Describe questions will generally be about ....
Internal, operating and macro environmental factors.
Define Marketing
Marketing is the process of identifying, anticipating, and satisfying the needs and wants of customers in a mutually beneficial exchange process.
The four key components are:
The right products that appeal to customers
Pricing products correctly to attract customers
Effective promotion to entice customers
Convenient and efficient distribution for ease of purchase
What are the two types of market research businesses may undertake
Primary and secondary research
Define market segmentation
Refers to the categorizing of customers into groups based on common characteristics
Identify the 4 Ps of marketing.
Product
Price
Promotion
Place
Identify two main influences on operations the external operating or MACRO environments.
EOE: Customers and Suppliers
MACRO: Government regulations, environmental sustainability
Identify characteristics of each section of a SWOT Analysis
S and W should be internal and current
O and T should be external or future
All points should include analysis of why it is a S, W, O or T.
Define the Growth stage of the business life cycle
The growth stage of a business is the movement of a business into either an established state or an expansion state. This means the business is either growing into new markets or is establishing its presence in the industry.
Identify the three marketing objectives in the growth stage.
Sales, Market Share, Brand Awareness
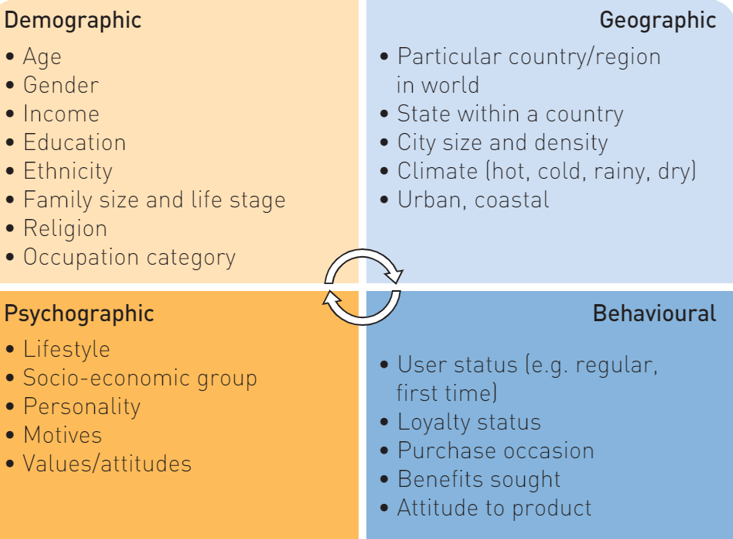
Identify the four segments of market segmentation used for target marketing
Behavioural segmentation
Geographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation
Why would a business trademark a product?
Intellectual Property (IP) Protection: During the growth stage, businesses must establish strong IP protection to avoid the risk of competitors copying their marketing strategies.
Risks of Not Trademarking: Without a trademark, businesses face legal and financial risks, including potential rebranding, lawsuits for IP infringement, and inability to stop copycats.
Identify two strategies to improve productivity
Training and developing employee skills
Boosting employee motivation
Updating technology and equipment
Efficiently managing inputs
Identify what needs to be done within synthesis.
1. Identify relationship/s, pattern/s and trend/s
2. Implications of the R, P, T on the business situation
3. Draw conclusions for what this means for the business overall
What is included in resource markets?
Resource markets include businesses that gather and sell raw materials, like agriculture, mining, and fishing.
What are the four main factors that influence consumer behaviour
Psychological factors
Socio-cultural factors
Economic factors
Government regulation
Define Target Market
A target market is a particular market segment(s) that a business focuses its marketing activities on.
Identify three key factors in determining the price of a product or service.
The type of product
Other products are known as speciality items
The cost of producing a unit
The ability of customers to pay
The demand for a product
The sensitivity of demand to price changes
Competitors
Pricing points
The objectives of the business
Capacity
The stage in the product life cycle
The rest of the marketing mix
Identify two areas of materials management that are important for a business
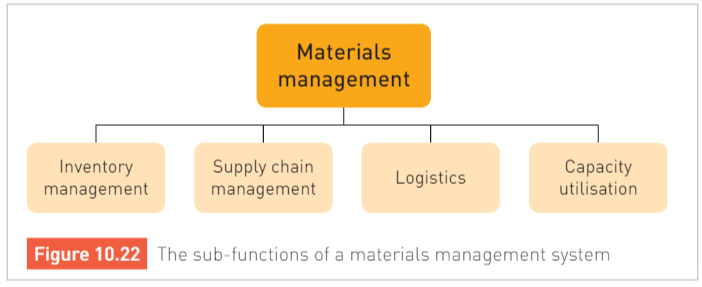
Identify what an evaluation response should include.
1. Strategy being evaluated
2. Criteria used for evaluation (efficiency, Effectiveness, Competitiveness and/or Stakeholder Satisfaction)
3. Thoroughly justified decision
4. appropriate recommendations
Identify two challenges a business may face in the growth stage.
Dealing with rapid growth
Avoid getting too comfortable in the market or overextending
Expanding into new markets that are too small to support all the competing businesses
Neglecting its current customer base in the pursuit of a new market or a larger market share.
Competition can come from businesses that are already in the new market or from new businesses entering the established market.
The owner relinquishing control of some areas to reliable staff, who will contribute to the business according to its goals and objectives.
Define brand loyalty
When consumers become committed to a brand and make repeat purchases.
What is the purpose of differentiation?
To make products stand out and give them a unique selling proposition.
Explain what personal selling is as a promotional strategy with an example.
A two-way communication process where the message can be tailored to the individual customer
Greatest strengths are the ability to immediately give feedback to consumers and the opportunity to build lasting relationships that can lead to repeat sales.
Provide a relevant example
Identify the three levels of quality management
Quality Control (QC)
Quality assurance (QA)
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Identify the factors of a PESTLE Analysis and what each point should include.
Political, Economic, Social Cultural, Technological, Legal, Environmental.
Each point should include explanation of the factor from the external environment and analysis of how this will impact the business.
What is the difference between a mass market and a niche market?
A mass market targets all consumers, while a niche market focuses on a small, specialized group.
What are 3 key aspects of a brand used in marketing
Name, Symbol, sign or design, colours, motto or tagline.
Identify three characteristics of two different market segments.
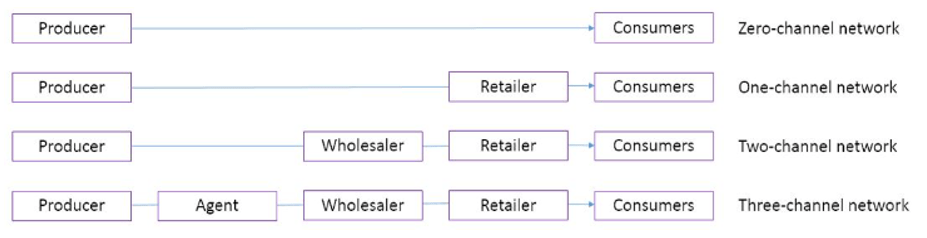
Provide 3 examples of different distribution cha
Explain the difference between quality control and quality assurance.
Quality Control (QC):
· Focuses on identifying defects in the final product.
· Involves inspection and testing to ensure products meet specified standards.
· Reactive process – aims to catch and fix problems after they occur.
Quality Assurance (QA):
· Ensures that processes are in place to prevent defects.
· Focuses on improving production processes to meet quality standards.
Proactive approach – aims to prevent problems before they arise.