Most common cause of avascular necrosis in adults
Corticosteroid use
Others: alcohol, anticonvulsants, anticoagulants, thyroid replacement therapy
17 yo with sickle-cell anemia presents with thigh pain
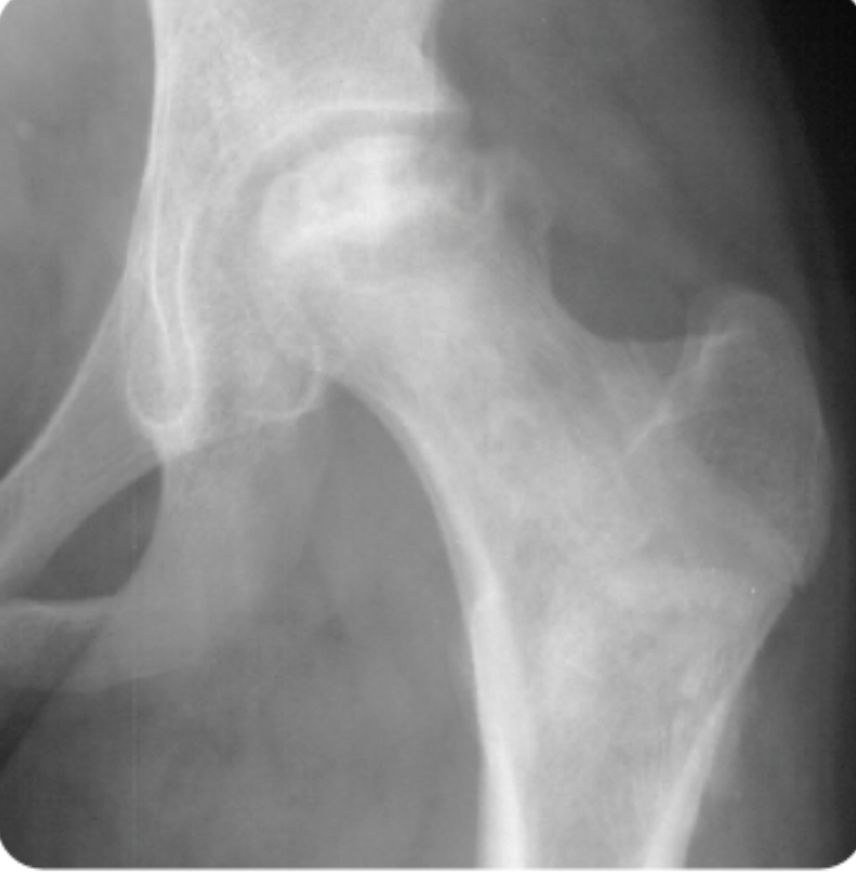
Avascular Necrosis
- Ischemic bone death of the femoral head after compromise of its blood supply
- Most commonly caused by sickle cell disease in children
- Most common site: femoral head
- Dx: X-rays might show findings (late), but diagnosis is made by MRI
Predominant physical exam finding of osteomyelitis?
Point tenderness over the infected segment
In chronic osteomyelitis, the involucrum or sequestrum (fragments of necrotic bone separated from healthy bone) may be palpated, and sinus tracts that fistulize to the skin may be noted.
