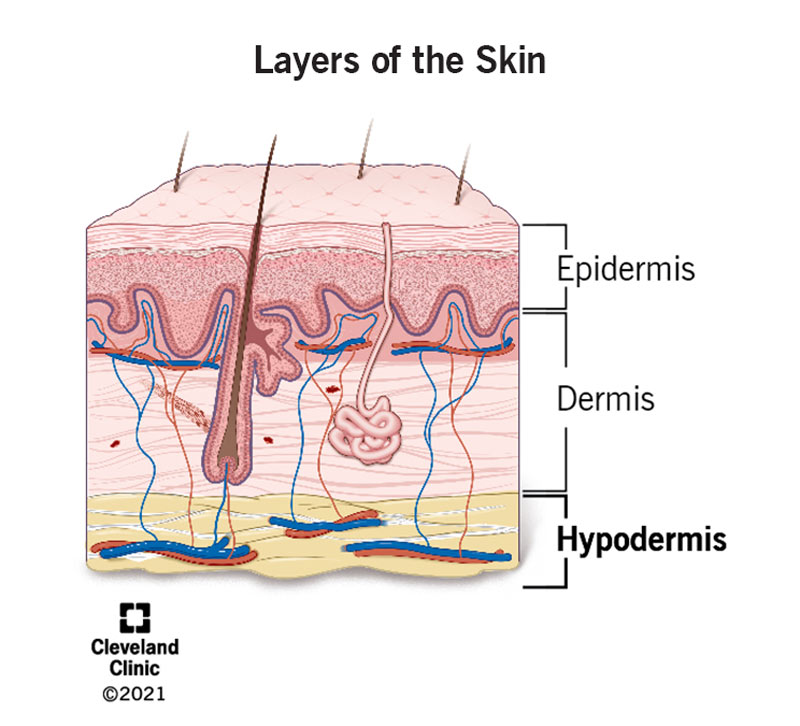
The three layers of skin tissue are
Epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous
Which of the following is not a topical medication used for burns?
A. Bactracin
B. Mafenide acetate
C. Hydrocortisone
D. Silver sulfadiazine
True or false. For major burns, initiate IV access with large-bore catheter.
True. Hypovolemia is a concern with major burns, so starting an IV with a large bore catheter is crucial for fluid resuscitation.

Which of the following should be increased to prevent tissue breakdown and promote healing?
A. Fiber
B. Fats
C. Proteins
D. Carbohydrates
C. Proteins
It is necessary to increase caloric intake to meet increased metabolic demands and prevent hypoglycemia.
Inhalation injury is a major complication of burns. Which of the following is the PRIORITY nursing action for an inhalation injury?
A. Monitor I&O
B. Provide oxygen at 100%
C. Apply topical silver sulfadiazine to affected area
D. Ensure adequate rest
B. Provide oxygen at 100%
ABCs framework.
Which layers of skin are damaged in deep partial thickness burns?
A. The epidermis only
B. The epidermis and part of the dermis
C. The epidermis, dermis, and underlying subcutaneous fat
D. All layers of the skin and bones, muscle, fascia
B. The epidermis and part of the dermis
Superficial: epidermis
Superficial partial thickness: the entire epidermis
Deep partial thickness: the entire epidermis and some of the dermis
Full thickness: entire epidermis and dermis, possible damage to subcutaneous tissue
Deep full thickness: damage to all layers of the skin that extends to the muscle, fascia, and bones
Which of the following intravenous medications is used for pain management in pediatric patients suffering from burns?
A. Aspirin
B. Morphine
C. Diphenhydramine
D. Silver sulfadiazine
Opioid analgesia with morphine is administered via continues infusion prior to procedures.
Silver sulfadiazine is used for burns but it is a topical agent, not an intravenous analgesic.
Septic shock is one of the serious complications of burns. Which of the following is not an associated manifestation of shock?
A. Tachycardia
B. Increased urine output
C. Spiking fever
D. Confusion
B. Increased urine output
Decreased urine output is an assessment finding associated with shock. Urine output should be maintained at 30 mL/hr for children >30 kg.
True or False. Enteral nutrition, rather than parenteral nutrition, is generally preferred in burn patients who require nutritional support.
True
Early enteral nutrition has been associated with improved GI function in pediatric burn patients (UpToDate).
False.
Shock and sepsis are major complications of burns due to hypovolemia.
A 3-year-old child presents to the ED with burns covering both lower extremities. Which of the following percentage of total body surface area would the nurse document?
A. 20%
B. 30%
C. 40%
D. 50%
B. 30%

