A 48-year-old woman with a history of hypercholesterolemia is referred to the cardiologist because of activity-induced chest pain. She describes chest tightness that develops after walking several blocks and is relieved with rest. The physician prescribes tablets that the patient is to place under her tongue during episodes of chest pain.
At low doses, this medication likely ________ preload and _________ myocardial oxygen demand
Decreases preload, decreases myocardial oxygen demand
67
A 26-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine checkup. The patient has no complaints. Pulse is 73/min, respirations are 12/min, and blood pressure is 120/78 mm Hg. Upon seeing the needle for a blood draw, the patient says he suddenly feels lightheaded and nauseated. The staff offers reassurance. The patient wishes to proceed but passes out when the blood draw begins. The patient is laid flat on the table. Pulse is now 52/min, respirations are 13/min, and blood pressure is 100/73 mm Hg. The patient regains consciousness within a few minutes.
This stimuli would most likely induce a pattern similar to the patient’s central nervous system activity after seeing the needle but under normal circumstances
Carotid massage
73
Infective endocarditis is commonly caused by these three bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus, viridans streptococci, and enterococci.
A 64-year-old woman comes to the clinic because of progressive shortness of breath and fatigue. She had frequent streptococcal throat infections as a child and has a history of a heart murmur. On physical examination, a heart murmur is detected. The ECG shows left atrial enlargement.
The heart murmur this patient most likely has can be described as
Mid-diastolic rumble with an opening snap at the apex
69
A 56-year-old man comes to the office because of chest tightness that worsens with exertion and is relieved by rest. His previous medical history is significant for coronary artery disease. His vital signs and physical exam are normal. He is prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin and metoprolol.
An explanation of the benefit of metoprolol for this patient.
Reducing the heart rate lengthens the duration of diastole, increasing coronary artery filling
78
A 57-year-old man comes to the office to establish care. He has no known medical history or prior surgeries. Pulse is 72/min and blood pressure is 145/93 mm Hg. Laboratory testing reveals a hemoglobin A1c of 6.9% and microalbuminuria. The patient is diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and is informed of a medication that can reduce his blood pressure and slow the damaging effects of diabetes on his renal and cardiovascular systems.
This is the most likely adverse effect of the medication.
Hyperkalemia
64
A 68-year-old man presents with acute-onset right-arm weakness and facial droop. His medical history is significant for hypertension. On physical examination, the physician notes hemiparesis and decreased sensation of the right upper extremity and lower face. The patient has normal cardiac auscultation except for an irregular rhythm with a rate of about 130 beats/min. Serum troponin is normal. The ECG is shown. A thromboembolic event is suspected.
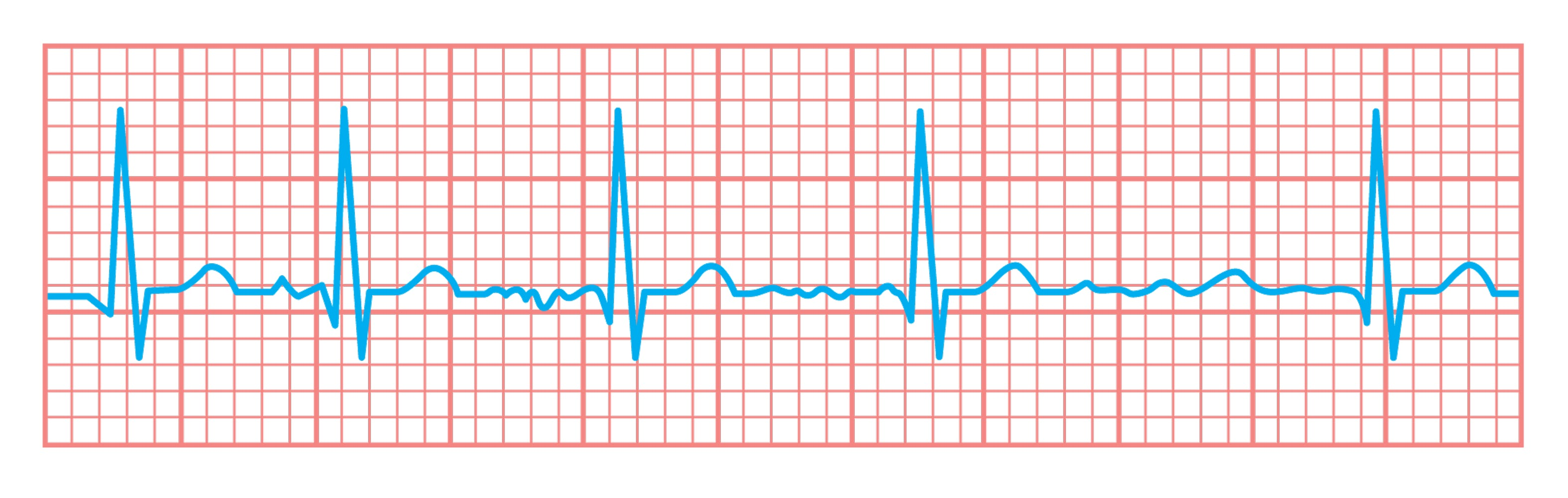
The embolized thrombus likely originated from this structure.
