Is this a longitudinal or transverse wave?
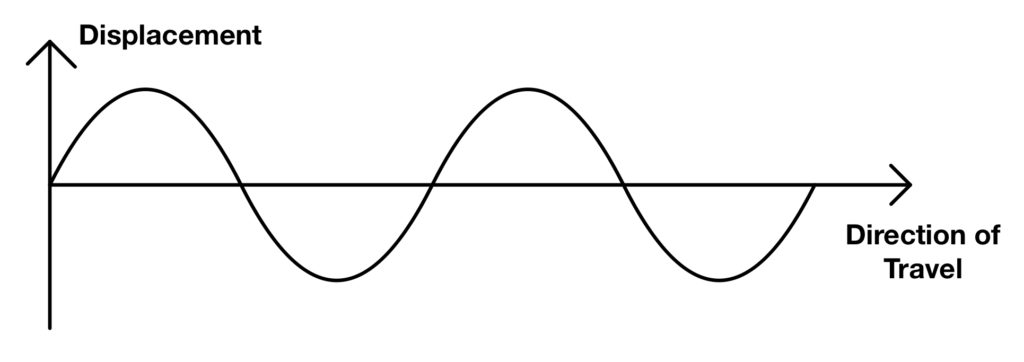
Transverse
Thinking of the kazoo lab, what happened to the sound as you lengthened the straw?
The pitch (frequency) got lower
Which kind of light has the longest wavelength?
Radio waves
What color of light does our sun mainly emit?
Green
Is sound a longitudinal or transverse wave?
Longitudinal
An organ pipe produces a musical note with a wavelength of 2.72 m. What is the frequency of this note if the speed of sound is 348 m/s?
128 Hz
Which kind of light has the highest energy?
Gamma waves
Wi-Fi routers use multiple channels, so not all the internet traffic is crammed in one lane.
What is the difference between these channels?
They have different frequencies
What is the amplitude of this wave?
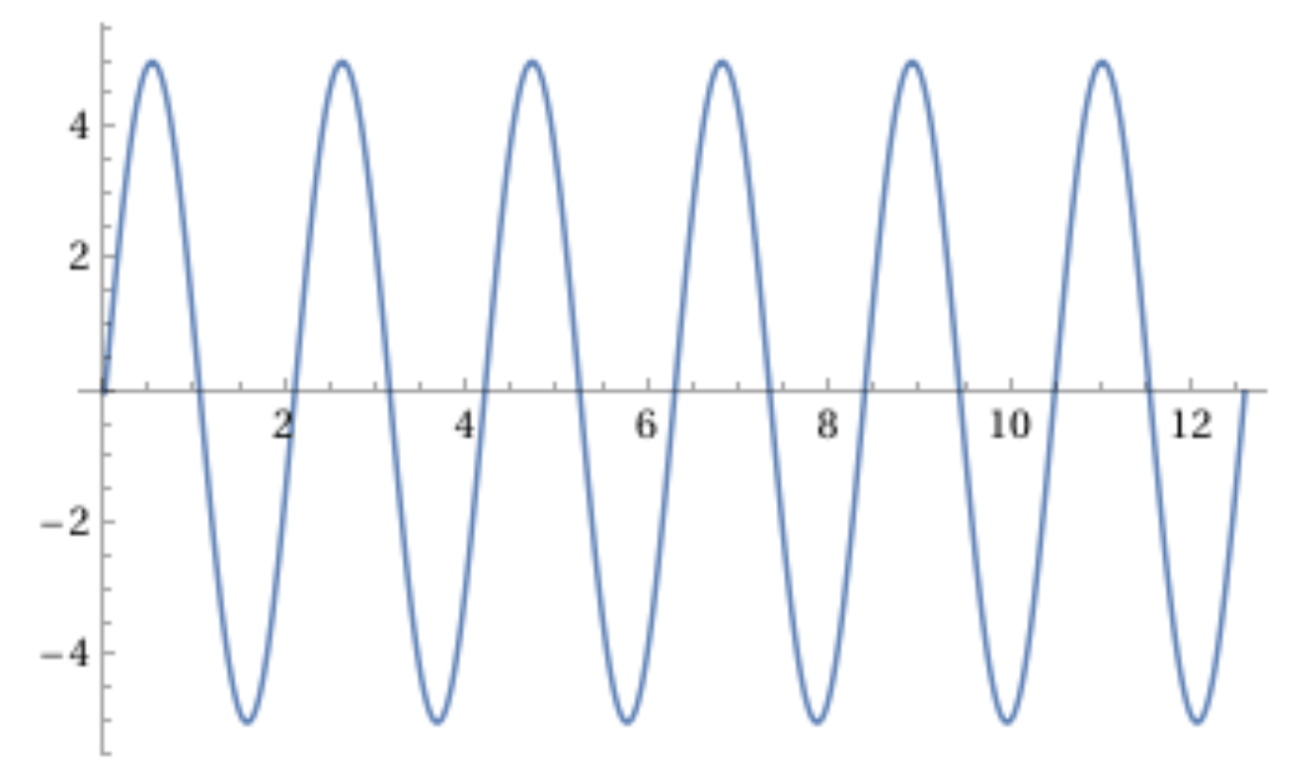
5
Which medium does sound travel best in (solid, liquid, or gas)?
Solid
True or false: All electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed
True
(speed of light is constant)
What is this called?
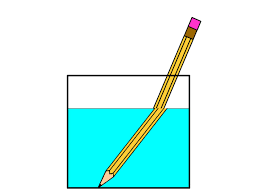
Refraction
(redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another)
What is the period of this wave? Assume the x-axis represents time.

About 2 seconds
Explain the Doppler effect of sound.
When a sound source or observer moves toward each other, the detected sound waves are compressed, leading to a shorter wavelength and a higher perceived frequency or pitch. Conversely, when they move away from each other, the waves are stretched out, resulting in a longer wavelength and a lower perceived frequency.
What kind of relationship do wavelength and energy have for the EM spectrum?
Inverse
What does this diagram represent?
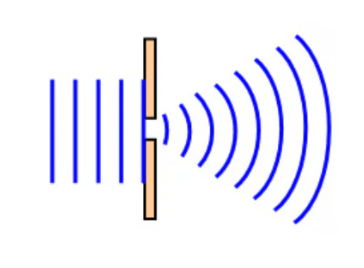
Diffraction
(waves bend or spread out as they pass around an obstacle or through a narrow opening)
What is the frequency of this wave? Assume the x-axis represents time.

0.5 Hz
How do noise canceling headphones work?
The headphones observe the ambient sound wave and then produce an anti-phase wave to counteract the sound through destructive interference.
Name all the kinds of light on the EM spectrum in order from lowest energy to highest energy.
Radio, Microwaves, Infrared, Visibile, Ultraviolet, X-ray, Gamma
Explain the Doppler effect of light.
When a source moves away, light waves are stretched, shifting to longer wavelengths and lower frequencies (redshifted); when it moves towards, waves are compressed, resulting in shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies (blueshifted).