growth hormone
What is the disorder where the membranes surrounding the brain become inflamed?
What keeps the blood from flowing in the wrong direction?
Valves
What is a semitransparent membrane which moves back and forth in response to sound waves?
Ear drum or tympanic membrane
Over production of growth hormone IN ADULTHOOD
Acromegaly
Hormone released by the Pineal Gland
What is Melatonin?
What is the primary visual cortex of the cerebrum?
Occipital
What blood type is the universal donor?
What blood type is the universal acceptor?
Donor = O
Acceptor= AB
Which part of the eye is able to constrict or dilate to regulate the amount of light entering the eye?
Pupil
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is caused by
Autoimmune disease that attacks the cells of the pancreas
Growth hormone, prolactin and thyroid stimulating hormone are all secreted by.
Anterior pituitary
What region of the brain controls blood pressure, cardiac rate, and respiratory functions?
medulla or brainstem
What structure is located between the left atrium and left ventricle?
Mitral/ bicuspid
Where are the adrenal glands located?
On top of the kidneys
When the heart fails to pump an adequate amount of blood to meet tissue needs, this is known as.
Congestive heart failure
Hormone level in the blood stream are controlled by what system?
Negative feedback
Controls decision making and critical thinking
What is the Frontal Lobe
Explain which artery and which vein are exceptions to the typical characteristics of arteries and veins.
- While arteries generally carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, the pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood away from the heart (to the lungs).
—While veins generally carry deoxygenated blood to the heart, the pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood to the heart (from the lungs).
What structure distributes blood to the entire body?
Aorta
Which of the following disorders commonly results in fatigue and weight gain in adults?
Hypothyroidism
Hashimotos
The endocrine system is made up of cells, tissues, and organs which are collectively called endocrine___________ that release substances called _______________ that act on cells called________ cekls.
Glands
Hormones
Target Cells
What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
Double the points, what is the general idea of what each does....the little funny saying is fine.
Sympathetic and parasympathetic
sym- fight or flight
para - rest and digest
What is the correct pathway of blood through the heart starting in the vena cava, not including valves or blood vessels.
Vena Cava -> right atrium -> right ventricle-> Lungs -> Left Atrium -> left ventricle -> Aorta
Three small bones in the middle ear bridge the_________ and the ___________.
eardrum
Inner ear
Which of the following causes the lens or its capsule to slowly become cloud and opaque
cataracts
Explain how the nervous system and endocrine system are alike and how they are different.
Similarities:
—Both oversee cell-to-cell communication using chemical signals that bind to receptor molecules.
Differences:
—Cells of the nervous system = neurons / of the endocrine system = glandular epithelium —Chemical signals of the nervous system = neurotransmitter / of the endocrine system = hormones —Nervous system sends message within seconds / endocrine system = seconds to hours —Messages of the nervous system are very brief / messages of the endocrine system = brief or can last for days
Identify 3 different types of receptors, where they would be located and their function.
Answer:
Chemoreceptors - located in the nose and mouth / stimulated by changes in the concentration of certain chemicals.
Pain receptors - located throughout the body / stimulated by tissue damage
Thermoreceptors - located in epithelial tissues / stimulated by changes in temperature
Mechanoreceptors - located in epithelial tissues and the ear / stimulated by changes in pressure or movement
Photoreceptors - located in the eye / stimulated by light energy
Identify 3 major functions of blood.
Answer:
—transports oxygen, wastes, and hormones throughout the body —maintains the stability of interstitial fluids —distributes heat —link the body's internal and external environments —defends the body from pathogens (white blood cells) —clots/repairs wounds
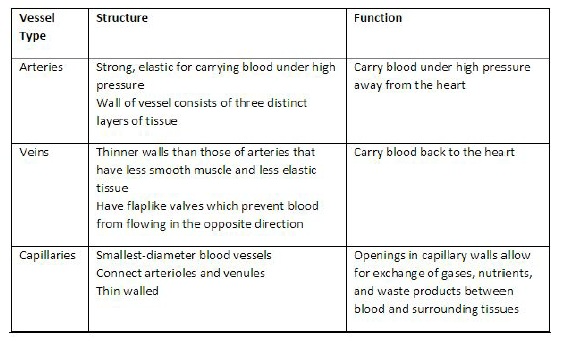
Identify the three major types of blood vessels and compare/contrast their structure and function.
In each below scenario give your expected diagnosis.
A) Patient A complains of thirst and frequent urination
B) Patient B has a fractured bone and is an elderly female. This is the 3rd time she has fractured a bone in the last year.
C) Patient C, a 45 year old male comes in to your office after having grown numerous inches in one year.
Answer:
a.) Patient A most likely is suffering from diabetes, which occurs due to a deficiency of insulin. This results in high levels of glucose in the blood because there is not enough insulin to convert the glucose to glycogen, for storage. A test for glucose, or sugar, in the blood would reveal high glucose levels in diabetics.
b.) Patient B most likely is suffering from osteoporosis, which causes bones to become fragile and break. It is often caused by low levels of calcium in the bones, or higher than normal levels of calcium in the blood. An under-active thyroid gland, which secrets calcitonin, or an overactive parathyroid, which secrets PTH, could be responsible. A test for blood calcium levels would help determine if either of these are the reason for the break.
c.) This patient most likely has acromegaly, which is caused by the oversecretion of growth hormone. To test for this, blood levels of GH can be evaluated.