Left atrial appendage
64
A 17-year-old boy comes to his physician because of recurrent bouts of dizziness and palpitations. Six weeks ago, he had a red rash on his trunk, and he has had fatigue and intermittent joint pains in the intervening days. He is previously healthy. A cardiac rhythm strip is shown.
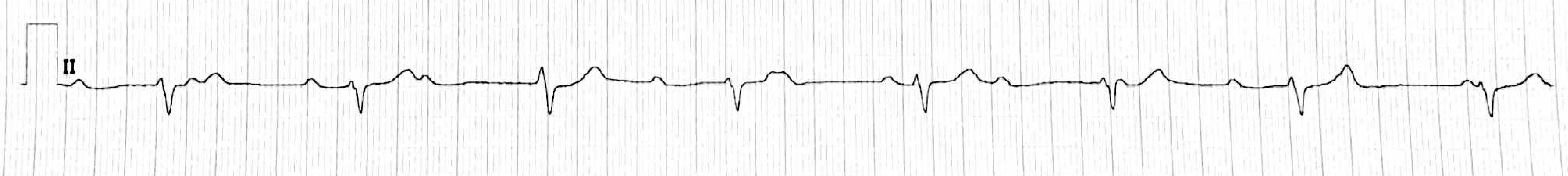
This is the most likely diagnosis
Lyme Disease
63
A 2-week-old premature boy is examined in the neonatal intensive care unit. His mother recently immigrated to the United States, has never received immunizations, and did not receive any prenatal care. Physical examination of the infant discloses a wide pulse pressure and a continuous murmur. Echocardiography shows the continued presence of a structure derived from the 6th aortic arch.
The child's condition is likely caused by an infection during pregnancy involving this pathogen.
A positive single-stranded RNA virus of the genus Rubivirus
62
A 31-year-old woman comes to the clinic reporting urinary frequency and weight gain that began after a psychiatric episode for which she was hospitalized for bipolar disorder 3 months ago. During her hospitalization, she began drug treatment, and her symptoms eventually resolved. She now plans to become pregnant with her partner. Physical examination reveals an enlarged thyroid gland and a mild tremor in her hands.
If this patient became pregnant while taking her current med, this is the likely fetal abnormality.
Ebstein anomaly
71
A 57-year-old man comes to the physician because of flushing that lasts 20 to 30 minutes after he takes his new lipid-lowering medication. He began taking this drug 6 months ago as an adjunct to a first-line agent started a year ago that did not adequately control his LDL cholesterol level. Today, his laboratory values show low total cholesterol, low LDL cholesterol, and significantly higher HDL cholesterol concentrations.
The new adjunct medication is likely affecting his laboratory values by
Reduced hepatic triglyceride and VLDL cholesterol synthesis
52
A 65-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of chest pain and difficulty breathing. He is diagnosed with an acute inferior wall ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and quickly taken for percutaneous coronary intervention, which is successful. Eighteen hours later, he is stable and comfortable with normal vital signs and physical examination. Ten minutes later he becomes pulseless and unconscious. An ECG is shown.