True or False. Products with lanolin can help with pruritis related to burns.
False. Topical agents high in lanolin should be avoided in as these will worsen pruritis (UpToDate).
Nurses are responsible for helping prevent infection in patients with burns. All of the following are interventions for infection prevention except:
A. Restricting plants and flowers
B. Limiting visitors
C. Administering tetanus toxoid if indicated
D. Avoiding frequent position changes
D. Avoiding frequent position changes
The nurse should assist the patient to change positions frequently to prevent contractures and prolonged pressure.
Name another profession a child with burns would also work with besides the medical team and nurses.
Physical therapy, home health services, occupation therapy, and social services.
Which psychosocial nursing diagnosis is an associated complication of severe burns in adolescents?
A. Risk for infection
B. Impaired tissue integrity
C. Disturbed body image
D. Deficient fluid volume
C. Disturbed body image
Which of the following is not a risk factor for burns in the pediatric population?
A. Abuse
B. Neglect
C. Family history of burns
D. Lack of supervision
C. Family history of burns
Abuse, neglect, and lack of supervision are risk factors for burns in children.
A _____ is a skin graft obtained from animals for partial thickness burn wounds.
A. Allograft
B. Autograft
C. Xenograft
D. Homograft
C. Xenograft
Allografts, autografts, and homografts are different types of grafts obtained from human skin. Allografts and homografts are from human cadavers, whereas autografts are from the client.
True or False. In patients with major burns, it is important to provide 100% supplemental oxygen and monitor vital signs.
True.
Maintaining airway and ventilation, and watching vitals signs for changes that may indicate shock are very important nursing considerations for burns.
Which of the following is not advised to teach a client about burn prevention?
A. Avoid sun exposure between 1000 and 1400
B. Wear protective clothing
C. Apply sunscreen to prevent sunburn
D. Visit tanning bed instead of outdoor exposure to sunlight
D. Visit tanning bed instead of outdoor exposure to sunlight
Limiting sun exposure, wearing protective clothing, and using SPF are all good teaching points to prevent sunburn. The nurse should not teach a patient to use tanning beds as these can be associated with burns and skin cancer.
True or False. Pulmonary problems are a complication of burns that may require the patient to be intubated or have a tracheostomy.
Maintaining the airway via intubation, sometimes tracheostomy, is necessary if a burn patient has pulmonary complications.
A. CBC
B. ABGs
C. Urinalysis
D. Blood electrolytes
E. Liver enzymes
A, B, C, D, E
All of these are expected to be ordered for burns. Random glucose levels and BUN are also labs commonly evaluated for burns.
True or False. Active range of motion should be avoided during hydrotherapy.
False.
Active range of motion should be encouraged during hydrotherapy.

Which of the following vitamins and minerals are encouraged in patients with burns to facilitate cell ground and aid in wound healing? Select all that apply
A. Vitamin A
B. Vitamin B12
C. Vitamin C
D. Folate
E. Zinc
A. Vitamin A
C. Vitamin C
E. Zinc
What is a growth and developmental change following a burn in a child?
Delays in growth and weight for up to three years following the burn injuries.
Increased risk of bone remodeling.
When changing dressings, which of the following nursing actions should be performed to prevent wound infections?
A. Use surgical aseptic technique with dressing changes.
B. Use clean technique with dressing changes.
C. Infections are not a complication of burns.
D. Wear normal non-sterile gloves when changing dressings.
A. Use surgical aseptic technique with dressing changes.
Changing wound dressing is a sterile process for burns because of the high risk for infection.