Most common primary cancer associated with osteoblastic metastases
Prostate cancer, small cell lung cancer
Osteolytic metastasis
multiple myeloma, thyroid cancer, kidney cancer, melanoma non-small cell lung cancer
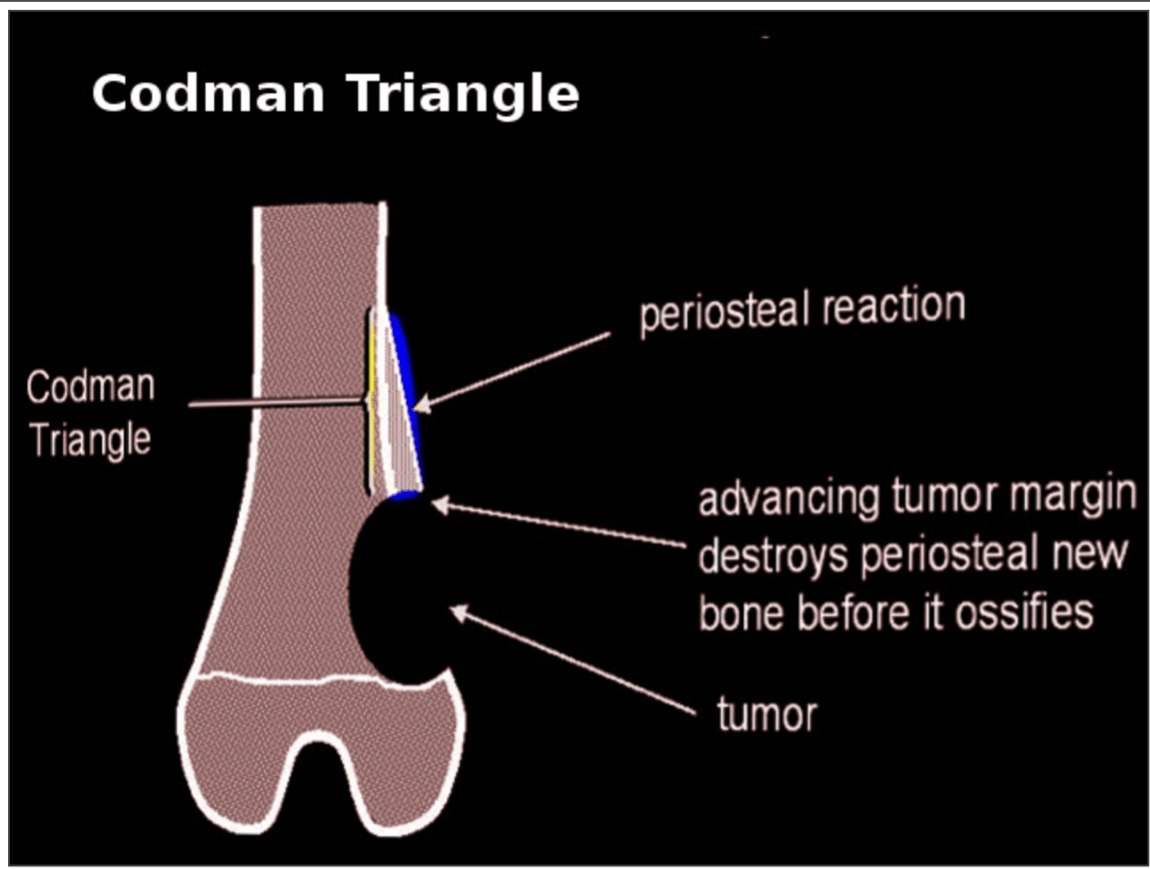
CODMAN TRIANGLE
Radiographic sign that appears as a raised triangle of bone on the edge of a growing lesion. It's a type of periosteal reaction that occurs when a bone lesion lifts the periosteum away from the bone, preventing new bone from forming
Most severe complication seen with hip dislocations
Avascular necrosis of the femoral head
The incidence of AVN of the femoral head occurs in 5% of patients who undergo prompt reduction, but increases to 50% if reduced > 6 hours after injury.
