This fracture affects the bimalleolar fracture that occurs at the ankle, affects medial (tibia) and lateral (fibula) malleolus.

What is Pott's fracture?
Describe whiplash.
What is partial or complete dislocation of cervical vertebrae?
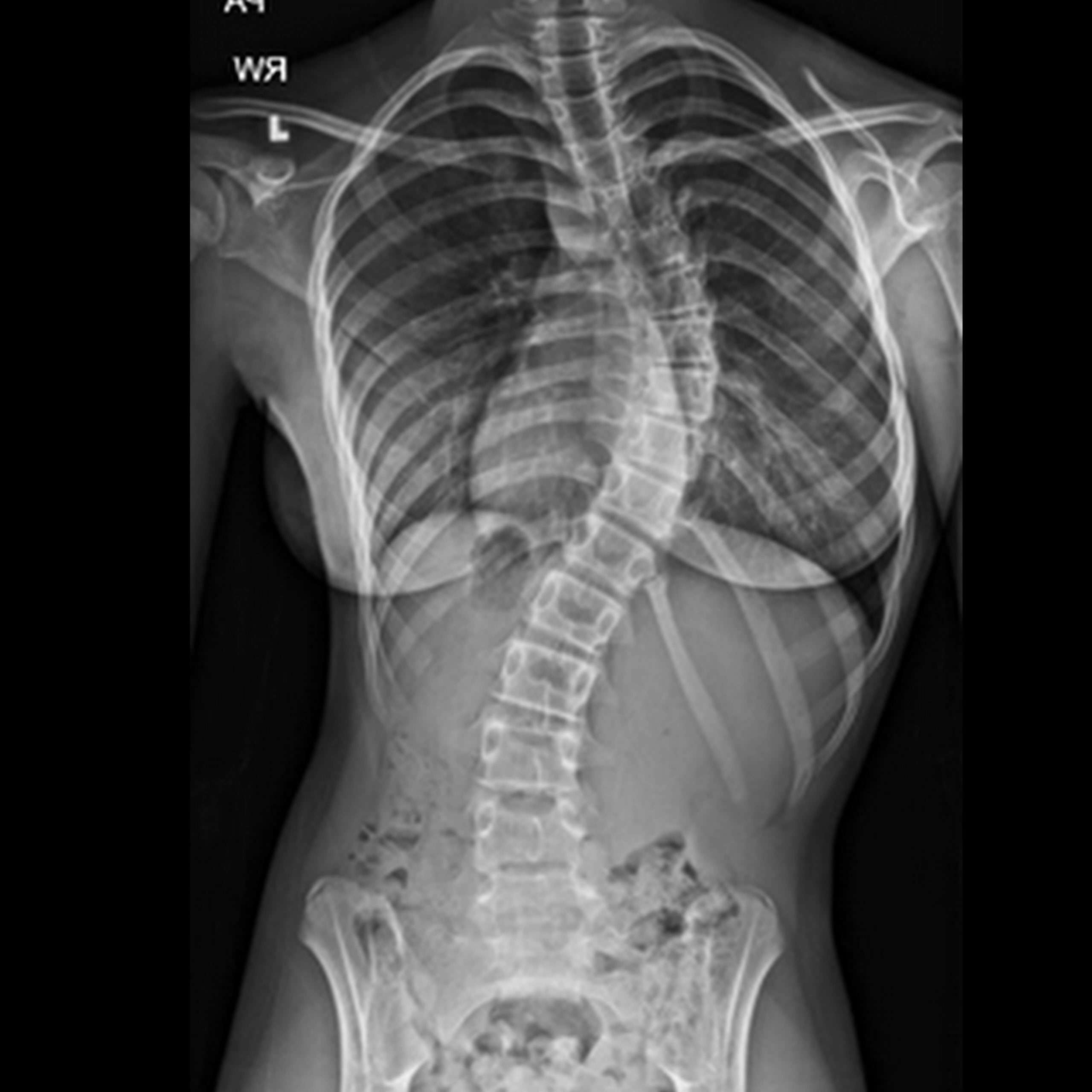
Describe scoliosis.
