The study of the structures and shape of the human body
anatomy
This system provides the framework for muscles to cause movement
skeletal
The muscular system is only made of _ muscle
skeletal
The brain is part of the
nervous system
Cell membranes protect the cell; skin protects the body
Boundaries
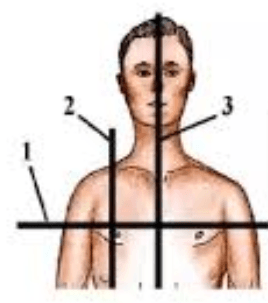
What is #3
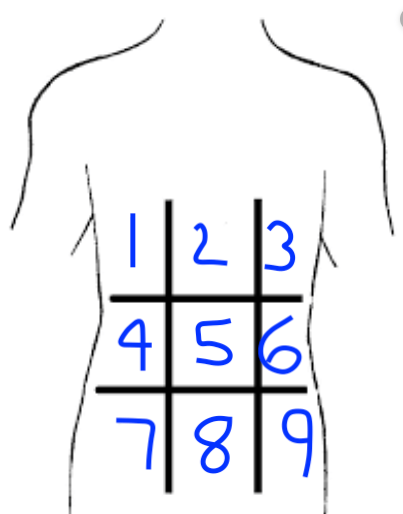
Left hypochondriac region
The study of how the body and its parts work
physiology
The structure of an organ is directly related to its
function
Sensory receptors are part of the
nervous system
The _ system is made of the heart and blood vessels
cardiovascular
The __ system supplies the body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
respiratory
blood flows; urine flows; walking; food passes through the digestive system
movement
What is C?
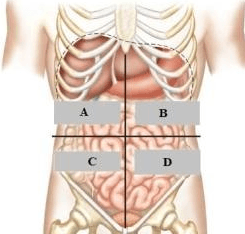
Lower right quadrant
blood cells are formed in the
cavities or marrow of the bones
The smallest level of organization in the body
chemical
Kidneys are a part of the _ system
urinary or excretory
The function of the endocrine system is to produce _ and release them into the bloodstream.
hormones
The _ system is made of the glands in your body
endocrine
breaking down food
digestion
What do we call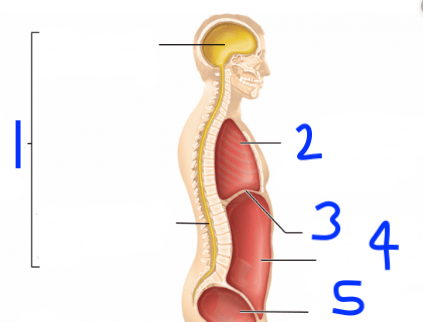 numbers 4 and 5 combined?
numbers 4 and 5 combined?
abdominopelvic cavity
What is number 2?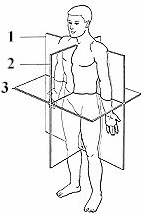
midsaggital plane
Cells come together to make up
tissues
The sole function of skeletal muscles is to
cause movement
One function of the nervous system is to respond to
irritants or stimuli
The _ system breaks down food into nutrients
digestive
removal of waste
excretion
What kind of section is # 2?
parasaggital
The head is _ to the heart
superior
Organ systems do not work _ of each other
independently
The _ system filters nitrogen containing waste as well as maintaining the body's balance of water and electrolytes.
Urinary or excretory
What system is responsible for maintaining a correct pH balance in the blood?
The function of hormones is to
regulate other structures
ability to sense changes (stimuli); irritability
Responsiveness
What do we call #1?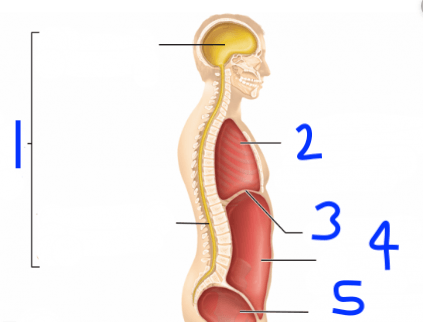
dorsal cavity
What is number 3?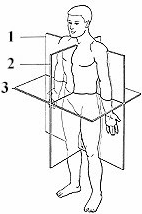
transverse plane
Nutrients, oxygen, water, appropriate temperature, and appropriate atmospheric pressure are all considered _
Survival needs
The lymphatic system is made of lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, __ and tonsils
spleen
Which of the following are not a part of the endocrine system?
pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, gallbladder, pancreas, pineal, basal ganglia, ovaries, testes, hypothalamus, thymus
gallbladder, basal ganglia, hypothalamus
What system does the gall bladder belong to?
the digestive system
multiplication of body cells for growth and maintenance
reproduction
What cavity is the eye in?
orbital cavity
The shoulder is _ to the elbow
proximal
The stomach is _ to the abdominal muscle
deep
The pharynx and larynx are part of the _ system
respiratory
Which organ is a part of both the endocrine and digestive systems?
pancreas
The function of the lymphatic system is to __ the blood and help with __
clean the blood; help with immunity
All of the chemical reactions that take place in the body
metabolism
What is the cavity between the vertebrae called?
synovial cavity
What is number 1?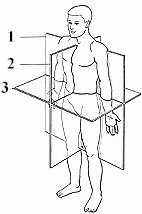
Coronal Plane