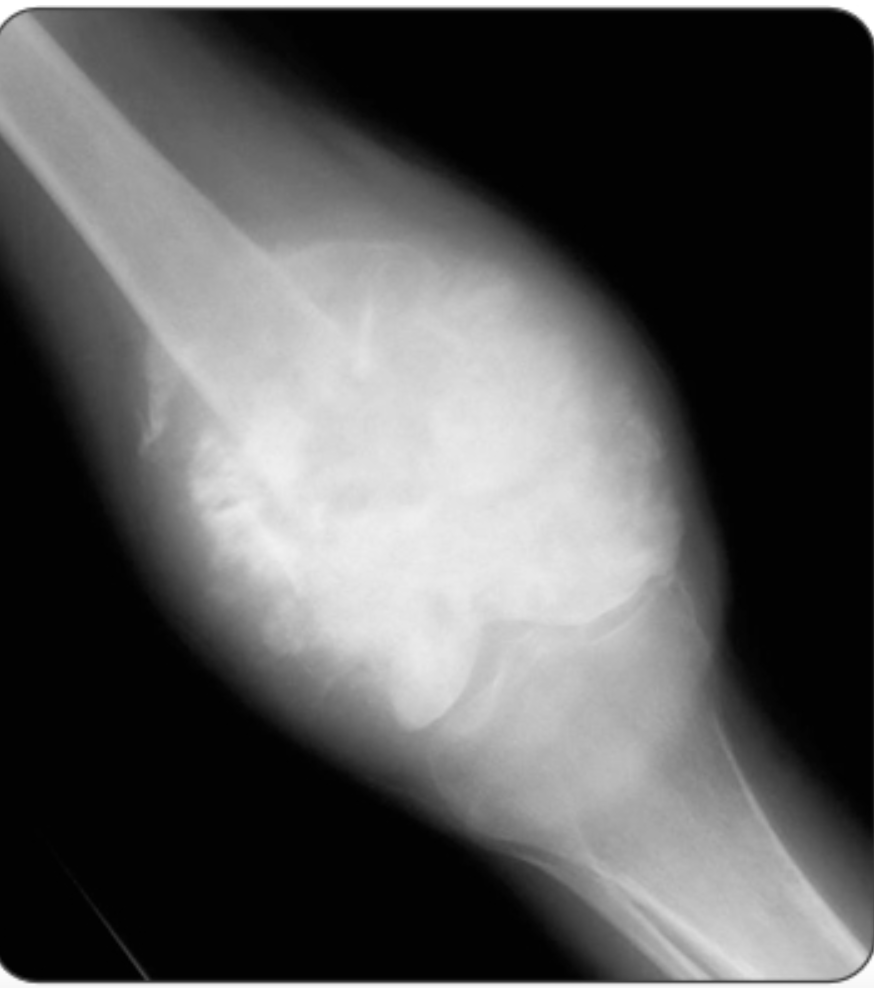
Most likely diagnosis in this 13 yo boy with progressive right knee pain over the past 6 weeks
Osteosarcoma (sunburst pattern on x-ray)
Most common primary malignant bone tumor in children
Primary tumor: metaphyses of long bones (particularly distal femur and proximal tibia)
Metastases -lungs , skeletal system, regional lymph nodes
Two most common organisms that cause osteomyelitis in human/animal bites?
Eikenella corrodens and Pasteurella multocida
Treatment: Penicillin +/- Amox-clav
Alt: Third gen cephalosporin/bactrim
A 25-year-old man presents to the emergency department with knee pain. This morning he slipped on the ice and felt a pop in his knee. On physical exam, his left knee appears to have a moderate effusion with limited range of motion and medial joint line tenderness. An X-ray of the left knee is performed. A pedunculated, bony exostosis with well-defined margins is seen along the distal lateral femur on the anteroposterior view of the knee. What is the most likely diagnosis of the bone lesion?
Osteochondroma
Benign tumor, cartilage-capped bony spur arising on the external surface of the bone
Boys>Girls
Found near end of long bones
Often incidental finding
Monitor with serial imaging for changes
Common cause of osteomyelitis in puncture wound through a rubber-soled shoe
Pseudomonas
-Levofloxacin and early follow-up
Which of the following children is most likely to have Legg-Calvé-Perthes?