What is spine curves sideways, S or C shape?
Tissue that bone is made up of.
What is Osseous tissue (a dense, supportive connective tissue; composed of specialized cells and solid extracellular matrix with collagen fibers).
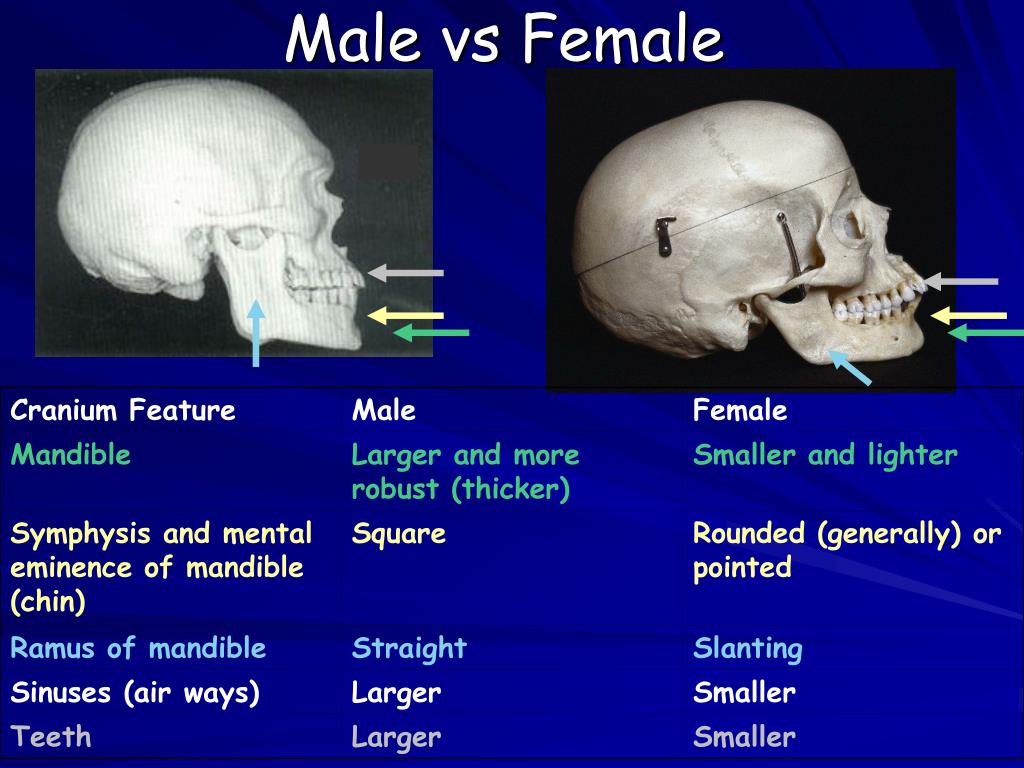
Describe some differences between male and female skulls.
What are
Identify the fracture below and its characteristics.
What is Comminuted fracture? What is fracture that shatters the bone into multiple bony fragments?
Describe Lordosis.
What is excessive inward curvature of the spine? 
Describe kyphosis.
What is excessive rounding of the back?
The functions of the skeletal system. (Hint there are six but list atleast three).
What is
•Support – for body and soft organs
•Protection – of brain, spinal cord, vital organs
•Anchorage – skeletal muscles use bones as levers to move body
•Mineral storage – bone is reservoir for calcium and phosphate
•Blood cell formation – occurs in red marrow cavities of bones
•Triglyceride (fat) storage – stored in yellow marrow cavities of bones
What is Talus, Calcaneus (heel bone), Cuboid, Navicular, Medial cuneiform, Intermediate cuneiform, and Lateral cuneiform.
Mneumonic for tarsal bones :Tall (Talus), Camels (Calcaneus), Never (Navicular), Consume (3 Cuneiforms– medial, intermediate, lateral), and Cubes (Cuboid)
Identify the two fractures below.

