The smallest functional unit in all living things
Cell
Making energy. Most organisms do it by taking in O2 and excreting CO2
Respiration
Another name for organs within the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
Viscera
a body part is above another part
superior
A type of homeostatic mechanism that results in unstable conditions for a short amount of time; such as childbirth
Positive feedback mechanism
Target cells
The arm
brachial
Anything that has weight and takes up space
Matter
The condition of a stable internal environment
Homeostasis
Breaking down food into usable nutrients for absorption into the blood
Digestion
The compartment between the right and left thoracic cavities that contains the heart, esophagus, trachea, and thymus
Mediastinum
towards the front
anterior
Referring to a plane that divides the body into superior and inferior portions.
Transverse
The sum of all chemical reactions in the body that break substances down and build them up
Metabolism
The space in front of the elbow
Antecubital
How do you find atomic weight?
Adding protons and neutrons
Proteins are made up of building blocks called ________.
Amino acids
The most abundant chemical in all living systems
Water
The membrane that covers each lung
Visceral pleura
The wrist is ________ to the elbow.
distal
Label the body cavities.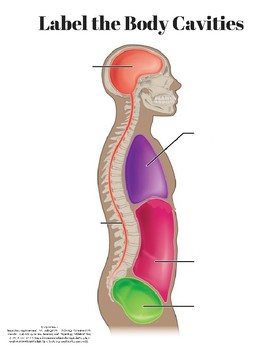
Orange: Cranial cavity
Red: Vertebral cavity
Purple: Thoracic cavity
Pink: Abdominal cavity
Green: Pelvic cavity
Left upper quadrant
popliteal
What chemical is necessary for cells to release energy from glucose?
Oxygen
Name three of the four macromolecules that make up human cells
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
Fluid found outside of the cell; such as plasma
Extracellular fluid
The membrane surrounding the heart that is outside the serous fluid (hint: another membrane is closer to the surface than this one.)
Parietal pericardium
Describe anatomical position
_________ provide information about stimuli in the internal environment while ____________ bring about responses that alter conditions in the internal environment.
Effectors
The appendix is found here...
Right lower quadrant
the neck
Cervical
Where are electrons found in atoms? How many can be in the first layer?
Floating around the nucleus in shells, 2 in first layer.
What are the levels of organization starting at a macromolecule level?
macromolecule
cell
tissue
organ
organ system
organism
A form of energy that is a product of metabolic activity
Heat
The name of the cavity that separates the membranes of the abdominopelvic region.
structures on the same side
Name 7 organ systems.
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Nervous
Muscular
Skeletal
Digestive
Endocrine
Lymphatic
Urinary
Reproductive
Integumentary
What are examples of monosaccharides?
Galactose, glucose, fructose
The armpit
Axillary
An acid contains more _______ ions while a base contains more ________ ions.
Hydrogen, hydroxide.
Name the five characteristics of life
reproduction
responsiveness
movement
metabolism
The ability of an organism to sense change within its body
Responsiveness
The gallbladder is found here...
Right upper quadrant
Which other cavity is located within the mediastinum?
What lipids are important in hormone production?
Steroids
Much like an air conditioning system, our body attempt to correct an alteration to a set point. What is this called?
Negative feedback system
The muscle separating the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities (hint: it aids in breathing)
diaphragm
What are the four elements that make up organic molecules?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen