Why, in terms of atomic structure, do atoms bond?
To achieve a full outermost electron shell OR to achieve a full valence electron shell
What type of bonding involves freely moving electrons?
Metallic
True or false. Ionic compounds have lower mp/bp than covalent compounds
False--ionic compounds melt and boil at hotter temperatures than covalent compounds
Write the name of the following compound: BrF5
Bromine Pentafluoride
An atom of which element reacts with an atom of hydrogen to form a bond with the least degree of polarity?
a) C b) F c) N d) O
a) C
What is the name of the group that tends not to bond or react?
Noble gases (the name not the number)
In an ionic bond, electrons transfer from what to what?
metal to nonmetal
What type of compound is always soluble in water?
Ionic
Element M is a metal and its chloride has the formula MCl2. What is the name of the group on the Periodic Table that element M most likely belongs to?
Alkaline Earth Metals (the name, not the group #)
What is the bond polarity AND the molecular polarity of CH4?
Bond polarity = polar
Molecular polarity = nonpolar
How many bonds can an atom of sulfur form?
2
Which of the following is a molecular compound?
a) KCl b) SrO c) FeS d) HBr
d) HBr (molecular means covalent)
Which of the following can conduct electricity only in the aqueous state?
a) Cu b) HCl c) Ag d) SrS
d) SrS (ionic can only conduct when dissolved in water or melted into a liquid)
Draw the Lewis electron-dot diagram for a molecule of oxygen
Explain, in terms of intermolecular forces, why water has a higher boiling point than hydrogen.
When a bond is formed between atoms, what energy change occurs? (is it released, absorbed, or does it stay the same?)
Energy is released
What type of bonding involves electrons being shared unequally?
polar covalent bond
Explain, in terms of electrons, why metallic substances conduct electricity in all phases.
Because they have freely moving electrons.
Draw the Lewis electron-dot diagram for potassium bromide
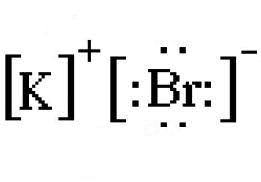
Explain, in terms of charge distribution, why water is a polar molecule
It has an asymmetrical distribution of charge OR an uneven/unequal charge distribution
For the following chemical reaction, is it an endothermic or exothermic process? MgS(s) --> Mg(s) + S(s)
endothermic (must absorb energy to break bonds)
What type of bonding is present in the compound NaClO?
Ionic and covalent
(whenever more than 2 elements, check table E for a polyatomic. Polyatomics are covalently bonded and the bond with the metal is ionic)
Quartz is an example of a network solid - a macromolecule with covalent bonds. Do network solids have high or low melting/boiling points?
HIGH--covalent compounds tend to have low mp/bp but because of the structure of network solids, they have very high mp/bp
What is the name of the compound TiO?
titanium(II) oxide
Explain, in terms of molecular polarity, why methane is not soluble in water
Methane is nonpolar and water is polar; in order to be soluble, they must have similar polarities