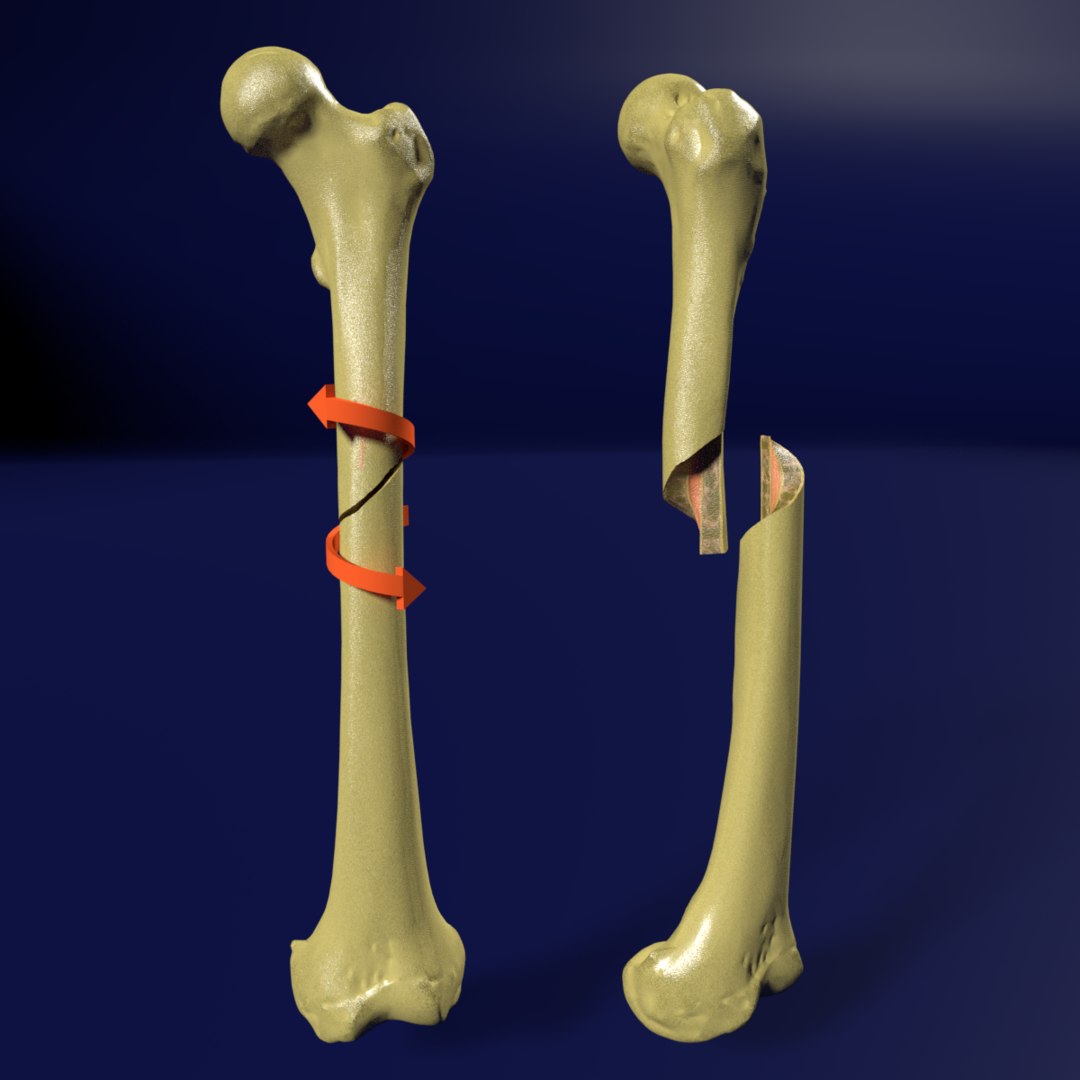
What is transverse fracture (bone break along the long axis)? What is spiral fracture (break in the bone that is produced by twisting stresses that spread along the length of the bone)?
