Most common breast lesion in adolescents and young adults
Fibroadenoma
Most common location for distant metastases
Bone
What is the name of the suspensory ligaments of the breast
The majority of lymphatic drainage of the breast is through which lymph node basin?
Axilla (97%)
The rest is via the internal mammary notes (1-2%).
True or False: LCIS is a premalignant lesion
False: LCIS is considered a marker for the development of breast cancer but is not premalignant
Most common cause of bloody nipple discharge
Intraductal papilloma
-treatment: subareolar resection
What is the most likely type of breast cancer to develop in a patient with LCIS?
Ductal carcinoma (70%)
A patient presents after breast surgery with a winged scapula. What nerve was injured and what muscle does it innervate?
Winged scapula:
-injury to long thoracic nerve
-innervates serratus anterior muscle
Most likely cause of hyperesthesia of the inner upper aspect of teh ipsilateral arm after axillary dissection
2nd intercostobrachial cutaneous nerve
What is the sensitivity and specificity of mammography for breast cancer screening?
90% for both
What is the diagnosis and what is the treatment?
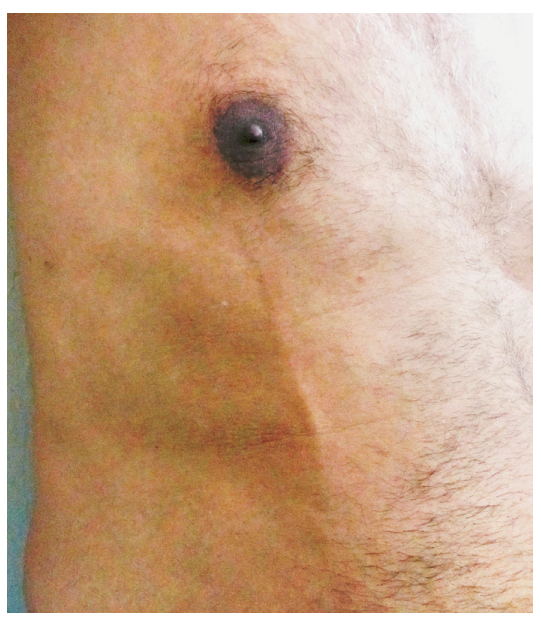
Mondor's Disease: superficial vein thrombophlebitis --NSAIDs
What is the most important prognostic staging factor for breast cancer
Nodal status
What is the valveless venous plexus responsible for direct hematogenous spread of breast cancer to the spine
Batson's Plexus
Indication to perform a sentinel lymph node biopsy for DCIS
If patient is undergoing mastectomy
Inherited breast cancer syndrome associated with an increased incidence of adrenocortical cancers, brain tumors, leukemias, soft tissue adn osteosarcomas in the same family
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
FNA of a breast lesion demonstrates histologic appearance of broad sheets of cohesive cells with nuclei in uniform shape and size.
Fibroadenoma
True or false: the prognosis for breast cancer is poorer in men than in women, stage for stage.
False: prognosis is the same stage for stage, however the overall prognosis is poorer in men secondary to later stage at presentation
Level I: lateral to the pectoralis minor
Level II: posterior to the pectoralis minor
Level III: medial to the pectoralis minor
Incidence of lymphedema after sentinel lymph node biopsy
2-4% (compared to axillary dissection: 15-30%)
Most aggressive subtype of DCIS
Comedo pattern
Syndrome associated with absence of pectoralis muscle, amastia, and hypoplasia of the chest wall
Poland Syndrome
Name 3 indications for radiation after mastectomy
Indications for radiation after mastectomy
-tumor >5cm, 4+ positive LNs, extracapsular nodal invasion, fixed axillary nodes or internal mammary nodes, inflammatory cancer, positive margins, skin/chest wall involvement
Name of nodes between the pectoralis minor and major muscles
Rotter nodes
Risk of lymph node metastasis with DCIS
<2%
How much does LCIS increase the chance of developing breast cancer?
LCIS: 9-Fold
ALH: 4-fold