These are one consideration for TISSUE valve replacement and one consideration of MECHANICAL valve replacement.
What is the following?
-TISSUE lasts up to 20 years
-MECHANICAL requires life-long anticoagulation
The equation for cardiac output.
What is the following?
Cardiac Output = Heart Rate x Stroke Volume
Frequency of epicardial wire dressing care.
What is every 2 days and PRN?
This complication is when a large amount of fluid accumulates around the pericardium after epicardial wire removal.
What is cardiac tamponade?
This is when pacemaker settings need to be verified by a nurse.
What is the beginning of every shift, during bedside shift report, and with any changes in patient condition?
Procedure in which surgeon removes part of the thickened septum between the ventricles.
What is a septal myectomy?
This valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle.
What is the mitral valve?
Prior to transfer to 6E or 6E PCU, this must be removed and a cap placed on the RIJ Introducer (Cordis).
What is the Single Lumen Infusion Catheter (SLIC)?
This is when should chest tube output be concerning following cardiac surgery.
What is greater than 100ml/hr or a sudden decrease in output?
Procedure requires the placement of a lumbar drain to monitor perfusion to the spinal cord.
What is a Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair (TEVAR)?
The blood vessel that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs.
What is the pulmonary artery?
These are three things you would teach a new nurse caring for a patient with a fresh sternal incision.
What are the following?
-No tegaderm on incision
-No creams or ointments should be placed on incision
-Dressing to be removed on POD #2 and should only be replaced if drainage is present
-Dermabond should remain in place ~ 14 days and staples will be removed at post-op appointment
-Hand hygeine!
In the event a cardiac surgery patient requires resuscitation, these should be brought to the bedside.
What is the code cart and the open chest cart?
In this mode, when a QRS complex is sensed a ventricular beat is inhibited.
What is VVI?
What are increased risks post-operatively of the following?
Excessive bleeding
Pleural effusions
Phrenic nerve injury d/t pleurotomy
Prolonged pain (> 3 months)
Risk of Deep Sternal Wound Infection (DSWI)
This is the filling pressures of the ventricles at the end of diastole.
What is preload?
What should be infusing through the RIJ Introducer (Cordis) at all times.
What is minimum of 10 mL/hr KVO?
These labs should be monitored if concern of bleeding is suspected.
What is hemoglobin, hematocrit, and coagulation labs?
The is the 3-letter code for the temporary pacemaker's emergency mode.
What is DOO?
Procedure indicated for patients with both an aortic root aneurysm and subsequent aortic valve issues.
What is a Bentall Procedure (Aortic Root Replacement with Composite Valved Graft)?
This is cardiac output adjusted to individual body size.
What is cardiac index?
Requirements following epicardial wire removal.
What are VS and cardiac tamponade symptom assessment Q15 min x 1 hour, bedrest x1 hour, and cannot be transported off unit or to a lower level of care for four hours?
Immediately following cardiac surgery, this medication for the treatment of stroke is contraindicated.
What is tenectaplase?
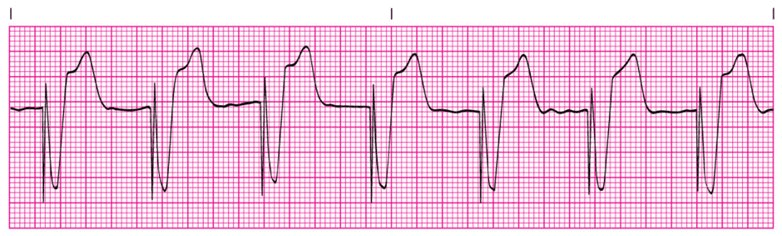
What is VVI?