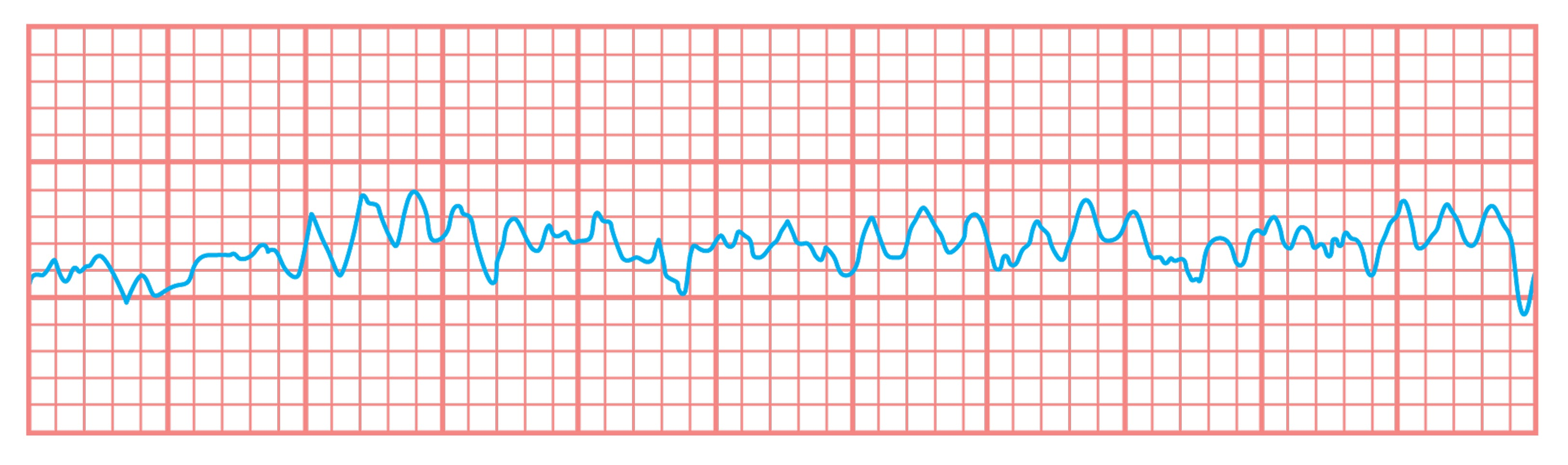
Which of the following could be the most likely mechanism for the patient’s abnormal ECG?
Reentrant circuits
57
A 45-year-old woman comes to the clinic with 1 week of fever, abdominal pain, and “tripping” with her left foot. She has a history of injectable drug use. Temperature is 38.7°C (101.6°F) and blood pressure is 170/110 mm Hg. Physical examination reveals cachexia with diffuse abdominal tenderness and tender erythematous skin nodules on the lower extremities. There is weakness of left foot extension and numbness on the left foot dorsum. Serum and blood studies show:
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN): 67 mg/dL
Creatinine: 3.4 mg/dL
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR): increased
Antinuclear antibody (ANA): negative
Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA): negative
Hepatitis B surface antigen: positive
Hepatitis B core antibody: positive
This is patient's likely disorder originated from this disease process.
Type III Hypersensitivity
52
A 56-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 30 minutes after slicing his arm while chopping wood, leading to significant blood loss. His blood pressure is 92/58 mm Hg. On examination, he appears lethargic and pale. His extremities are cool to the touch.
