What reactions link monomer units together? What reactions break up polymer units?
dehydration synthesis, hydrolysis
Place the most appropriate letter on each line. Each letter may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
a. simple diffusion; b. facilitated transport; c. active transport; d. co-transport; e. osmosis; f. endocytosis
____ H+ moving across a membrane through a channel
____ The Na+/K+ pump
____ Water moving through through lumen of the gut across the intestinal wall into the blood stream
____ O2 moving from the lungs into red blood cells
____ glucose moving into a cell driven by energy derived from simultaneous Na+ transport
B
C,D
A,E
A
D,C
What is the major difference in outcome of active transport versus facilitated diffusion?
active transport causes gradient to increase (goes against concentration); facilitated diffusion decreases a gradient (flows high to low)
What do the values of ΔG tell you about a reaction?
if delta G is negative, the reaction is exergonic. If delta G is positive, the reaction is endergonic.
Metabolic pathways can be regulated at different steps depending on the demands of the cell. ____________ loops use the product of a pathway to inhibit an enzyme at the beginning of the pathway.
negative feedback or feedback inhibition
What type of molecule is this? What properties does it have?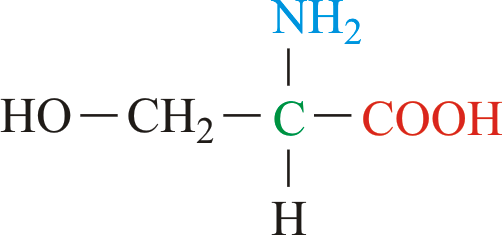
Amino acid; polar bond between O-H, can form H-bonds
Draw a simplified condensation reaction and explain it.
Also known as dehydration synthesis, two monomers come together and form an ester bond, and release a water molecule.
What protein makes the "coated pit" and helps internalize the membrane in receptor-mediated endocytosis?
Clathrin
Where is potential energy stored in organic molecules?
bonds
What is the net effect of reaction coupling on free energy?
a. The overall delta G becomes positive
b. the overall delta G becomes negative
c. the overall delta G becomes zero
d. there is no impact on delta G
b. the overall delta G becomes negative
Fats and oils are synthesized by adding three __________ to a _______ backbone by _________.
Fatty acid chains, glycerol, dehydration synthesis
What happens when animal cells are exposed to a hypertonic solution? hypotonic solution? isotonic solution?
Shrivel up; swell and explode; nothing
__________ are largely responsible for determining the functions of a cell membrane. _____________ associate with the membrane on one side, but do not enter the membrane. ____________ insert into the lipid bilayer, either partially or passing all the way through (transmembrane).
Membrane proteins; Peripheral Membrane Proteins; Integral Membrane Proteins
What is entropy? What is enthalpy? What is free energy? Write the equation relating all three.
entropy: measure of disorder
enthalpy: the total amount of energy in the reaction, usable and unusable
free energy: energy available to do work, the total amount of useable energy in the reaction

What factors impact on enzyme function? How?
Temperature: too hot= denature enzyme and it doesn't work
too cold= enzyme and substrate move more slowly and don't contact each other, reaction rate decrease
pH: too acidic or too basic environment, enzyme denatures, interferes with H-bonds and ionic bonds in the enzyme
salt concentration: will affect the ionic bonds holding an enzyme together and will denature it if the concentration is too high
A protein is held together by only H-bonds and disulfide bridges. What protein structure does it have?
tertiary
Say I have a cell membrane. I take out all the cholesterol in the membrane. What happens when the cell membrane gets cold? What about when it gets hot?
What are the 3 classes of active transport proteins? Define them.
Uniport - 1 molecule at a time
Cotransport - moves 2 at a time
Antiport - one solute goes one way while another goes the opposite way
Draw and label a free energy diagram for an enzymatic exothermic reaction.

Compare and contrast the active site and the allosteric site of enzymes.

Draw a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid.

What is endocytosis? Can you list and explain the various types of endocytosis explained in class?
definition: the taking in of matter by a living cell by invagination of its membrane to form a vacuole
phagocytosis: "cell-eating" a cell engulfs a solid particle to form an internal compartment
pinocytosis: "cell-drinking" the ingestion of liquid into a cell by the budding of small vesicles from the cell membrane
receptor-mediated endocytosis: specific molecules are ingested into the cell. The specificity results from a receptor-ligand interaction
Explain (or sketch) how a sodium-potassium pump works.
Changes shape to transport Na one way and K the other way
What is a "coupled reaction"? Write a simple example.
the energy required for one reaction is supplied by another reaction

100 amino acids ⇄ 1 100-amino acid polypeptide + 99 H2O
Describe this reaction. Catabolic or anabolic? Ender or exergonic? Does entropy increase or decrease?
anabolic, endergonic, decrease

