A survey that asks, what is your gender?
What is nominal
Q1-1.5xIQR
Q3+1.5xIQR
These are used to find
What is lower and upper boundaries
The three types of central frequencies
What is Mode, Median, Mean
The average distance from the mean
What is standard deviation
A specific characteristic of elements in data
What is a variable
What is ordinal
s/x
What is coefficient of variance
Sum of weighted data values/ Sum of the weights
What is weighted mean
Q3-Q1
What is the interquartile range.
Largest data value-Smallest data value/ Number of classes
What is approximate class width
Has a meaningful zero
What is ratio
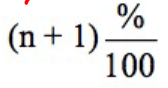
What is the quartile formula
The shape in general(not always) if the data shows
Mean>Median>Mode
What is positively skewed
It is very sensitive to extreme values or scores
What is range
The difference between cross-sectional and time-series data
What is cross-sectional is data at (approximately) one point of time and time-series is data over a period of time
It is always numeric
What is interval
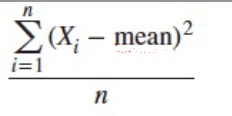
What is population variance
The only central tendency measure at the nominal level
What is mode
Steps to calculate percentiles, and show example
1. Order or rank the values first
2. Use the quartile formula to determine the position
3. Using position, determine the percentile value.
If extreme values go to the left the distribution is
Negatively skewed
Indicates the most appropriate data summarization and statistical analyses
What are scales of measurement
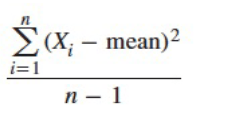
What is sample variance
Only used for quantitative data
What is mean
Used to compare distributions with different units or to compare distributions with the same units but very different means
What is coefficient of variance
Shows the total number of items with values less than or equal to the upper limit of each class.
What is a cumulative frequency distribution