Lack of growth hormone (GH) leads to short bones.
What is Pituitary dwarfism?
(Inadequate production of growth hormone leads to reduced epiphyseal cartilage activity and abnormally short bones.
Condition is becoming increasingly rare in U.S. because children can now be treated with synthetic human growth hormone.)
Results from overproduction of GH before puberty
What is Gigantism?
(Results from overproduction of growth hormone before puberty, while epiphyseal cartilage is still active.
The tallest man alive named Robert Wadlow grew to be 8ft 11in. He weighed 475 lbs and died at age 22 in 1940.)
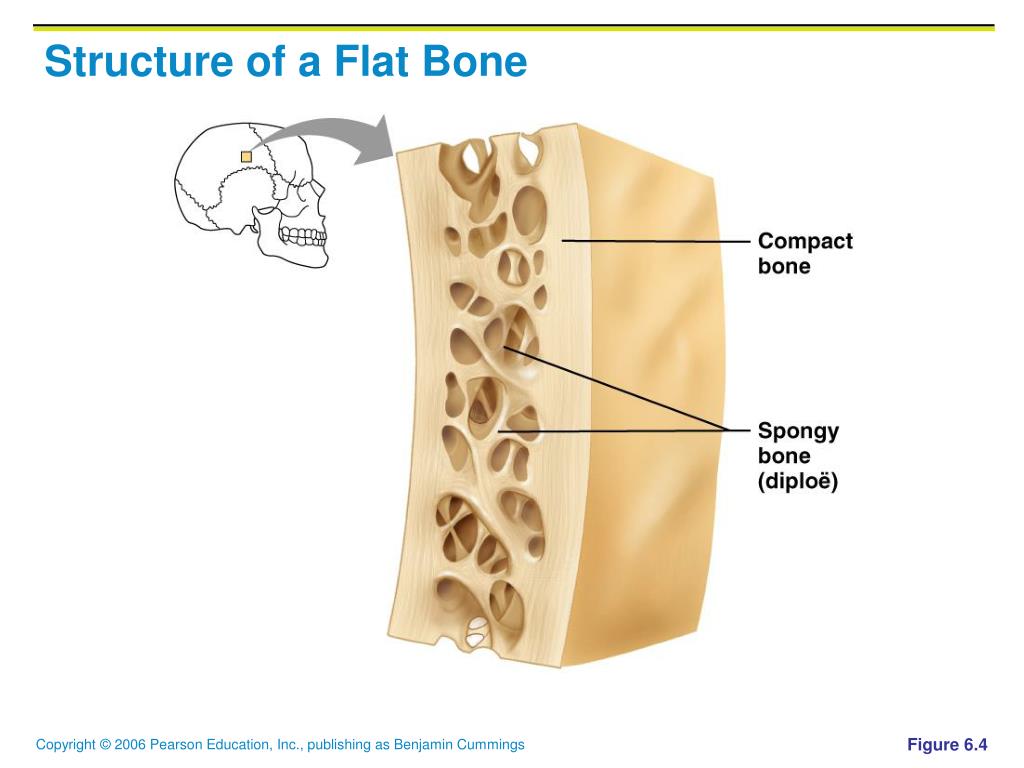
List the structures of flat bone and also provide example of flat bone.
What is the flat bone made of structure consisting of spongy bone between two layers of compact bone (cortex) and within the cranium, and the layer of spongy bone is called the diploë.
What are the parietal bones of the skull?
The carpal bones (bones in the wrist). (*hint there are 8 bones)
What are (from proximal to distal) Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform, Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, and Hamate.