A.11-year-old boy with 3 weeks of left knee pain with a tender prominence below the patella
B.14-year-old boy with 2 weeks of right thigh pain who favors external rotation during hip flexion
C.6-year-old girl with 1 month of limping and right knee pain without a history of trauma
D.8-year-old boy with an abnormal gait and unilateral limited hip abduction and internal rotation
D.8-year-old boy with an abnormal gait and unilateral limited hip abduction and internal rotation
Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease
- idiopathic avascular necrosis
- ~ 4–10 years of age
- Boys > girls
- Unilateral, intermittent limp (worse after activity)
- Most commonly caused by osteonecrosis of the proximal femoral head
- non-weight-bearing status on the affected limb or limbs and referral to a pediatric orthopedic surgeon. Most cases are nonsurgical
Plain radiographic findings consistent with osteomyelitis? (3)
Lucent lytic areas of cortical bone destruction (not detected on radiographs until approximately 50% of bone mineral is lost, which often takes up to 2 weeks from the onset of infection)
Periosteal reaction or elevation, osteopenia, involucrum (a layer of new bone growth), and sequestrum (fragments of necrotic bone separated from healthy bone)
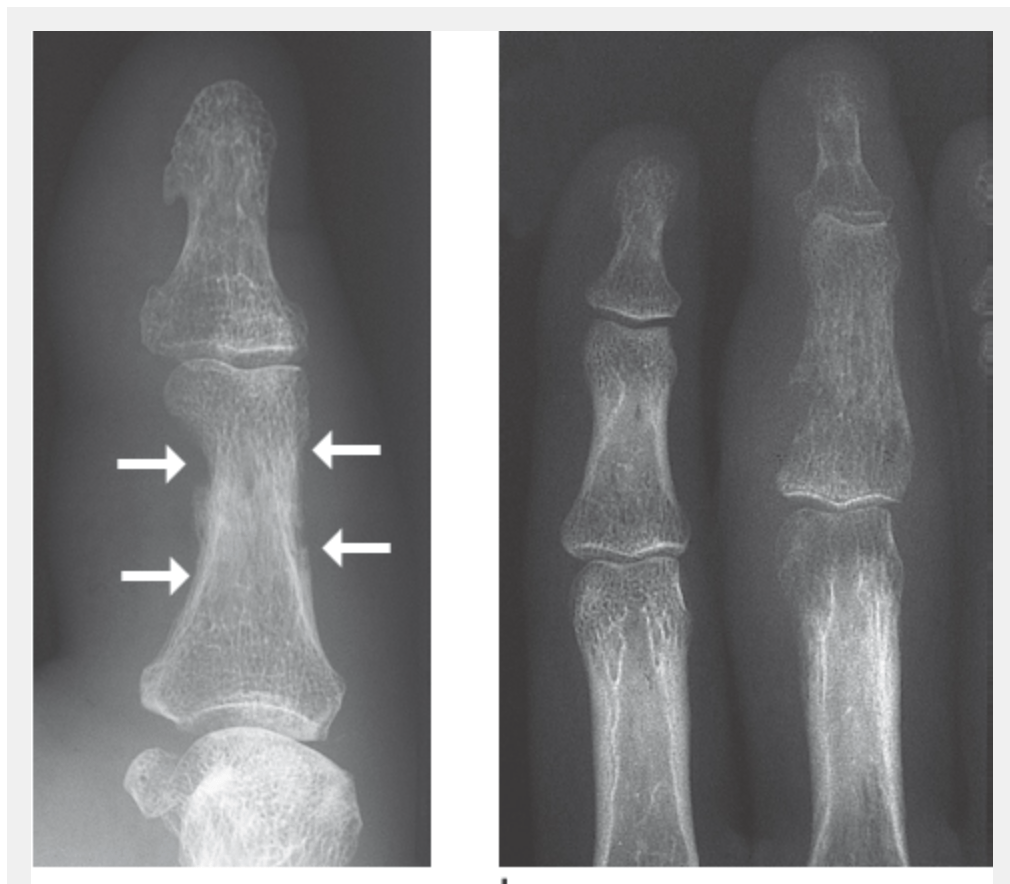
Left: Early signs of osteomyelitis on the proximal phalanx of the thumb in a massive soft-tissue infection. Evidence of periosteal thickening and discrete erosions in the compact bone
Right: Advanced stage of hematogenous osteomyelitis of the third middle phalanx. Moth-eaten osteolysis on the radial side along with periarticular osteopenia and soft-tissue swelling
Severe pain 3-5d after dental extraction. Exam with exposed bone without clot.
