Tissues are made out of?
What are cells?
The two ways that Epithelial Tissues are classified.
What are number of layers, and shape of cells?
What are the three types of cells found in connective tissue?
What are mast cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages.
The image represents what kind of tissue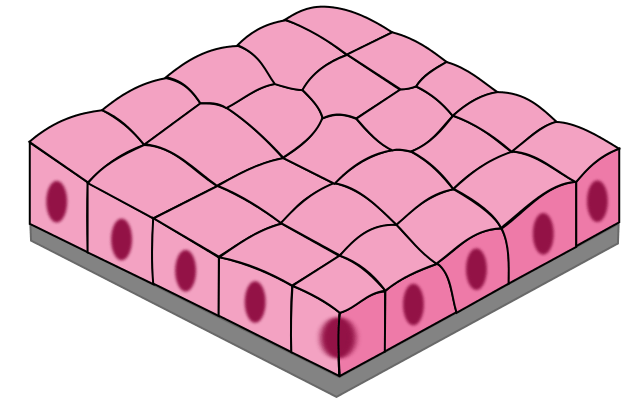
What is simple cubodial
Primary functions of connective tissue include.
What are support, protection, framework, fills space, stores fat, produces blood cells, fights infection.
This image represents what kind of tissue.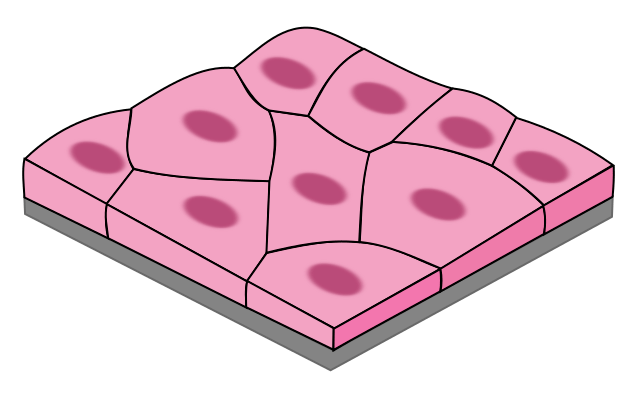
What is simple squamous.
Type of epithelial gland that secretes hormones.
What is endocrine gland?
Freebie
Freebie
What tissue is represented by the image?
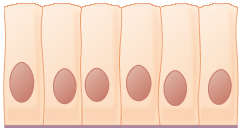
What is simple columnar?
The amount and type of fibers they have.
How are loose and dense connective tissues different?
What tissue is represented by the image?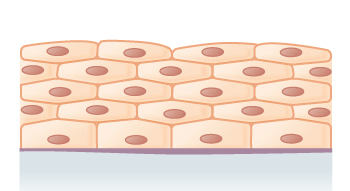
What is stratified squamous?
What kind of epithelial tissue is found in the bladder, because it has stretchable qualities.
What is transitional epithelium.
The five primary types of connective tissue.
What are adipose, cartilage, osseous (Bone), blood, loose connective, and fibrous connective?
Tissue type which regenerates well.
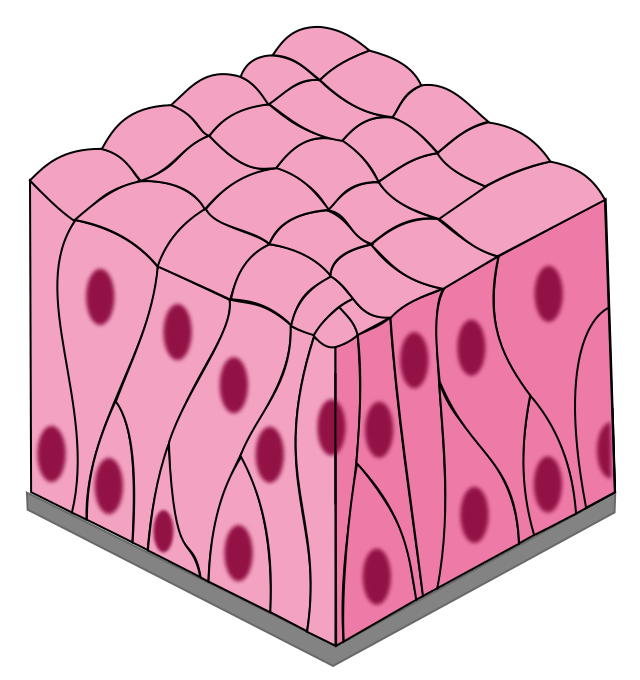
What is Pseudostratified columnar.