These vessels become filled with blood and are visible to the naked eye in right-sided heart failure
What is JVD?

Located in the right atrium, this is in charge of "setting the pace" of normal heart conduction
What is the Sinoatrial Node (SA)?
The nurse anticipates this laboratory marker to be elevated in patients with heart failure
What is Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP)?
What is the normal range?
Why else may BNP be elevated?
This medication class works by blocking β-adrenergic receptors, thus it decreases cardiac output. It is indicated for HF and HTN
What are beta blockers?
What vital signs should warn the nurse to hold this medication?
This eating plan is prescribed for patients with HTN. It consists of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, poultry, fish, and low-fat milk
What is the DASH Diet?
What does it stand for?
This modifiable risk factor contributes to the development, progression, and death attributed to peripheral artery disease.
What is smoking?
Located at the 5th intercostal space at the mid-clavicular line, this area is where you auscultate for which heart sound?
What is Mitral or Apical pulse? Also called point of maximum impulse (PMI)

What is sinus tachycardia?
What is the rate?
What are the causes?
The nurse is taking orthostatic vital signs. This change in vitals means the patient has orthostatic hypotension.
What is a drop of 20 mm Hg in SBP and/or rise in HR of 20 BPM?
These two medications are given to reduce platelet clumping and are used for CAD, stent maintenance, and PAD
What is Aspirin and Clopidogrel?
The nurse should caution patients to cease taking these medications if they experience muscle cramping.
What are statins?
What labs do we follow for patients taking these medications?
The nurse instructs the patient with aplastic anemia that they are at high-risk for this condition.
What is infection?
Nurse measure this daily to assess improvement in a patient's fluid status when they are experiencing heart failure
What are daily weights and intake and output?
This waveform represents ventricular depolarization
What is the QRS complex?
The nurse informs the patient to do this if chest pain remains after taking three nitroglycerin tablets
What is call 911?
This medication works in the Loop of Henle in the kidney and is used commonly for heart failure
What is furosemide (Lasix) or bumetanide (Bumex)?
What electrolyte should you monitor closely with this medication?
The nurse is teaching a patient about iron supplementation. The nurse informs the patient that this is a major side-effect of taking oral iron.
What is constipation?
What is teeth staining?
What are black stools?
These are measures (modifications) for a healthy lifestyle that can reduce HTN (must name three).
What are smoking cessation, sodium reduction, weight reduction, physical activity, and stress reduction?
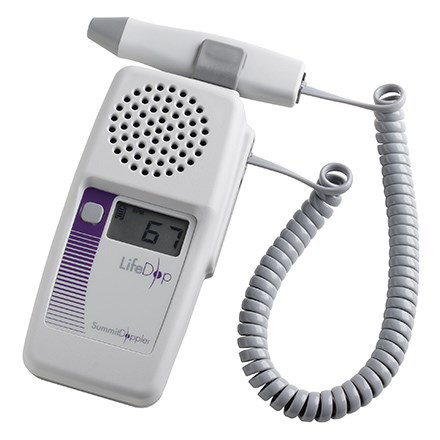
The nurse uses this bedside device to assess distal pulses in a patient with peripheral arterial disease
What is a doppler?

What is atrial fibrillation?
What is the rate?
What are the treatments?
The nurse knows to do this when a patient is experiencing angina with physical exertion
What is rest?
Patients should not combine this medication with sildenafil.
What is nitroglycerin?
A patient has just returned to the floor from having a pacemaker placed. The nurse should include this specific activity-restricted instruction in her teaching.
What is not lifting the arm above shoulder level on the affected side?
The nurse teaches about these complications of untreated HTN to patients (must name three)
What is CAD, HF, Stroke, PVD, Kidney failure, and retinal damage?
Nurses assess these after a patient returns from having a cardiac cath (must name at least TWO)
What are: Distal pulses, cardiac monitor/rhythm, vital signs, puncture site, capillary refill, color/temp of extremity?

What is ventricular tachycardia?
Name two types of VT
What are the treatments?
These letters (and their definitions) represent how nurses assess anginal pain
What is PQRST?
P-Precipitating events
Q-Quality of pain
R-Region/Radiation
S-Severity (0-10)
T-Timing
This positive inotrope increases cardiac contractility and can reach toxic levels when serum potassium levels are low.
What is digoxin?
What does toxicity look like?
A patient presents with elevated INR levels of 8. The nurse teaches the patient that she might be treated with this medication to reverse the effects of warfarin.
What is Vitamin K?
What foods are rich in Vitamin K?
The nurse should teach a patient that smokes and takes oral contraceptives that they are at high risk for this disease.
What are deep vein thromboses (DVT)?