A(n) ________ is a road map for the marketing activities of an organization for a specified future time period, such as one year or five years.
Marketing Plan
Marriage, Parenting, Children, Teenagers, Family, Empty Nesters, and Retirement.
Stages of the Family Life Cycle
The collection, recording, and analysis of information to aid in making marketing decisions
Marketing Research
Refers to the extent to which firms exploit opportunities, neutralize threats, and reduce expenses relative to the competition.
Competitive Advantage
A portfolio-planning model based on the premise that an organization’s products or services can be classified into four categories in relation to its largest competitor. The four categories are based on combinations of market growth and market share.
Boston Consulting Group Growth-Share Matrix (BCG Matrix)
Need identification, gathering of information, assessment of alternatives, the purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior
Stages of Purchasing Decision Process
A tool that uses two or three variables to graph the position of a brand in comparison to its competitors based upon consumer perceptions.
Perceptual Map
The group of consumers most likely to purchase an organization's goods and service is called the:
Target market
A group of similar products that may be sold to the same market segment or to different market segments to meet similar needs.
A product line
The activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.
Marketing
The way in which consumers receive, understand, and retain information
Selective perception
Gathering of information in a structured way to answer marketing research questions
Data collection
Sponsoring a community event, creating print or broadcast advertising, or distributing a direct mail campaign
Examples of traditional marketing activities
Selective exposure, selective attention, and selective retention
The three specific filters of selective perception
A framework that matches market segments and their relative size on one side of a table to products offered on the other side in order to spot underserved needs.
The market-product grid
Examines the effect of marketing in the context of the external environment
Macro marketing
A product in the growth stage is experiencing periods of:
Rising sales and profits
Developing a marketing mix (product, price, place, promotion, people, processes, and physical evidence) that satisfies a target market and creates "top of mind" awareness for the product, service, or brand.
Positioning
This era (1920 - 1960) was defined by having more goods than there were customers. Companies hired salespeople to actively promote products and find buyers.
The Sales Era
Cohort born 1946 to 1964
Baby Boomers
The process that establishes marketing objectives and has measurement tools in place for analysis to measure actual performance and to allow for adjustments where needed.
Control
A market of many sellers with similar products
Pure competition
Purchases that involve previously purchased goods or services that are subjected to some significant change, typically involving pricing or volume.
Modified rebuy
helps marketers define their growth strategies into four key quadrants: market penetration, product development, market development, and diversification 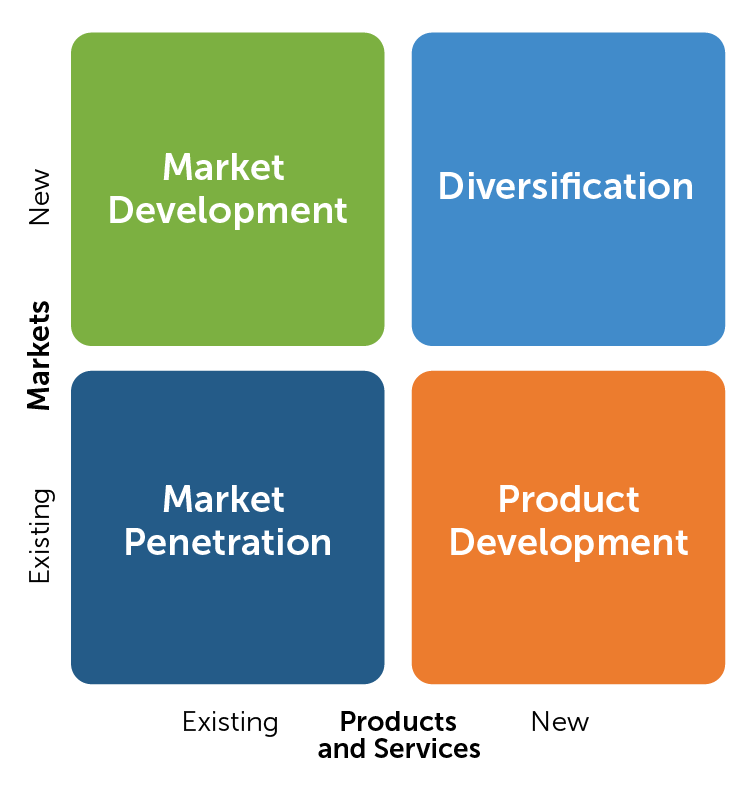
The Ansoff Matrix
A long-term strategy that touches on each stage of the customer cycle. Relationship marketing activities include soliciting feedback and testimonials from current customers, developing a loyalty program that rewards customers, emailing prospective clients, or meeting with current customers or prospective clients face-to-face.
Relationship Marketing
Studying the various reasons why personal, situational, psychological, and social interactions affect how people shop for products, use them, and potentially replace them.
Consumer buying behavior.
Provides a sense of where an organization sits related to the quality and relevance of its products, where it stands against its competitors, and where the market itself is going; a thorough situation analysis involves an accurate assessment of internal and external factors.
Situation Analysis