Which chamber of the heart forms the apex?
Left ventricle

What is the inner lining of all blood vessels called?
Endothelium

What event creates the first heart sound (S1)?
Closure of the AV valves
Why is a smooth, intact endothelium important for normal blood flow in vessels?
Because it reduces friction and prevents unwanted clot formation.
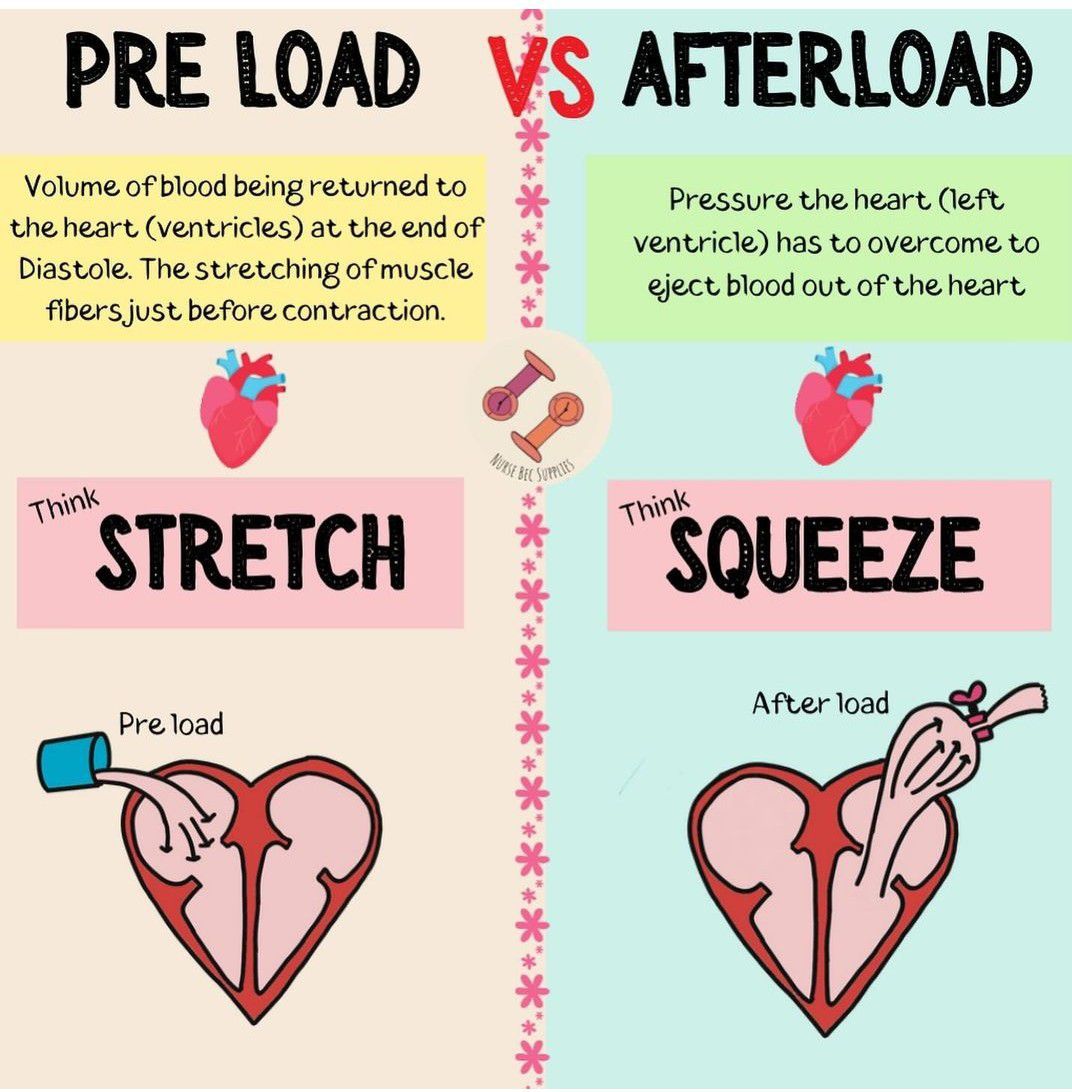
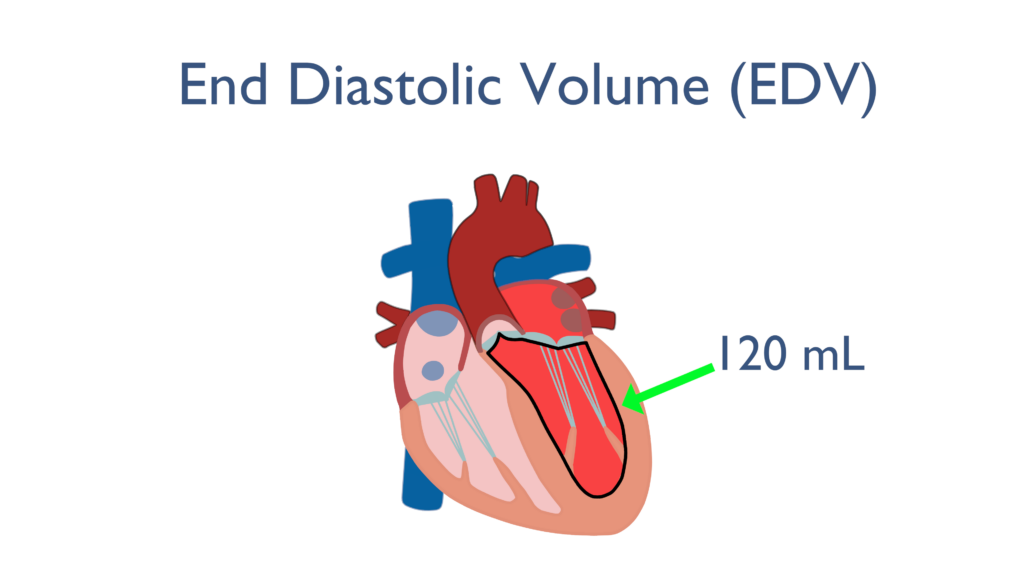
Define preload?
the volume of blood in a heart ventricle at the end of the relaxation phase (diastole) of the cardiac cycle

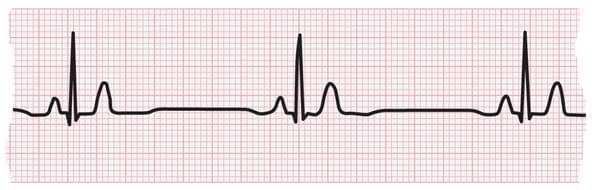
What electrical event does the P wave represent?
Atrial depolarization

What structure separates the right and left atria?
Interatrial septum
What is the innermost layer of a vessel wall?
Tunica intima

What event creates the second heart sound (S2)?
Closure of the semilunar valves
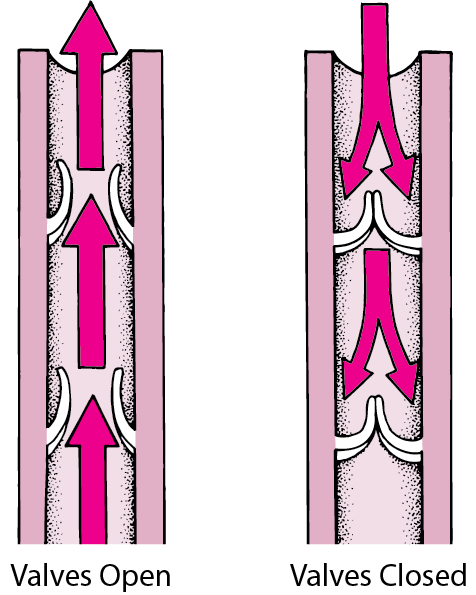
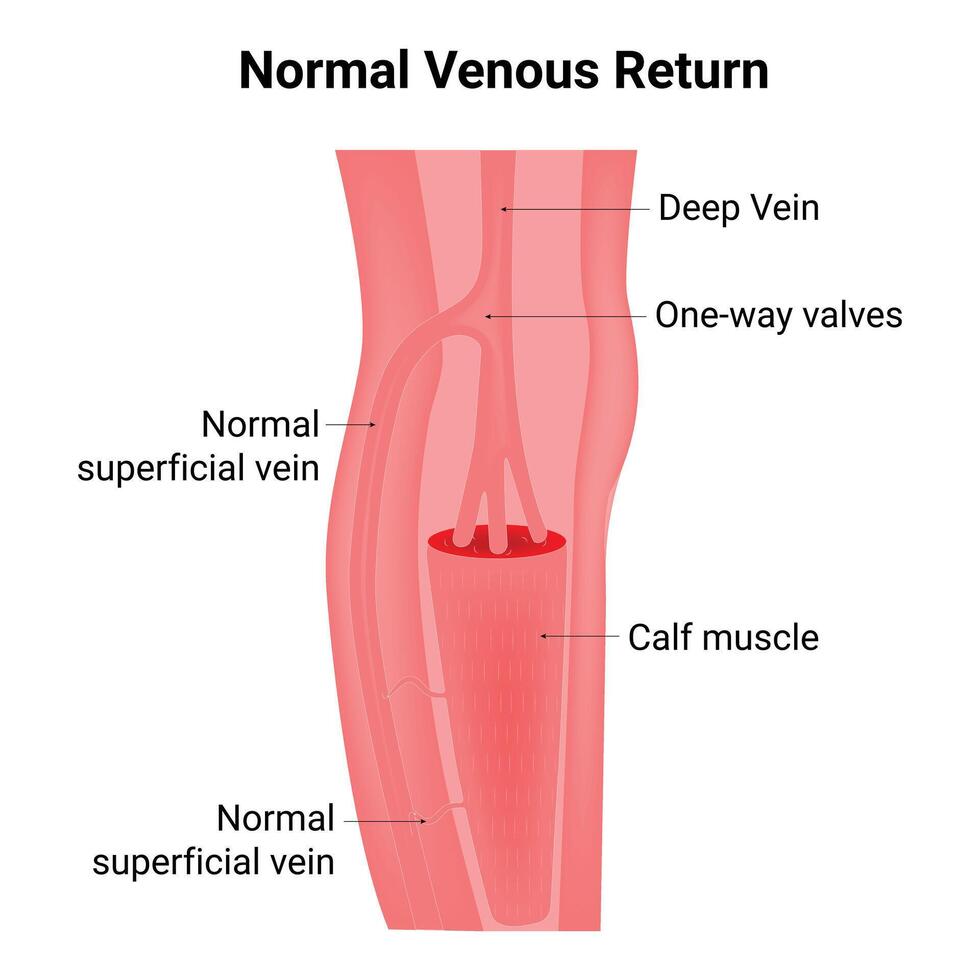
What mechanism helps move blood through veins in the legs when you’re standing or walking?
the skeletal pump

What is ejection fraction (EF)?
The percentage of EDV ejected with each beat

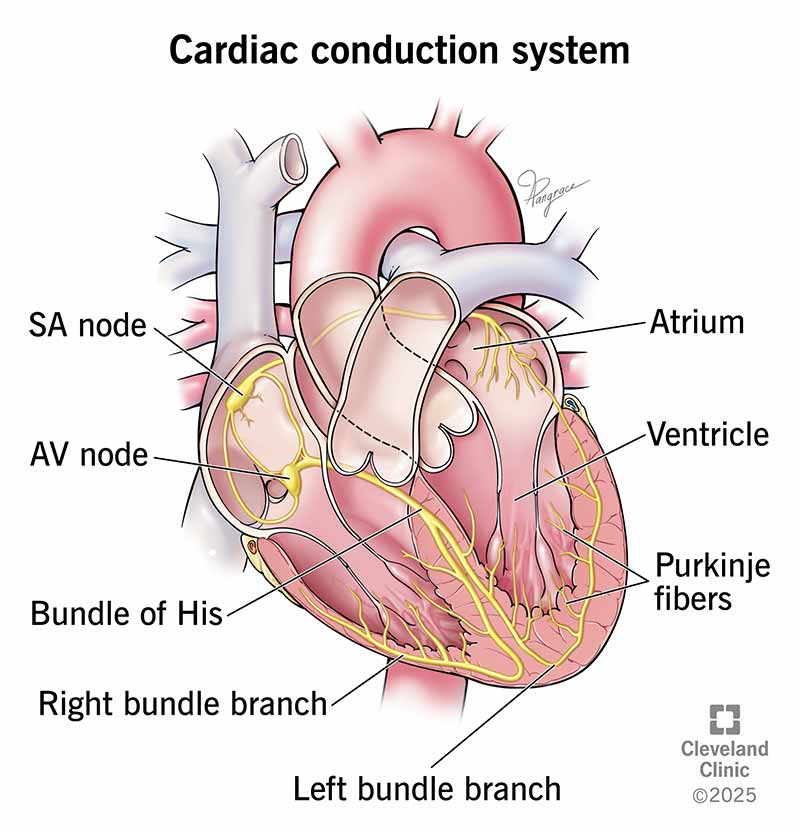
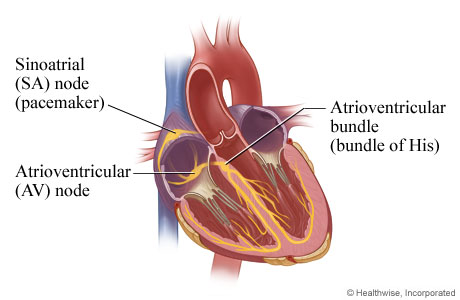
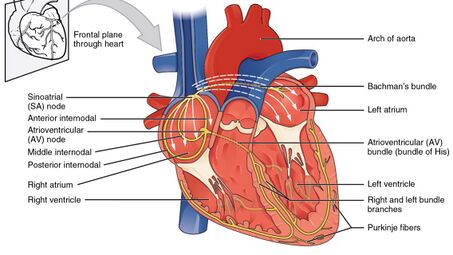
What conduction structure initiates the electrical impulse that starts each heartbeat?
SA node
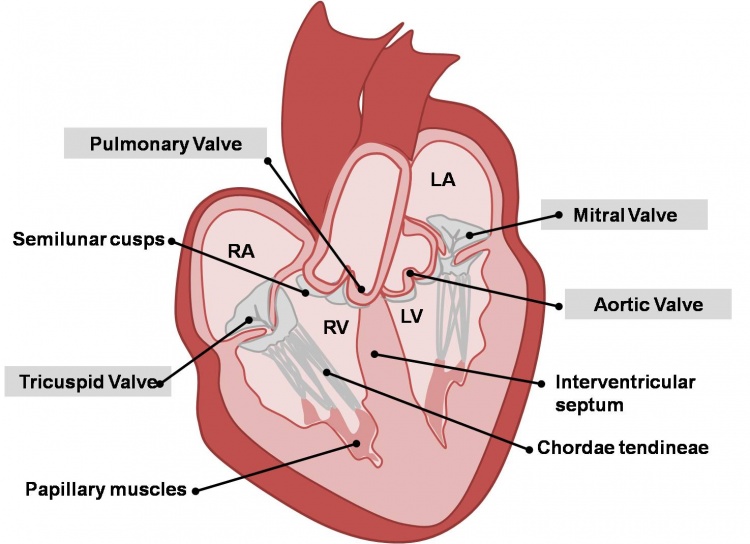
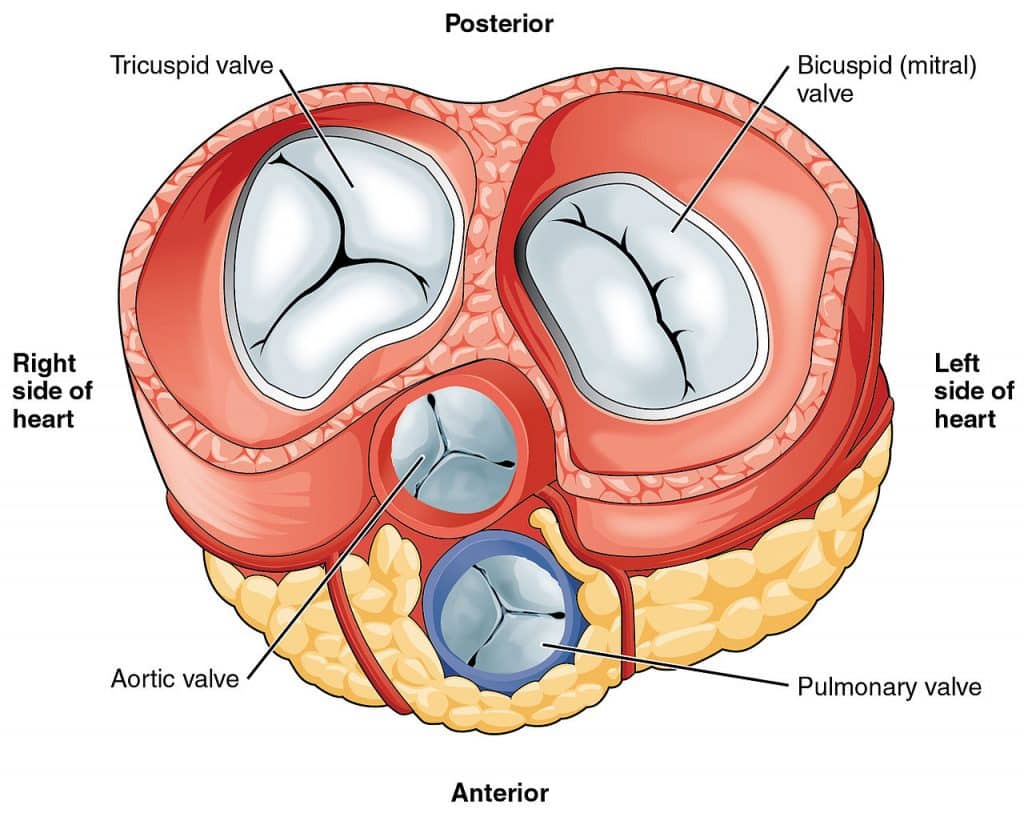
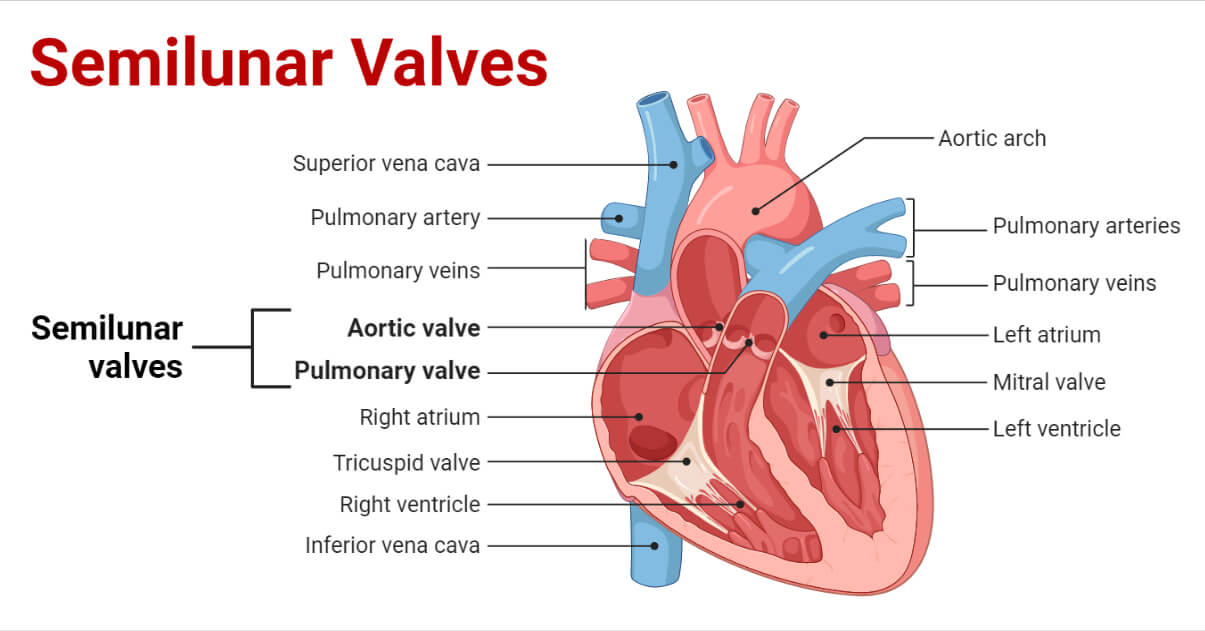
Which valve guards the opening from the right ventricle to the pulmonary trunk?
Pulmonic semilunar valve
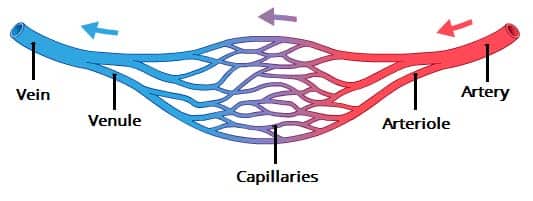
What vessels contain valves to prevent backflow?
Veins
During which phase are the ventricles filling with blood?
Diastole
What type of artery helps dampen the pulse pressure from the heart?
Elastic arteries

What is end-diastolic volume (EDV)?
The volume of blood in a ventricle at the end of diastole.
What electrical event does the QRS complex represent?
Ventricular depolarization

Which valve is located between the right atrium and right ventricle?
Tricuspid valve

What vessels return oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart?
Pulmonary veins

Which ventricle generates higher pressure?
The left ventricle
What is the term for the ease with which a vessel can expand?
Compliance

What is afterload?
The pressure the ventricle must overcome to eject blood
Which part of the heart produces the slowest intrinsic heart rate if it becomes the pacemaker?
The ventricles
What structure separates the right and left ventricles?
Interventricular septum
What type of artery has many elastic fibers in its wall?
Elastic arteries
What part of the heart normally sets the heart’s pace?
SA node
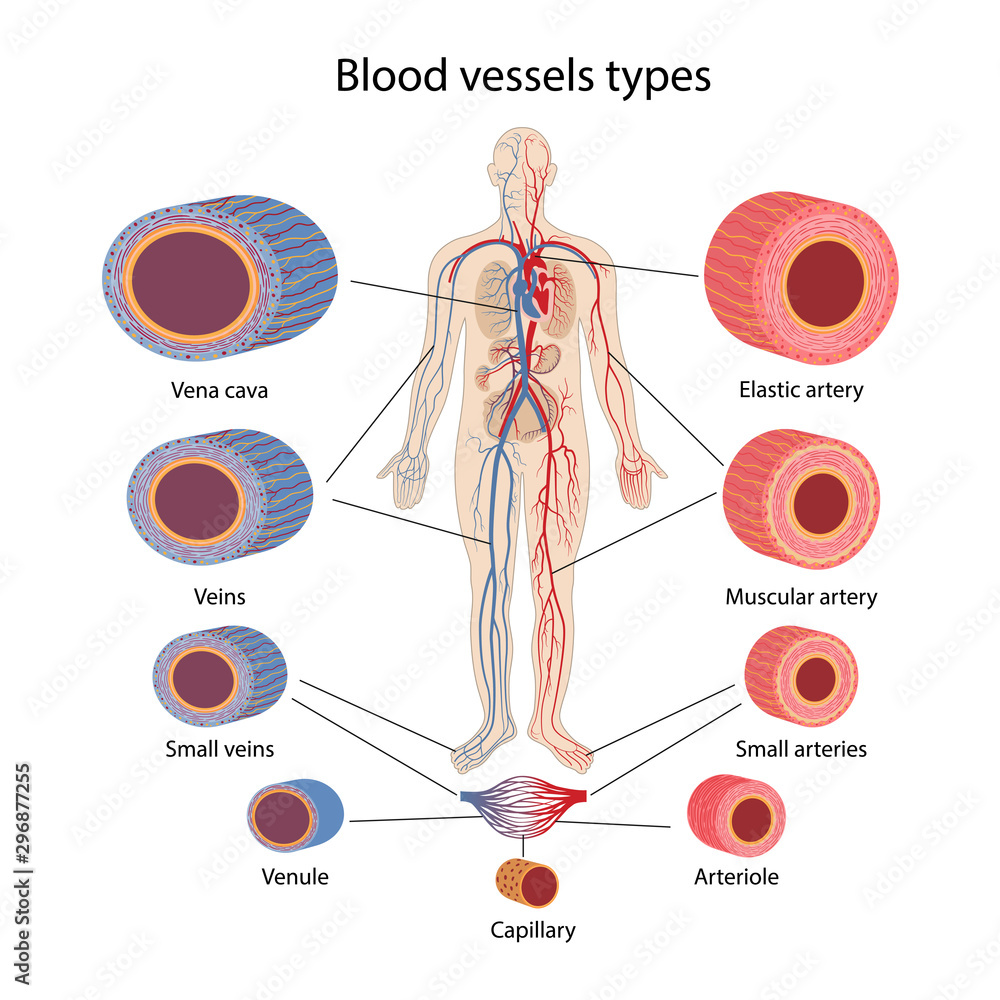
Draw each of the following blood vessels and label one structural feature of each: arteriole, venule, capillary, artery and vein. Also explain why this is true
artery, arteriole, capillary, venule, and vein this system buffers delicate vessels from high pressure
This is the volume of blood that returns to the heart each minute.
What is venous return?
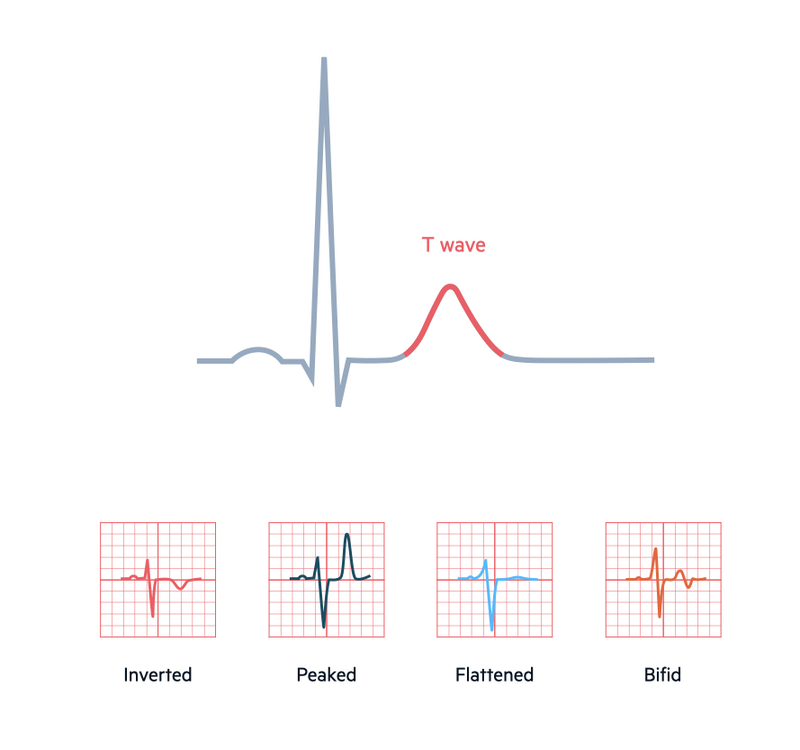
What electrical event does the T wave represent?
