechiae on the scalp. The remainder of PE findings are normal.
Of the following, the BEST next step in the management of this condition is:
A. head ultrasonography
B. serial hemoglobin levels
C. serial physical examinations
D. serum bilirubin levels
What is C. serial physical examinations
(caput succedaneum)
12-day old male neonate in the NICU, ex-26 weeker, tolerating NG feeds @ 20 cal/oz EBM @ 80 ml/kg/day, receiving parenteral nutrition through a central intravenous line. He develops apnea, bradycardia, and oxygen desaturation requiring an increase in CPAP from 6 to 8 cm H2O, and FiO2 from 0.23 to 0.40. His mean upper limb cuff BP has ranged from 18 to 25 mm Hg for the past hour. He has a WBC of 22k with 40 % neutrophils, 25% bands. Blood cultures are pending.
Of the following, the BEST treatment for this neonate is intravenous
A. ampicillin and cefotaxime
B. ampicillin and gentamicin
C. meropenem and oxacillin
D. vancomycin and gentamicin
What is: D. Vancomycin + Gentamicin
2 day old male, Full term, home birth, did not receive any medications at time of or after delivery, exclusively breastfed presents with:
-blood in stool, scattered petechiae over the abdomen and blood oozing from the umbilical cord.
Underlying Etiology?
What is Vitamin K Deficiency
Approximately 50% of neonates with TEF/EA will have associated _____, _____, _____, (TEF/EA), _____ and _____ anomalies. This association is given the acronym ______.
What ARE: Vertebral, Anorectal, Cardiac, Renal and Limb anomalies. This association is given the acronym VACTERL.
APGAR scores should be assessed at __ and __ minutes after birth for all neonates.
What are 1 and 5 minutes.
Neonates at high-risk for hypoglycemia include those who are:
- _______
- _______
- _______
- _______
What are: (will receive credit for at least 3/4)
- Small for Gestational Age
- Large for Gestational Age
- Born to mothers with Diabetes
- Late Preterm (34w0d to 36w6d)
pppPOTTER syndrome:
fetal renal agenesis ---> severe oligohydramnios
----> ______ _______.
:(
What is pulmonary HYPOPLASIA.
- Fetal urine contributes significantly to amniotic fluid volume.
- Amniotic fluid is necessary for fetal lung development.
- Fetal renal agenesis results in severe oligohydramnios which leads to pulmonary hypoplasia.
- A ________ is a blood collection in the SUB-periosteal area caused by injury to the veins beneath the periosteum from birth trauma.
- This finding is typically seen 24 hours after birth as a firm swelling, which increases in size over a few days and resolves spontaneously over 2 to 3 weeks.
- Because of the sub-periosteal location, the swelling ___does/does not___ cross suture lines; this differentiates it from ...(other one)...
- A large one can increase the risk for significant ______; blood breakdown in the lesion contributes to the neonate’s level of unconjugated _______.
- What is: CEPHALOHEMATOMA
- What is: DOES NOT CROSS suture lines (restricted to one area of the head)
- What is: significant JAUNDICE
- What is: BILIRUBIN
Neonatal Sepsis in NICU: early-onset vs. late-onset
- Early: occurs within the first week after birth
- Late: occurs 7 or more days after birth
- Early: antibiotics of choice (2)
- Late: antibiotics of choice (2)
- What is: Ampicillin and Gentamicin
- What is: Vancomycin and Gentamicin
Ampicillin, gentamicin, cefotaxime, and meropenem are all effective against gram-negative bacteria.
Vancomycin is effective against coagulase-negative staphylococci.
2 day old male, Full term, home birth, did not receive any medications at time of or after delivery, exclusively breastfed presents with:
-blood in stool, scattered petechiae over the abdomen and blood oozing from the umbilical cord.
Diagnosis?
What is hemorrhagic disease of the newborn
Chest radiography showing an orogastric tube terminating at the cervical level of the esophagus is diagnostic for _______; if there is also air in the stomach, the diagnosis is ______.

What is: esophageal atresia
What is: tracheoesophageal fistula
Components of the APGAR score include:
What are: color (Appearance), heart rate (Pulse), reflex irritability (Grimace), muscle tone (Activity), and Respiratory effort
Symptoms of neonatal ______ may include: irritability, tremors, jitteriness, exaggerated Moro reflex, high-pitched cry, seizures, lethargy, floppiness, cyanosis, apnea, poor feeding.
When to treat:
Symptomatic + BG < ___ mg/dl ---> IV glucose!
What is hypoglycemia
What is 40 mg/dl
pppPOTTER syndrome:
Bilateral renal ____ + severe ___-hydramnios
What is renal AGENESIS and OLIGO-hydramnios
- ___________ is a common newborn scalp swelling found immediately after birth.
- It is a collection of blood/serous fluid just beneath the SKIN and above the periosteal layer of the SCALP.
- It typically ___crosses/does not cross___ suture lines and resolves spontaneously within 48 to 72 hours.
- This condition does not need further evaluation in cases with classic presentations.
- What is: Caput succedaneum
- What is: Crosses suture lines
Neonatal Sepsis in NICU: early-onset vs. late-onset
- Early: occurs within the first __ days after birth
- Late: occurs __+ days after birth
- Early: caused by maternal vertical transmission of microorganisms (3 bugs, name them)
- Late: postnatally acquired, caused by immature defense barriers, immature immune systems, invasive interventions, & comorbidities of prematurity. (2 classes of bugs, name them)
- What is the first week of after birth
- What is 7 or more days after birth
- What is Group B Streptococci, E. Coli, Listeria
- What is Coagulase-negative Staphylococci and Gram negative bacteria