Alveolar osteitis aka dry socket
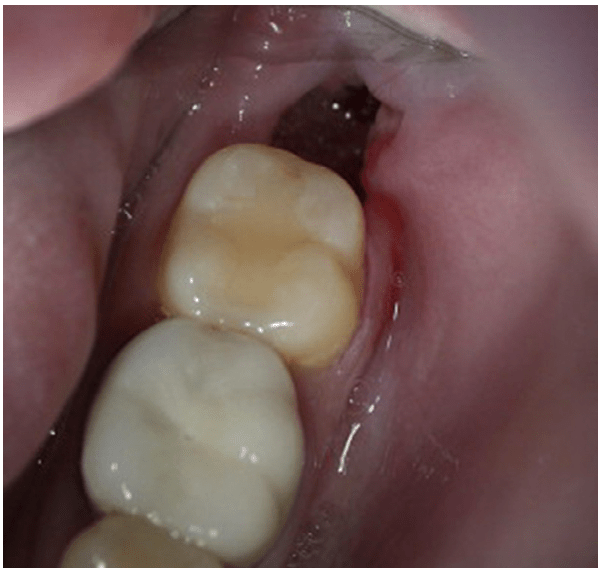
Localized osteomyelitis due to loss of protective clot
Management: irrigate with saline, iodoform guaze, eugenol (oil of clove), abx if needed (signs of infection), PAIN CONTROL and oral surgery referral
Most common site of osteosarcoma in children?
A. Distal femur
B. Lumbar vertebrae
C. Proximal femur
D. Proximal tibia
Distal femur
Osteosarcoma pearls:
Patient will be 10 to 20 years old or > 65
Pain, swelling that awakens at night
X-ray will show Codman triangle, sunburst pattern
Most common location: long bone metaphyses
Most common malignant bone tumor
Denosumab use and mechanism of action?
Osteoporosis; inhibits osteoclast maturation
Why is the femoral head prone to avascular necrosis?
Watershed zone

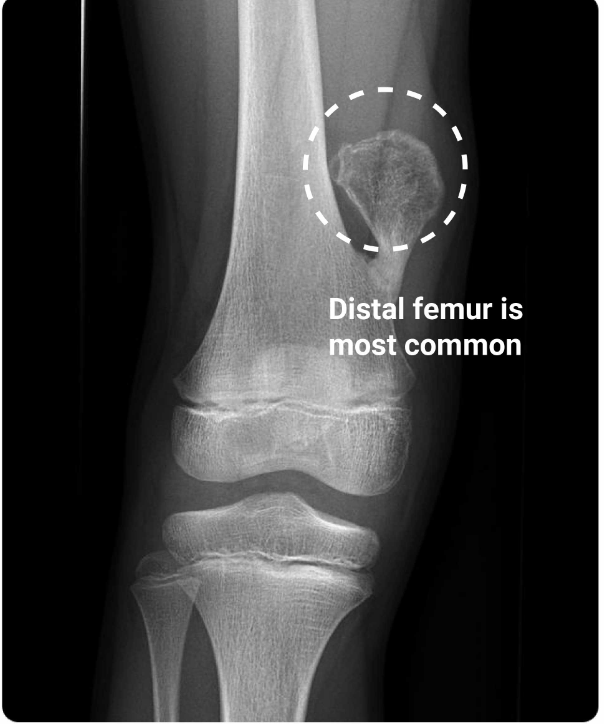
30 yo presenting with several weeks of knee pain and swelling. X-rays shows multicystic osteolytic lesions (Soap bubble sign)
Giant cell tumor
-locally aggressive benign tumor commonly in epiphysis of long bones
- arising from giant cells of the bone marrow
Back pain, fever, and immunocompromised. 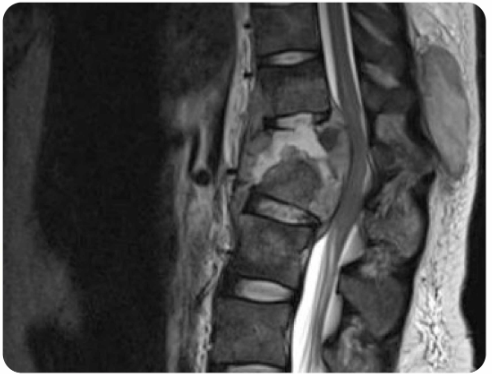
Pott Disease (Tuberculous Spondylitis)
- Most common form of skeletal TB
Osteomyelitis of the spine is generally caused by hematogenous spread and seeding of the bone by bacteria, resulting in inflammation of the bone and periosteum. Injection drug use, spinal surgery, and tuberculosis of the spine (Pott disease), can all cause vertebral osteomyelitis.
Painless mass in femur, occurs in adolescence (M>F), XR: "onion peel"