A helpful mnemonic: Some – Scaphoid, Lovers – Lunate, Try – Triquetrum, Positions – Pisiform, That – Trapezium, They – Trapezoid, Can't – Capitate, Handle – Hamate. 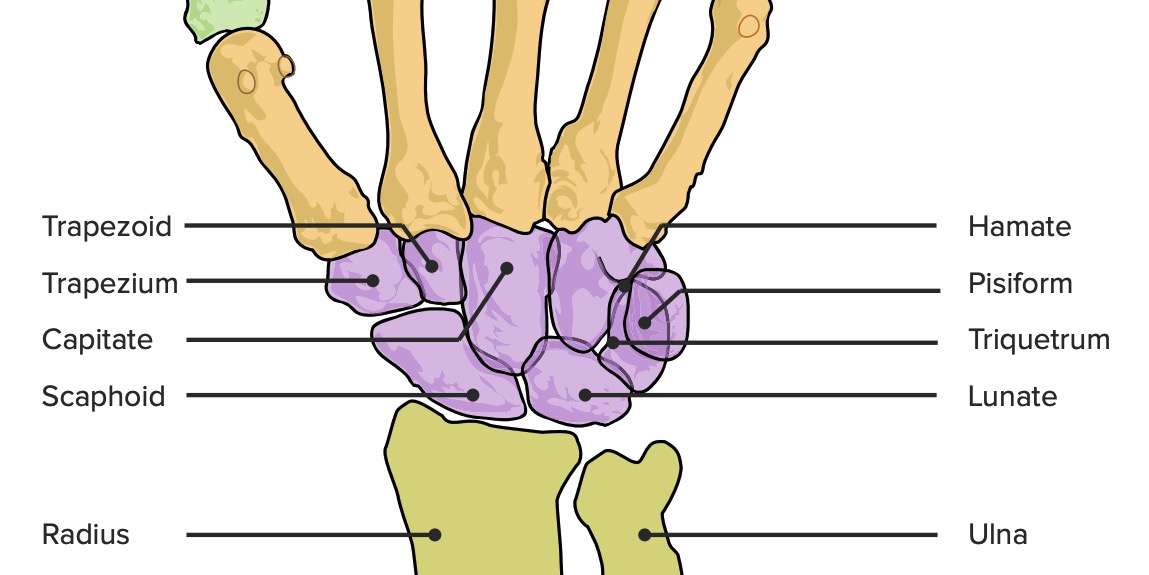
This fracture can stop growth and identify the process through which the fracture occurs.
What is an Epiphyseal fracture? What is fracture that involves the bone matrix undergoing calcification and chondrocytes are dying?
Results from excess GH after epiphyseal closure.
What is Acromegaly?
*(If the growth hormone level rises abnormally after epiphyseal closure, the skeleton does not grow longer.
Instead, bones get thicker, especially in the face, jaw, and hands. These physical changes occur in the disorder). *
Osteogenesis Imperfecta has different types.
What are the 3 types:
Mild: Type I - mild fragile bones, few fractures, and minimal malfunction of the limbs.
Moderate: Type IV, V, VI, and VII - less than average height, with short leg limbs, fractures when learning to walk, Scoliosis, compression of the vertebrae, fractures in long bone, ligament laxity, and bowed long bones are common.