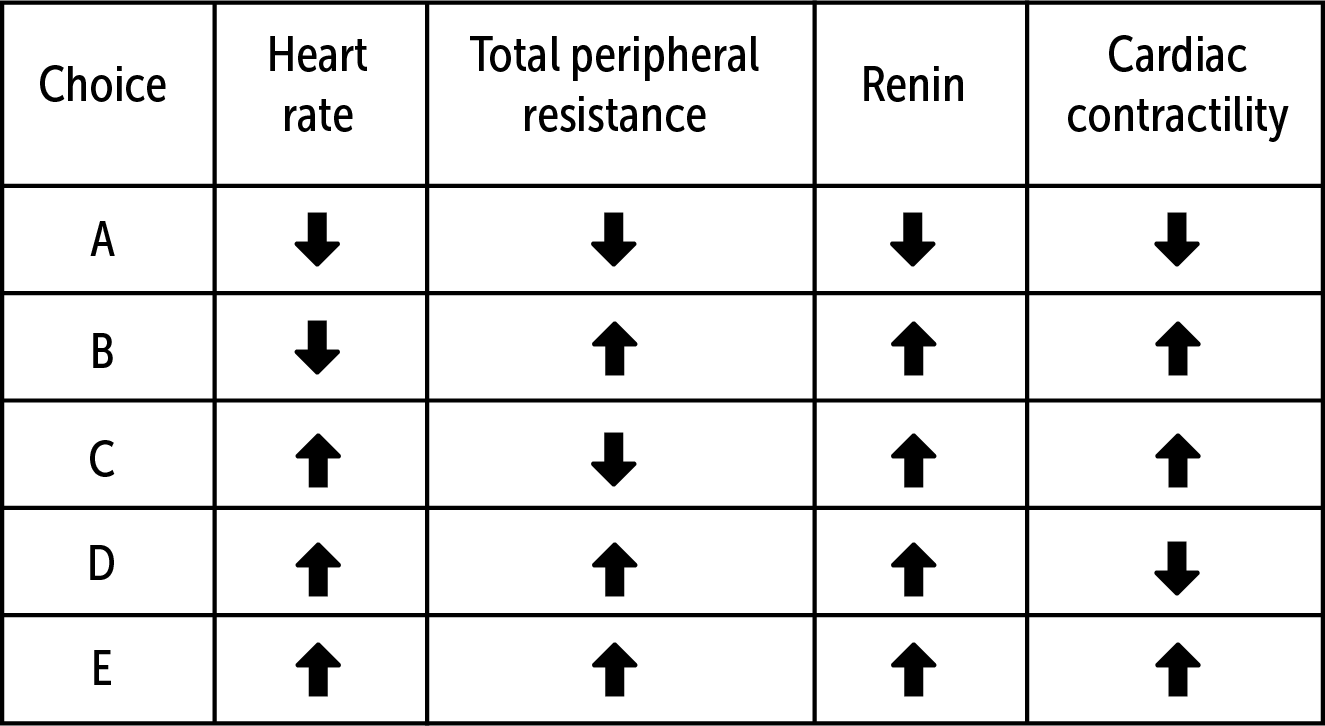
These are the set of findings that represent the body’s physiologic reaction within the first 30 minutes of this patient’s injury
E
60
A 67-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of diaphoresis and crushing chest pain that radiates down his left arm. Pulse is 55/min and blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg. An ECG is shown. The troponin I level is 7.1 ng/mL.