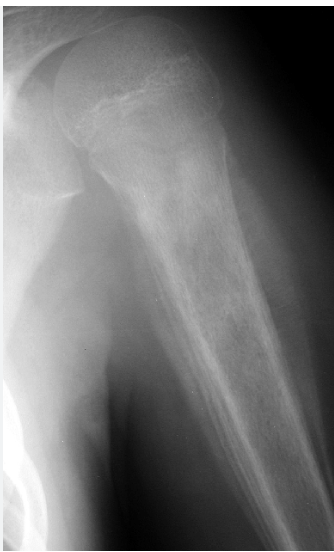
Ewing sarcoma
Highly malignant bone tumor arising from neuroectodermal cells
Primary tumor: often diaphyses of long bones (particularly femur, tibia, fibula, and humerus) and bones of the pelvis
Metastasis: lungs, skeletal system, bone marrow
A 14-year-old boy presents to the ED with leg pain for 2 weeks. He reports no recent illness or trauma. His symptoms are exacerbated during basketball practice at school. He has point tenderness over his right anterior tibia. There is no evidence of patellar dislocation or knee instability. His muscular compartments are soft. His lower extremity muscle strength and reflexes are intact. Which of the following conditions is most likely responsible for his symptoms?
A.Reactive arthritis
B.Superficial thrombophlebitis
C.Tibial apophysitis
D.Transient synovitis
C. Tibial apophysitis (Osgood-Schlatter Disease)
Young adolescent athletes, 10–15 years old
Knee pain with activities that cause quadriceps contractions (e.g., running, jumping)
PE will show tenderness over the tibial tubercle and with knee extension against resistance
Management includes ice, NSAIDs, acetaminophen, quadriceps stretching
An 18-year-old hurdler gets tripped up and falls, contacting the running track through his hyperextended left wrist. He presents to the ED with dorsolateral wrist pain, erythema, edema, and anatomic snuffbox tenderness. Initial anteroposterior, lateral, and oblique radiographs are negative for fracture.
Suspected diagnosis, ED management, and follow-up?