Severe or most severe: Type II, III, and VIII
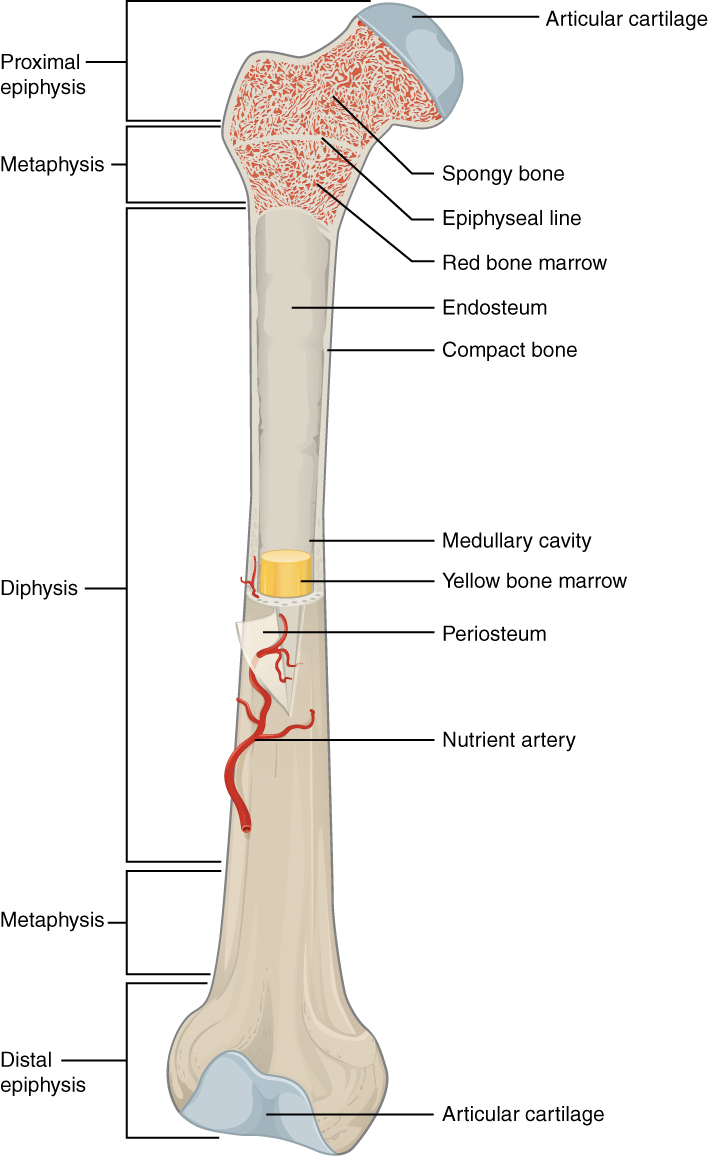
List the structures of long bone (hint there are three parts) also provide example of long bone.
What is structure of a long bone: Diaphysis (shaft) Wall of compact bone and central space called medullary cavity (marrow cavity), Epiphysis (wide part at each end) and mostly spongy bone (trabecular bone), and Metaphysis where diaphysis and epiphysis meet.
Examples in the arm are Humerus, Radius, Ulna, and Scapula. In the legs they are Femur, Tibia, and Fibula. In the Fingers and toes they are Metacarpals, Metatarsals, and Phalanges.
Describe some differences between male and female pelvis and the reason for modification in female pelvis.
What are (shown in diagram below)?
In female, why does the pubic symphysis loosen, and sacro-iliac ligaments loosen, thereby increasing size of pelvic inlet and outlet?

Identify the fracture below and how to distinguish this from other fractures, also what population is at risk for this fracture and why?

What is Greenstick fracture and how it occurs when bone breaks only on one side and the other side bends? What occurs in children whose long bones have not fully ossified?
Clubfoot is exaggerated longitudinal arch and is caused by shortened ACHILLES tendon. Describe how the feet are turned and explain the method used to correct this.

What are feet are turned in medially and inverted? What is Ponseti Method?
Not a diease question. :(
(Sorry for the misleading/gaslighting) :(
There are four types of bone cells.
What are Osteogenic cells (stem cells found in periosteum and endosteum), Osteoblasts (build bone), Osteocytes (mature bone), and Osteoclasts (break down bone)?
Identify the components of bone matrix (hint there are two). Then identify what happens if there is a deficiency in that component of the matrix.
What are collogen fibers (provide strength and slight flexibility) and hydroxyapatite crystals (provide hardness and as strong as steel-reinforced concrete)? Why is bone too bendable when hydroxyapatite crystals removed, and why is bone too brittle when collogen removed?
Nutrition affects the bone heavily. List 5 nutrition things that affect bone.
Calcium, phosphate: and other minerals needed for normal bone growth and maintenance.
Vitamin D3: needed for synthesizing the hormone calcitriol in the kidneys and essential for normal calcium and phosphate ion absorption in digestive tract and produced in skin or obtained from diet
Vitamin C: needed for collagen synthesis and also stimulates osteoblast differentiation.
Vitamin A: stimulates osteoblast activity.