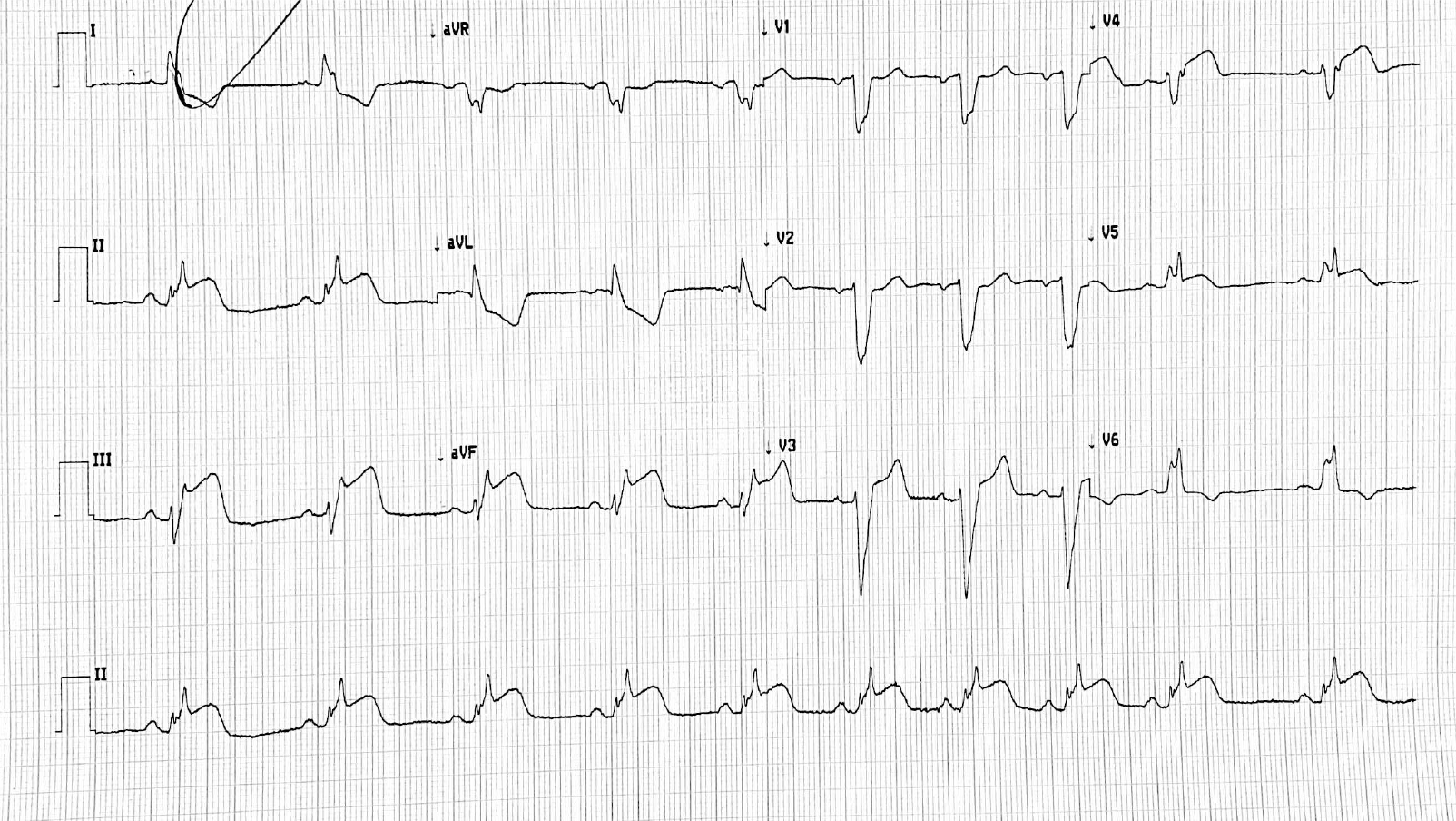
The patient's symptoms are likely caused by occlusion of this structure.
Right Coronary Artery
61
A 68-year-old man with a history of hypertension comes to the emergency department because of palpitations and lightheadedness for the past 5 hours. On physical examination, the patient has an irregularly irregular pulse. ECG findings are shown. Blood pressure is 165/95 mm Hg.
The most appropriate drug for the long-term management of this patient’s condition is
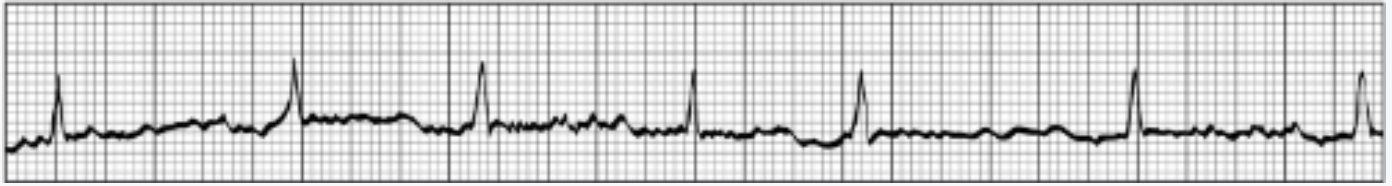
Rivaroxaban
41
A researcher is investigating the metabolic mechanisms responsible for controlling dilation and constriction of the coronary arteries. He takes blood samples from the coronary arteries of mice and analyzes the metabolites. He then compares the samples to those of mice that have been engaged in strenuous physical activity for more than 10 min. His study of the findings assumes the physiology of mice is similar to that of humans.