Scaphoid Fracture, thumb spica splint, repeat X-ray in 2 weeks
- Risks: fall on an outstretched hand (FOOSH)
- Sx: dorsal radial wrist pain with decreased range of motion
- PE: anatomical snuffbox tenderness
- Dx: clinical; X-ray, CT, bone scan, (MRI most accurate); many fractures will be missed on X-ray immediately after the injury
- Tx: thumb spica splint
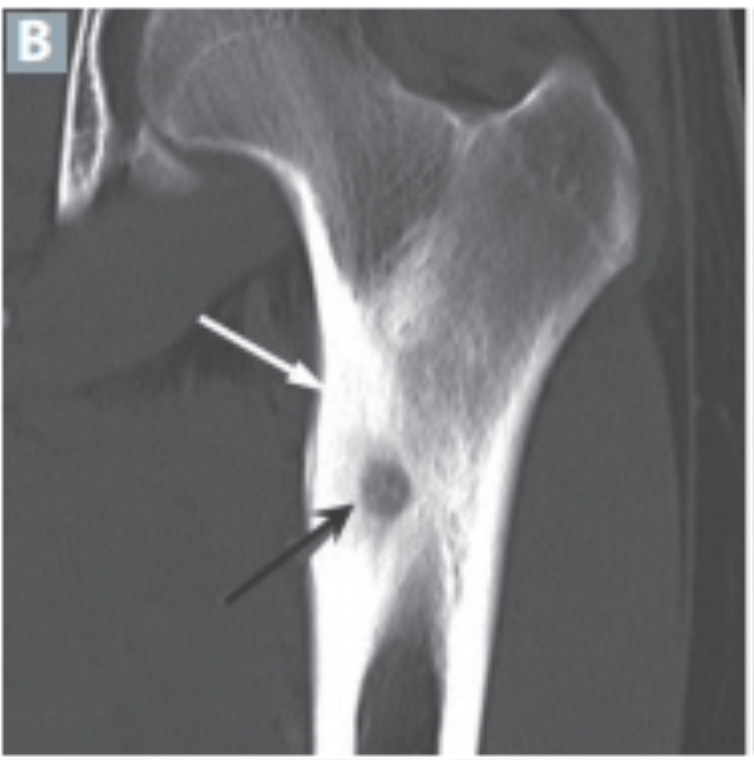
Bone pain worse at night. Name and management
Osteoid osteoma
-benign bone lesion seen on X-ray as intensely reactive bone around a radiolucent nidus most often in the lower extremities
-Age 10-35 yrs, Boys>Girls, long bones, nocturnal pain
-NSAIDS
Most common cause of osteomyelitis:
General?
Sickle cell?
Post-traumatic?
Post-surgical?
Infants < 3 months?
- General: Staphylococcus aureus
- Sickle cell: Salmonella, S. aureus
- Post-traumatic: polymicrobial
- Post-surgical: S. aureus, S. epidermidis
- Children < 4, no culture growth: Kingella kingae
- Infants < 3 mo: Group B Streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae)
A 67-year-old man presents with low back pain, fatigue and generalized weakness, weight loss x2 months. Which of the following laboratory findings would raise the highest suspicion for the most likely diagnosis?
