Infants with facial port-wine stains are at risk for what syndrome?
Infants with lower extremity port-wine stains are at risk for what syndrome?
Name 1 additional feature of each syndrome.
Sturge Weber – neuro/ophtho complications such as seizures, ID, hemiparesis, glaucoma

Klippel-Trenaunay – progressive limb/soft tissue overgrowth, lymphatic malformations, varicose veins


BONUS: What location on the face is the highest risk for Sturge-Weber?
Babies generally have the ability to soothe themselves back to sleep at ___ months. Nighttime feedings are a learned association and not strictly necessary after ___ months. Starting around __ months, a baby may suddenly have increased difficulty with falling asleep due to normal separation anxiety.
3-4 months
4-6 months
8-9 months
BONUS: The best way to promote development of self soothing skills is...?
How does the time course in Duchenne vs. Becker differ in the following: Age of presentation, Wheelchair bound, Life-span
Duchenne: Presents 2-6 y/o, Wheelchair bound by ~12, death in early 20s
Becker: Presents 7-8 y/o, Wheelchair bound by 20s or later (much more variable course), death in 40s-50s
BONUS: What gene/protein is affected?
Which two food allergies are children most likely to outgrow? Which food allergies are most likely to persist (name at least 2/4)?
Most likely: Egg, milk
Least likely: peanut, tree nut, shellfish, fish
BONUS: What is the most common allergy that patients with eczema have?
Consider Iron Deficiency Anemia and Beta Thalassemia minor. For each condition, state whether MCV, RDW, and total RBC number is low/normal/high.
IDA: Low MCV, High RDW, Dec total RBCs
Beta-Thal: Low MCV, Normal RDW, Normal/High total RBCs
BONUS: What is the Mentzer index, how does it compare between IDA + Beta thal minor?
Infantile hemangiomas in the following locations cause increased risk of what complications/underlying problems?
Periorbital
Mandible or chin
Midline lumbosacral
Multiple cutaneous (>5)
Periorbital → ocular complications (80%!) including vision impairment, even blindness
Mandible or chin → airway compromise
Midline lumbosacral → spina bifida
Multiple cutaneous (>5) → GI tract hemangiomas/GI bleed, other visceral hemangiomas
BONUS: A large facial hemangioma should raise your suspicion for which syndrome (and what are the components?)
Head banging usually begins at around ___ months and stops by ___ y/o.
Body rocking usually begins at around ___ months and stops by ___ y/o.
Both are most common at what time of day?
Head banging: starts at 8-9 months, stops by 4 y/o
Body rocking: starts at 6 months, stops by 2-3 y/o
More common at night time/bedtime (rocking usually 30 min; head banging can be short or last hours)
BONUS: Up to __% of NEUROLOGICALLY NORMAL children have issues with head banging or body rocking. (It is not diagnostic!!)
Spinal Muscular Atrophy type 1 (the most common) essentially always presents before age ___, and infants generally never achieve which motor milestone?
6 mos
Rolling or sitting
BONUS: These babies’ chests and legs have what characteristic appearances due to their severe weakness?
For each type of hypersensitivity reaction (I-IV), give the main mediator + mechanism. For BONUS: Give an example.
Type 1: IgE; Ab cross-linking induces mast cells + basophils to degranulate, leads to histamine → anaphylaxis, angioedema, seasonal allergies, certain drug allergy
Type 2: IgG; body develops Ab that cross reacts with own tissue, directly inducing cell or tissue destruction → ITP, AIHA, goodpasture, myasthenia, graves, etc etc
Type 3: IgG/IgA immune complex precipitation; “clog up” small vessels and activate complement → autoimmune diseases such as SLE, HSP, RA + drug reactions (serum sickness, arthus reaction)
Type 4: T-cell; previously sensitized T cell sees the antigen, activates macrophages → inflammation. Examples include TST, poison ivy, nickel reaction/allergic contact dermatitis, granulomatous disease, GVHD
When is the best time to test for G6PD deficiency: During a crisis, or after resolution of a crisis? Why?
AFTER a crisis; in the middle of a crisis, all the RBCs with abnormal levels of G6PD have hemolyzed, everything remaining has normal or near-normal levels.
BONUS: G6PD tends to be more severe in which ethnicity?
Answer the following questions for both neonatal acne and infantile acne: age of appearance, cause, presence/absence of comedones, potential for scarring, timeline for improvement.
Neonatal acne: appears at 2-4 weeks, due to hypersensitivity reaction to malassezia, no comedones, no scarring, resolves over 1-4 months.

Infantile acne: appears at 2-4 months, due to androgenic effects (not necessarily pathologic), yes comedones, yes scarring, resolves over 6-12 months.

BONUS: How do you treat these conditions?
How can you most effectively treat onychophagia (nail biting)?
POSITIVE REINFORCEMENT, by praising during periods where they are not biting; bitter nail polish generally shown to have no effect (child has to be motivated to want to stop for this to help)
BONUS: About ___% of children have this issue. In kids >10 y/o, it is much more common in boys/girls?
Consider Guillain-Barre and Transverse Myelitis. Which one causes alterations to pain/temperature sensation? Which one has bladder dysfunction?
Transverse myelitis: diminished pain/temperature, bladder dysfunction common
BONUS: Which one is sometimes the initial presentation of multiple sclerosis?
Name at least one way to reduce dust mite allergy burden.
Name at least one way to reduce cat/dog allergy burden.
Dust mites: zippered covers mattress/pillows, frequent laundering of linens, reduce humidity <50% (HEPA filters do not work; particles not airborne, too heavy)
Cat/dog: Remove from the house, HEPA filter
BONUS: For each allergen (tree, weeds, grass), name their classic “season.”
Peak age for stroke incidence in sickle cell patients is ___ y/o. If you suspect a stroke in a patient with SCD, the first step in treatment is ___.
2-5 y/o
Emergent exchange transfusion
BONUS: Pts who had a stroke should receive chronic RBC transfusions to keep HbS <__%?
What is aplasia cutis congenita? When it is in multiple locations, this should raise your suspicion for which genetic disorder?
congenital absence of skin+hair, usually in a spot on the scalp
Trisomy 13