Findings is most likely seen in mice undergoing physical activity
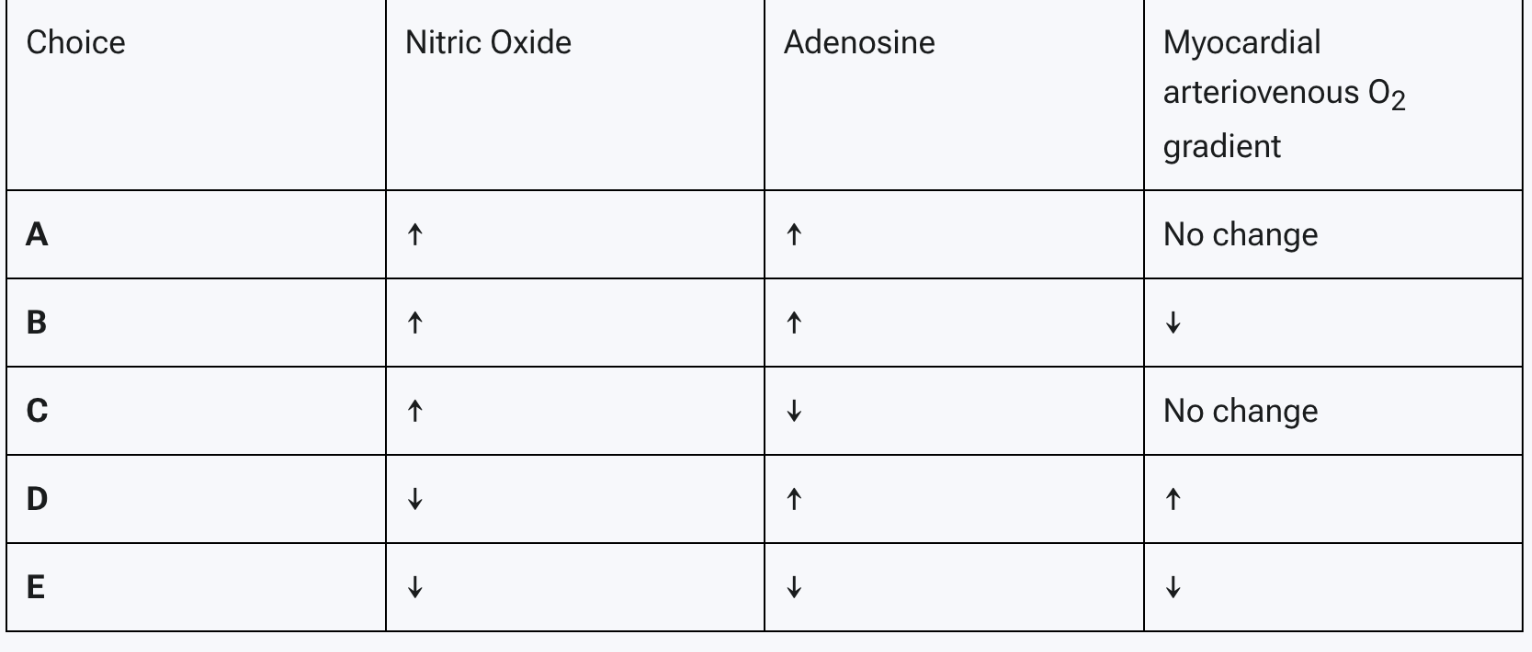
A
46
A 67-year-old man comes to the clinic because of 3 days of fever and malaise. He has end-stage renal disease and undergoes dialysis three times per week. Temperature is 38.2°C (100.8°F), pulse is 76/min and regular, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 134/78 mm Hg. Cardiac examination discloses a new late-systolic crescendo murmur with a pronounced mid-systolic click. Blood cultures are positive.