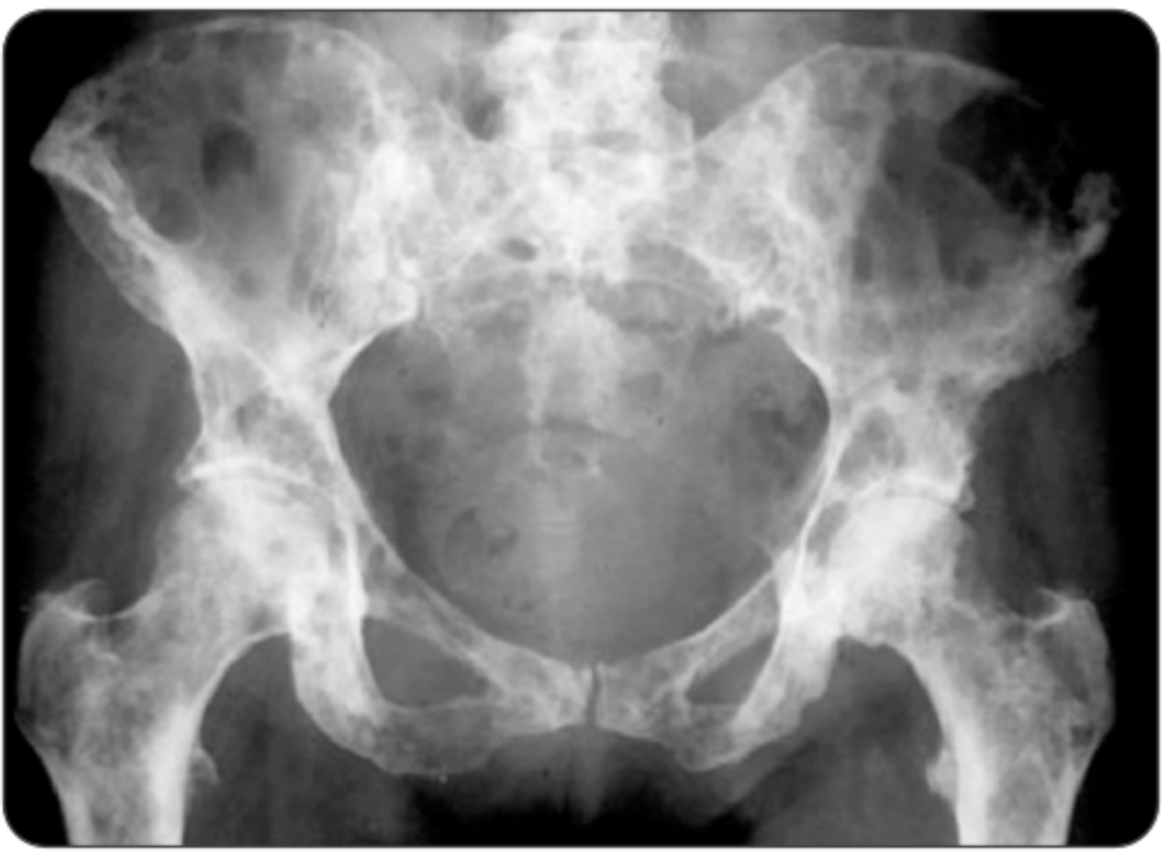
A. Hemoglobin 12.7 g/dL, serum creatinine 1.1 mg/dL, and serum protein 6.5 g/dL
B. Hemoglobin 16.1 g/dL, serum calcium 12.8 mg/dL, and serum creatinine 2.6 mg/dL
C. Hemoglobin 8.4 g/dL, serum calcium 13.8 mg/dL, and serum protein 9.8 g/dL
D. Hemoglobin 8.6 g/dL, serum creatinine 2.4 mg/dL, and 3+ proteinuria on urinalysis
C. Hemoglobin 8.4 g/dL, serum calcium 13.8 mg/dL, and serum protein 9.8 g/dL
Multiple Myeloma
- proliferation of neoplastic plasma cells producing excessive antibodies and monoclonal proteins, resulting in extensive bone marrow infiltration and skeletal destruction
- Typically found in older patients
- Back pain is the most common presenting symptom
- CRAB: hypercalcemia, renal insufficiency, anemia, lytic bone lesions or back pain
- X-ray: lytic lesions
A patient presents with a cervical spine injury that shows fractures of the bilateral anterior and posterior arches of C1. What are common risk factors associated with this type of fracture?
A. Age between 40 and 50 years old
B. Cycling collision
C. Osteoporosis
D. Skiing injury
C. Osteoporosis
Jefferson (Burst) Fracture
Risks factors include axial load injuries, osteoporosis, and neuromuscular diseases
History of trauma via axial loading (diving, football)
Most commonly caused by burst fracture of C1
Unstable fracture
Tx: halo vs surgery