Ventricular repolarization
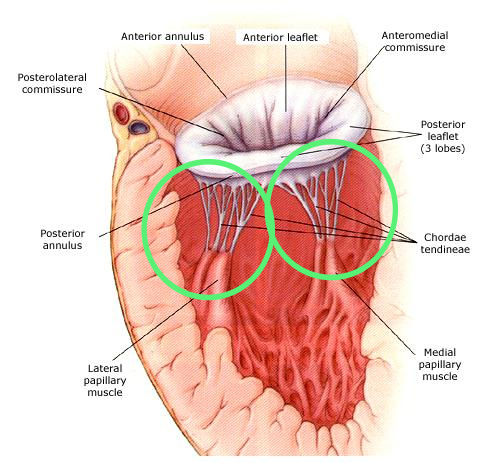
What thin strands attach AV valve leaflets to papillary muscles?
Chordae tendineae
What major artery leaves the right ventricle?
Pulmonary trunk (pulmonary artery)

What does increased sympathetic stimulation do to heart rate?
It increases heart rate
What force pushes fluid out of capillaries into tissues?
Capillary hydrostatic pressure

What is cardiac reserve?
The difference between resting cardiac output and maximal cardiac output

What fibers rapidly transmit impulses throughout the ventricles?
Purkinje fibers
“Draw the path of blood as it travels through the heart and lungs.” Your drawing must include:
Superior vena cava, Inferior vena cava, Right atrium,
Tricuspid valve, Right ventricle, Pulmonic valve, Pulmonary arteries, Lungs, Pulmonary veins, Left atrium, Mitral valve, Left ventricle, Aortic valve, Aorta

What are the small vessels that supply blood to the walls of large arteries and veins?
Vasa vasorum

What ion is most important for cardiac muscle contraction?
Calcium

Which vessels hold most of the body’s blood volume at any given time? and why?
Veins and compliance

Heart rate × stroke volume gives you which value?
cardiac output

“Why does a wave on the EKG move upward (positive) in some leads?”
Because the electrical impulse is traveling toward that lead’s positive electrode.