This describes the most likely causative pathogen in this patient.
Gram-positive, catalase-positive, coagulase-positive cocci that grow in clusters
49
A 27-year-old woman comes to clinic because she has been feeling "under the weather" for the past 2 weeks. She has a history of mitral valve prolapse with mitral regurgitation and underwent oral surgery 2 weeks ago. Temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F). A fundus photograph is shown. The skin shows 1- to 2-mm purple-red lesions on the legs and feet.
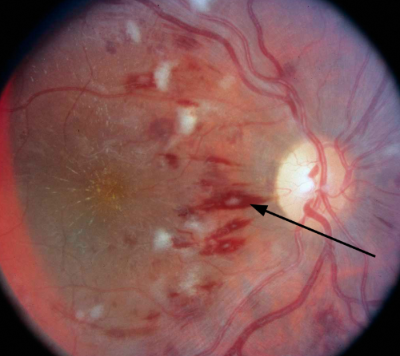
This is the pathogen likely causing this patient’s symptoms.
Streptococcus sanguinis
59
A 32-year-old woman comes to her physician because of increasing shortness of breath while walking up stairs. She has a history of a childhood heart murmur described as systolic, with a fixed, split S2 heart sound. Physical examination shows jugular venous distention, a right ventricular heave, and the hand findings shown in the photograph.
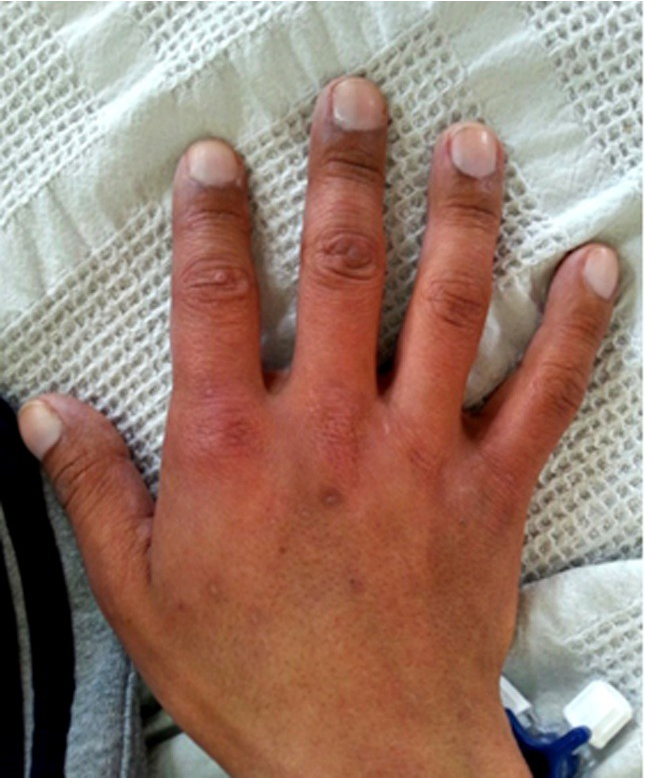
The most likely diagnosis.
