Why are the knees bent for an AP lumbar spine projection?
To reduce the lordotic curve and place the spine in contact with the x-ray table.
What is a Salter-Harris fracture?
Growth plate fractures-fractures that occur through the epiphyseal plate (epiphysis-rounded end of a long bone)
What is Bronchiectasis?
Chronic dilation of the bronchi and bronchioles associated with secondary infection
What is pitch?
the ratio of the distance the table moves during one 360 degree rotation to the total beam collimation
In multislice total beam collimation is a section width that takes into account number of detectors and beam width
What type of transport may use a slider board?
Stretcher transport
The body part that is perpendicular to the CR for a PA axial intercondyloid fossa projection
What is the tib-fib?
What is the medical term for free air seen under the right hemidiaphragm on an erect AP abdomen projection?
Pneumoperitoneum
Name one structure associated with the mediastinum.
heart, great vessels (Aorta, SVC, pulmonary arteries), trachea, esophagus, thymus, lyphatics, nerves, fibrous tissues and fat
Borders of mediastinum: sternum anteriorly, spine posteriorly and lungs laterally.
The special elements in the design of CT tubes is for what 2 reasons?
Increased heat capacity and heat dissipation
When spine has been cleared by a physician.
What is the name of a unilateral hip projection where the abducted leg is parallel to the table?
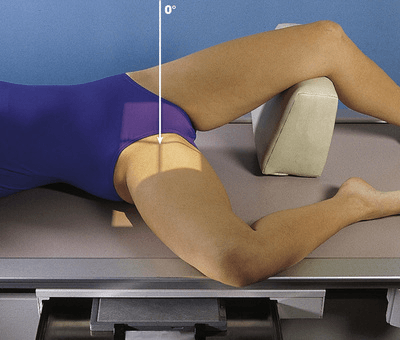 Lateral Hip (Lauenstein method)
Lateral Hip (Lauenstein method)
This is different than the frog leg which is called AP frog leg according to CAMRT comp profile (AP oblique modified cleaves according to Merrills)
What is a glioma?
The most common type of primary malignant brain tumor
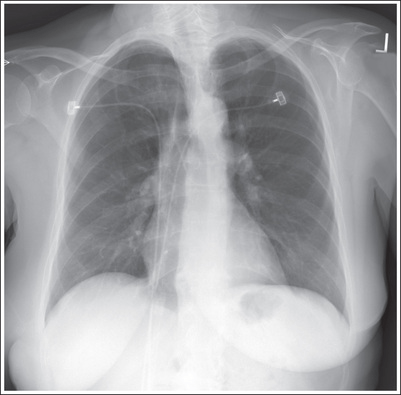
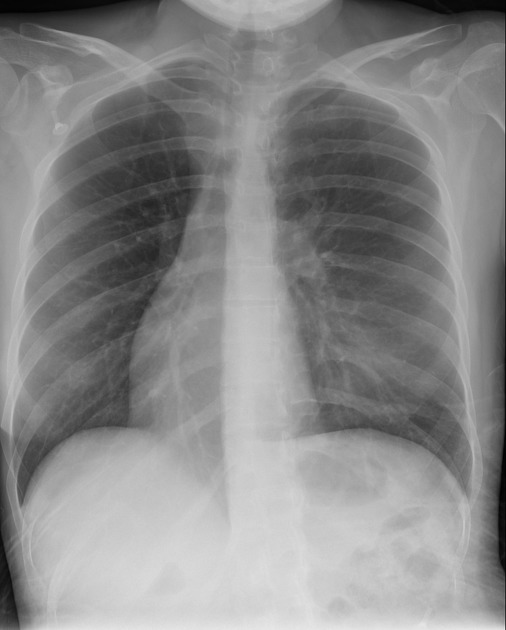
What issue if any is seen on this PA chest projection?
What structure is indicated by "T" on this image? 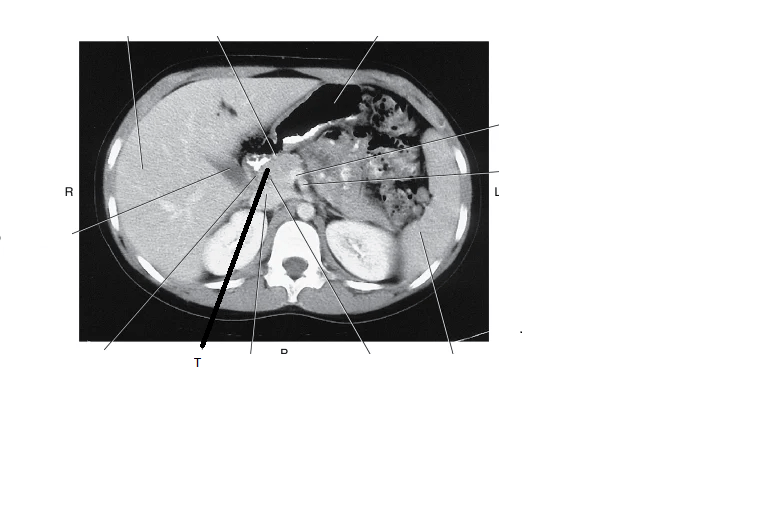
Head of the pancreas
What is the most appropriate oxygen administration device to provide a patient with 100% oxygen?