BONUS: Midline scalp lesions and encircled by thicker, darker hair, should raise your suspicion for which underlying neurological abnormality?
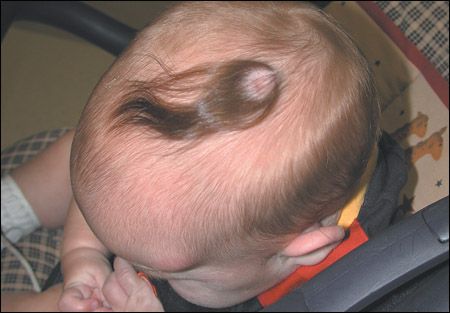
Thumb sucking behavior is common, and usually resolves spontaneously by what age?
Beyond this point, it can begin to cause ___ problems and the child should be referred to ___.
4 y/o
dental problems / refer to dentist
BONUS: If the behavior persists into adolescence, it is more common in boys/girls and a potential sign of…?
Which muscular dystrophy may manifest as difficulty releasing grip, tripping over feet (distal weakness)?
Myotonic dystrophy
BONUS: What is the inheritance pattern?
A child with a dermatophyte infection (currently being treated with griseofulvin) who suddenly develops a diffuse and itchy eczema-like rash is likely experiencing an “id reaction,” which is a type __ hypersensitivity reaction to ___.
Type IV hypersensitivity reaction to the dermatophyte itself



BONUS: What should you do next?
List the primary site of RBC formation in the fetus during the following time frames:
2-6 weeks
6 weeks - ~27 weeks (7 months)
~27 weeks - birth
2-6 weeks: yolk sac
6 weeks - ~27 weeks (7 months): Liver
~27 weeks - birth: Bone marrow

BONUS: Where is EPO produced by the fetus and newborn?
The phrases “coat sleeve,” “stocking,” “cape-like,” “bathing trunk,” or “garment-type” are often used to describe what type of birthmark? Furthermore, this birthmark has a ___% lifetime risk of malignant transformation, even in the first 5 years of life.
Large/giant congenital melanocytic nevi
6-8%

BONUS: Knowing small/medium vs large is important for understanding cancer risk…. At what point is a nevus classified as large?
Night terrors tend to peak at around ___ y/o and generally resolve by ___. Outside of good sleep hygiene / minimizing stress, what is the best way to prevent future episodes?
3-7 y/o
resolve by adolescence
prevent with "preemptive awakening" as they usually occur at the same time nightly
BONUS: Name at least 2 types of drugs that are thought to be associated with development of night terrors.
___ is usually the first sign of infant botulism. In addition to symmetric hypotonia and eventual areflexia, infants with botulism have no/copious secretions and no/normal pupillary response to light (both in contrast to babies with SMA).
Constipation
No secretions
No pupillary response
BONUS: Majority of US botulism cases are due to…?
A week after taking Bactrim for a MRSA abscess, a child develops slightly edematous, well-circumscribed lesions with a dusky erythematous hue that progress to central blistering followed by desquamation, crusting, and residual hyperpigmentation. What is this rash?
Fixed Drug Eruption
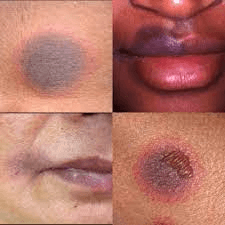

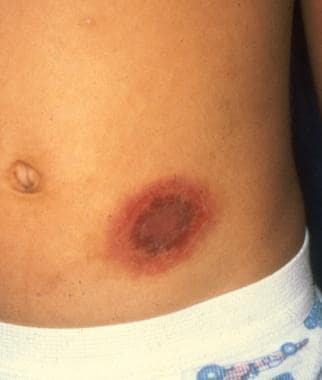
BONUS: If you give bactrim again, how long would it take the rash to appear?
Elevated HbA2 on Hgb electrophoresis is suggestive of…?
Beta thalassemia mutation
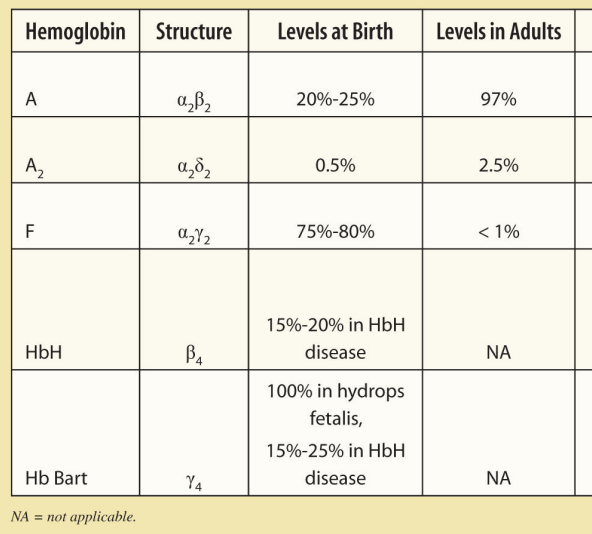
BONUS: Why? By this same logic, what other type of Hgb may be elevated?