Eisenmenger syndrome
60
A 65-year-old woman with a history of congestive heart failure (HF) comes to the clinic with worsening symptoms suggesting an HF exacerbation. She is treated with diuretics as well as a medication that has the effects shown in the graphs. The medication administered to this patient was most likely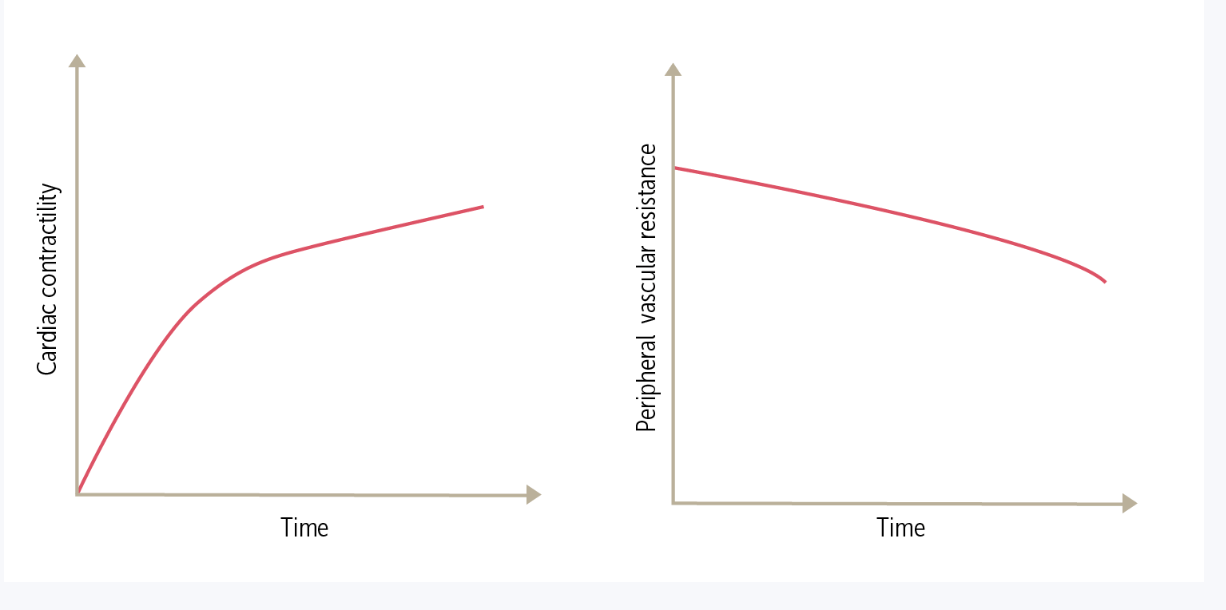
Milrinone
34
A 78-year-old man undergoes hemicolectomy for diverticulosis. On postoperative day 2, the patient develops sudden-onset altered mental status. Temperature is 38.8°C (102°F), pulse is 110/min, and blood pressure 85/45 mm Hg. Examination reveals bilateral inspiratory crackles in all lung fields with diffuse infiltrates on x-ray of the chest. His brain natriuretic peptide level is normal and partial pressure of oxygen is 60 mm Hg on 30% oxygen. Blood cultures are positive for Escherichia coli.
The main underlying cause of the patient’s hypoxemia is
Neutrophil release of proteases
36
A 53-year-old man comes to the clinic because of shortness of breath and wheezing for 2 days’ duration. Over the past 2 years he has had multiple hospital admissions for poorly controlled asthma. He also mentions occasionally experiencing numbness and tingling in his hands and feet. Additional medical history includes allergic rhinitis and chronic sinusitis. On physical examination he has wheezing across the posterior lung fields. In addition, there are palpable purpura distributed over his shins bilaterally and over the right elbow. Neurologic examination reveals weak ankle dorsiflexion on the right side. The blood eosinophil count is 1600/μL (normal: 30-500 cells/μL).
The target of the autoantibodies that are most likely elevated in this patient is this
Neutrophils
45
A 54-year-old woman comes to the clinic because of chest pain that has been occurring intermittently for the past 2 days. She reports that she first noticed the pain at home while recovering from a cold last week, but it has become frequent and bothersome. It is a sharp pain in the center of her chest that is worse with inspiration and coughing. She has a history of hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. Pulse is 72/min, and respirations are 15/min. There is no chest wall tenderness. X-ray of the chest and ECG are normal. D-Dimer is 0.10 mg/L, and troponin I is 0.01 ng/mL.
This is the most likely cause of the patient's chest pain.
Inflammation of the pleura
48
A 45-year-old man comes to the clinic because of shortness of breath and hoarseness for the past week. He was hospitalized in India during childhood for a major febrile illness. He is found to have mitral stenosis with an enlarged left atrium impinging on a nerve.
This muscle is controlled by a nerve that the affected nerve is a branch of
Palatoglossus
43