A nonrebreathing face mask 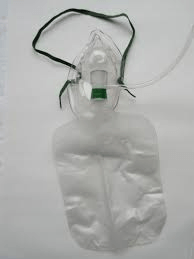
What adjustment to the CR can be made for the lateral cervicothoracic (Swimmers/Twinning projection) if the patient has limited ability to depress their shoulder?
3-5 degree caudal angle.
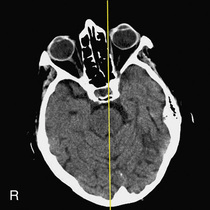
 What pathology is seen on this image?
What pathology is seen on this image?
Case courtesy of Dr Henry Knipe, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 55795
Dextrocardia
Where should the cathode of the x-ray tube be placed for an AP portable/mobile chest projection?
Inferior chest/diaphragm (thickest part) due to anode heel effect which is more pronounced with short SID, large field size and small anode angles
What positioning issue is seen here?
Head Rotation towards the right
What is your first response when while doing an PA chest x-ray, your patient collapses seemingly unconscious to the floor?
"Shake and Shout"
(first rule of first aid-may be a fainting, may be something more serious)
How should the CR be adjusted for a plantodorsal axial of the calcaneus if the patient cannot dorsiflex well?
Increase CR until it alignes with 5th MT and point of fibula (MQM)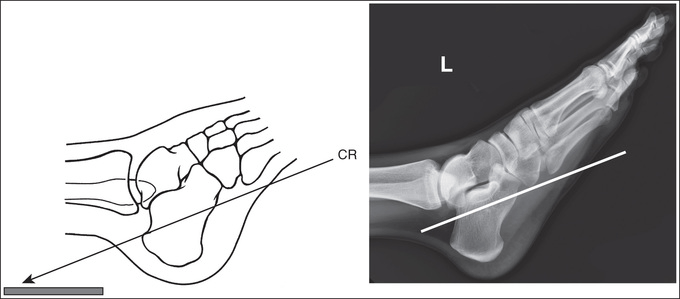
What urinary pathology is seen on this image? 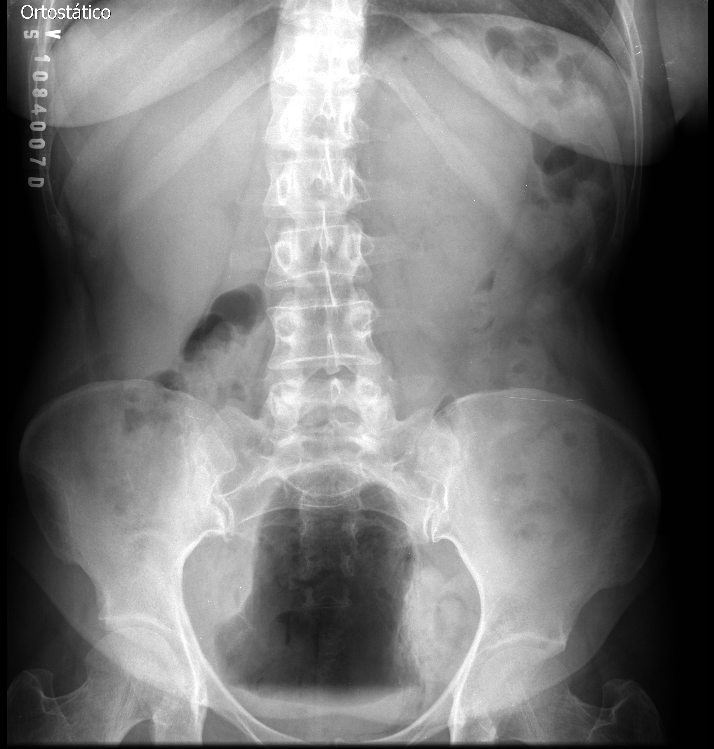
Cystitis (air seen in bladder is primary indicator)
Case courtesy of Dr Augusto César Vieira Teixeira, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 23558
What is the function of a Swan-Ganz or Pulmonary Arterial Catheter in an ICU patient?
Measures arterial pressures, pulmonary artery pressure and cardiac output. It is supposed to be placed in the main pulmonary artery/trunk 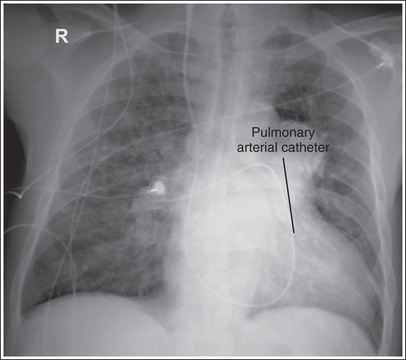
What type of cardiac CT scans the heart continually and generates image after the scan using the ECG data aquired?
What is your first priority when a patient in your care is experiencing a seizure?
Keep them safe, then when safe to do so, call for help.