A wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave's advance. Ex. Vibrations in a guitar string.
What is a Transverse Wave?

The highest part of a wave
What is a Crest?

The interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture
Diffraction

the combination of 2 or more electromagnetic wave forms to form a resultant wave
Interference
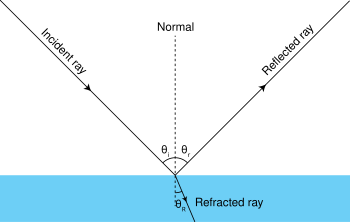
the angle between a reflected ray and the normal drawn at the point of incidence to a reflecting surface
What is Angle of Refraction?
Waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same direction of the wave propagation. Ex. Seismic P-Waves
What are Longitudinal Waves?

The lowest part of a wave
What is a Trough?

The redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another.
Refraction
when two waves of identical wavelengths are in phase, they form a new wave with an amplitude equal to the sum of their individual amplitudes
Constructive interference 
the angle between an incident ray and the perpendicular to the surface
What is the Angle of Incidence?

A wave that is an oscillation of matter. Ex. Stadium Waves
What is a Mechanical Wave?

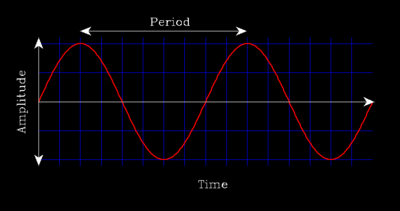
The time to complete one cycle.
What is a Period?
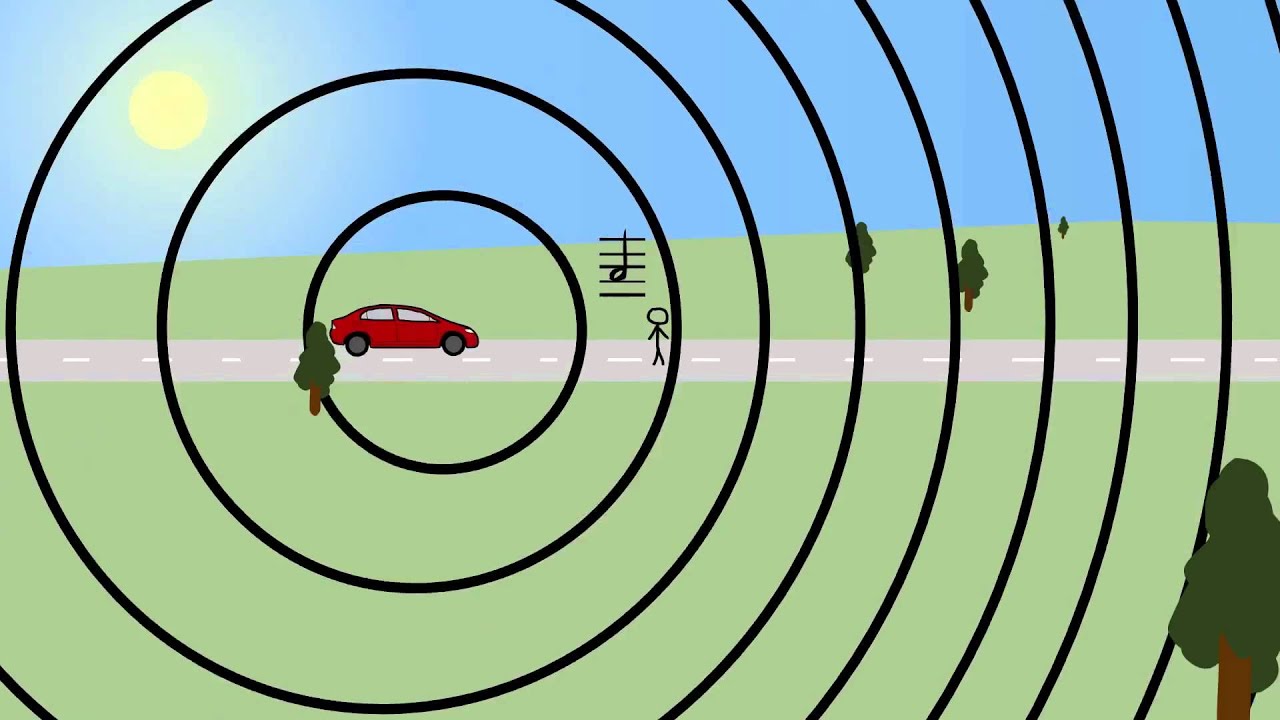
Include information for both light and sound - the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source.
Doppler Effect
when the maxima of two waves are 180 degrees out of phase
Destructive interference 
reflection of light or other waves or particles from a surface such that a ray incident on the surface is scattered at many angles rather than at just one angle as in the case of specular reflection.
What is Diffuse Reflection?

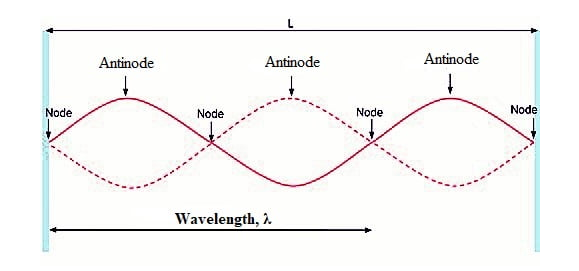
A wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. Ex. Notes on strings instruments
What is a Standing Wave?

A point along a standing wave where the wave has minimum amplitude.
What is a Node?

The change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated.
Reflection
the pulsation caused by the combination of two waves of slightly different frequencies
Beats 
a ray of light that strikes a surface
What is an Incident Ray?
A wave in which the particles of the medium move progressively in the direction of the wave propagation with the faster speed overtaking the slower speed. Ex. Water waves
What is a Traveling Wave?

A region of maximum amplitude situated between adjacent nodes in a vibrating body.
What is an Antinode?
Regular variation in magnitude or position around a central point.
Oscillation
the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts
Resonance 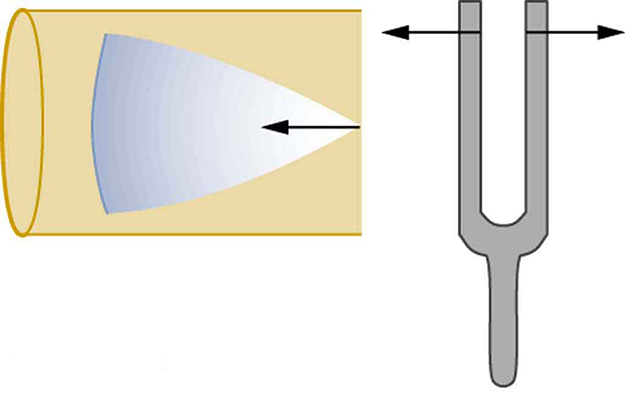
on reflection from a smooth surface, the angle of the reflected ray is equal to the angle of incident ray
What is the Law of Refraction?

